Bacteria Doc Worksheet and Answers
Worksheets are a valuable tool for educators and students alike to enhance learning and deepen understanding of a particular subject. When it comes to studying entities such as bacteria, having a well-designed worksheet can make all the difference. With the right worksheet, both educators and students can explore the various aspects of bacteria, identify key characteristics, and reinforce their knowledge through engaging exercises. In this blog post, we will take a closer look at the benefits of using worksheets to study and understand the fascinating world of bacteria.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is a bacterium?
A bacterium is a single-celled microorganism that lacks a distinct nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. They are found in diverse environments and can be beneficial, neutral, or harmful to humans and other organisms. Bacteria play critical roles in various ecological processes, such as nutrient cycling, and can be used in industries like food production and medicine.
What are the main characteristics of bacteria?
Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms that lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, making them prokaryotic. They have various shapes (spherical, rod-shaped, spiral) and sizes, can form colonies, and have cell walls typically composed of peptidoglycan. Bacteria reproduce asexually through binary fission and can exchange genetic material through horizontal gene transfer. They are metabolically diverse, capable of photosynthesis, fermentation, or respiration, and some are pathogenic while others have beneficial roles in ecosystems.
How do bacteria reproduce?
Bacteria reproduce through a process called binary fission, where a single bacterial cell divides into two identical daughter cells. During binary fission, the bacterial DNA is copied and then the cell divides into two separate cells, each containing a copy of the DNA. This process allows bacteria to rapidly multiply and increase their population.
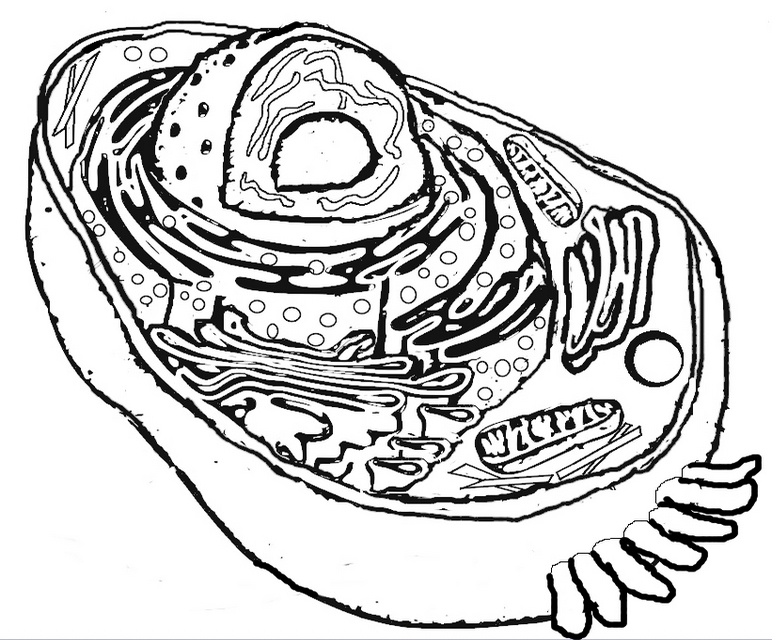
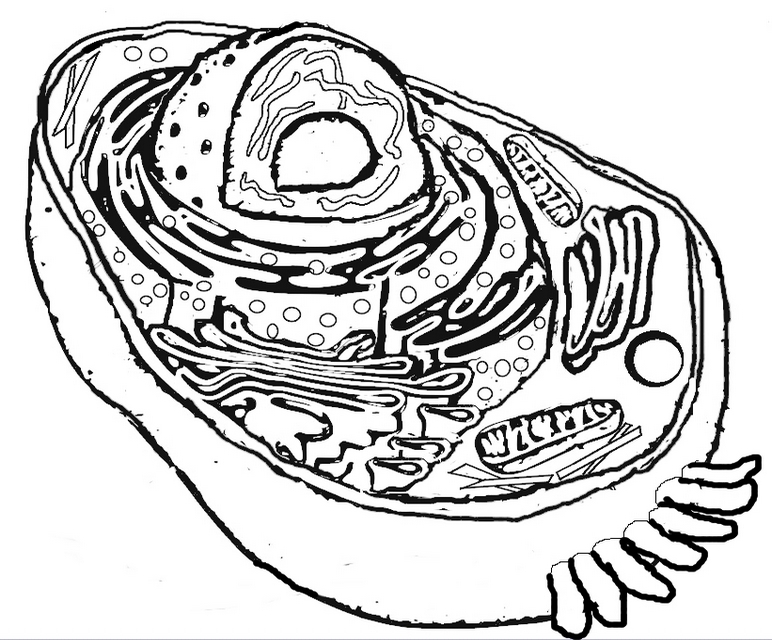
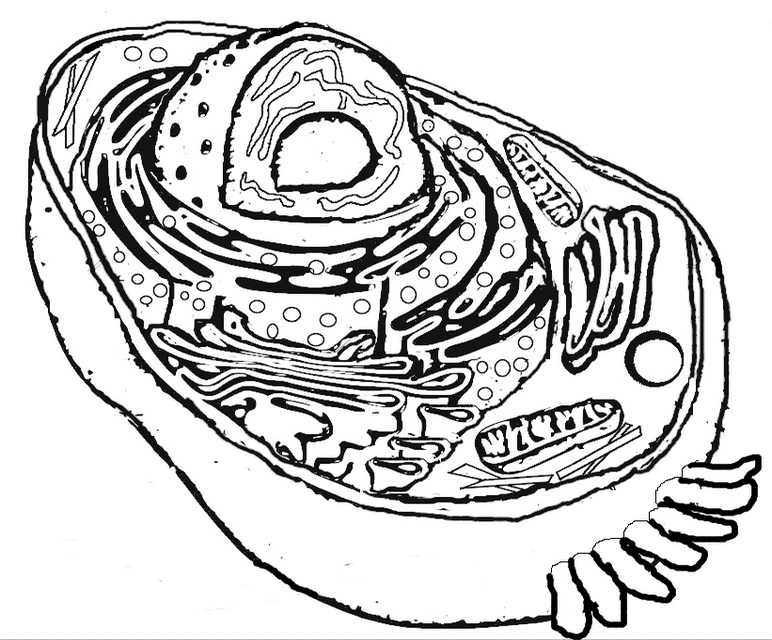
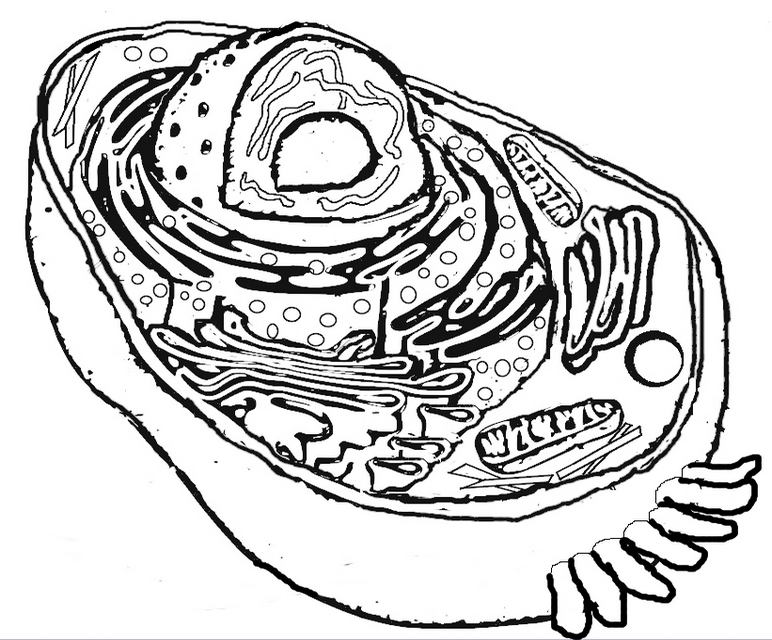
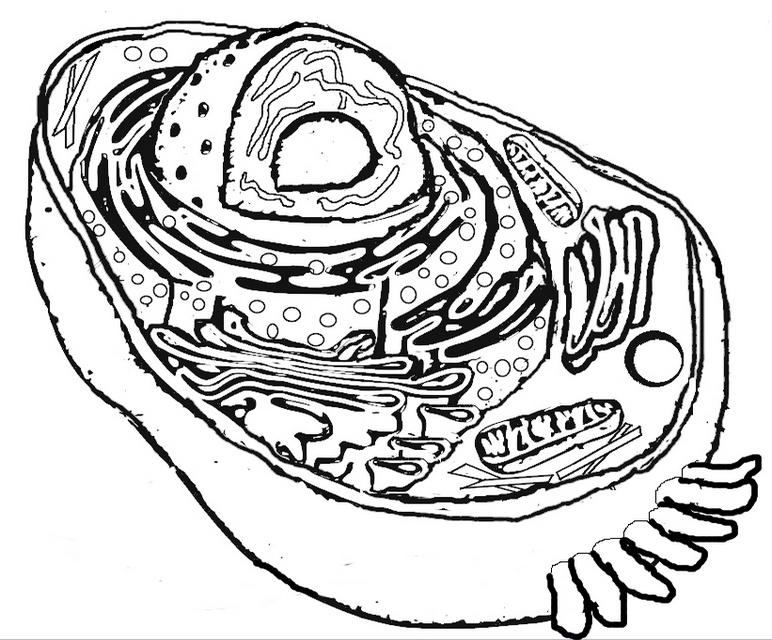
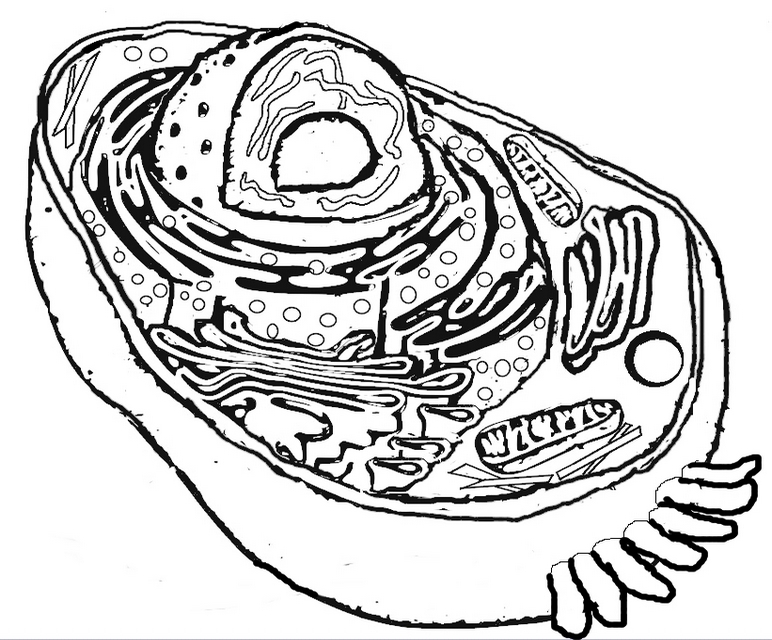
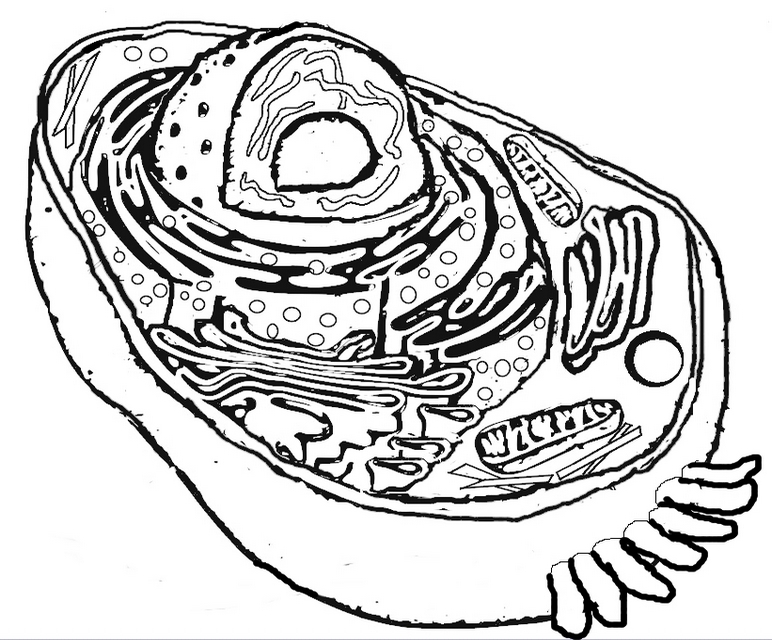
What is the structure of a bacterial cell?
A bacterial cell typically consists of a cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, genetic material (DNA), and sometimes flagella or pili for movement or attachment. The genetic material is usually circular DNA located in the nucleoid region, while ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis within the cytoplasm. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell, and the cell wall provides structure and protection.
How do bacteria obtain energy?
Bacteria obtain energy through a process called cellular respiration, where they break down organic molecules such as sugars and convert them into energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This process involves a series of biochemical reactions that take place in the bacteria's cell membranes or cytoplasm, ultimately providing the energy needed for various metabolic activities and growth.
What are the different types of bacterial metabolism?
There are three main types of bacterial metabolism: aerobic, anaerobic, and facultative. Aerobic bacteria require oxygen to carry out their metabolic processes, while anaerobic bacteria do not require oxygen and may even be harmed by its presence. Facultative bacteria can switch between aerobic and anaerobic metabolism depending on the availability of oxygen in their environment. Each type of metabolism enables bacteria to obtain energy and nutrients necessary for their survival and growth.
How do bacteria play a role in the environment?
Bacteria play a crucial role in the environment by participating in nutrient cycling, decomposition of organic matter, and aiding in the breakdown of pollutants. They also contribute to the health of ecosystems through their interactions with plants and animals, including symbiotic relationships that benefit both parties. Additionally, some bacteria can help regulate the Earth's atmosphere by producing and consuming gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide.
What are some examples of beneficial bacteria?
Beneficial bacteria include probiotics like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which support digestive health and boost the immune system. There are also nitrogen-fixing bacteria like Rhizobium that help plants convert atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form for growth, promoting healthy soil and plant growth. Other examples include bacteria that break down organic matter in composting processes, like Bacillus and Pseudomonas, contributing to nutrient recycling in ecosystems.
What are some examples of harmful bacteria?
Some examples of harmful bacteria include Clostridium botulinum (causes botulism), Escherichia coli (causes food poisoning), Staphylococcus aureus (causes skin infections and food poisoning), Salmonella species (causes gastrointestinal infections), and Streptococcus pneumoniae (causes pneumonia and meningitis).
How do antibiotics work against bacteria?
Antibiotics work against bacteria by either killing the bacteria or stopping their growth. They do this by targeting specific components of bacterial cells, such as cell walls or protein synthesis machinery, which are essential for bacterial survival. By disrupting these processes, antibiotics weaken the bacteria and allow the immune system to effectively eliminate the infection.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments