Sound Wave 4th Grade Worksheet
Are you searching for a helpful resource to reinforce your 4th grader's understanding of sound waves? Look no further! We have developed a carefully curated worksheet that focuses on the key concepts surrounding sound waves. This worksheet is perfect for parents and teachers who want to provide their 4th graders with additional practice in this topic. With clear instructions and engaging activities, this worksheet will help solidify your child's knowledge of sound waves.
Table of Images 👆
More 4th Grade Worksheets
4th Grade Elapsed Time WorksheetsIrregular Plural Worksheets 4th Grade
Rotational Symmetry Worksheets 4th Grade
Simple Circuit Worksheets 4th Grade
Long Division with Remainders Worksheets 4th Grade
Fourth Grade Reading Comp Worksheets
Reading Response Worksheets 4th Grade
4th Grade Essay Writing Worksheets
Worksheets 4th Grade Narrative Writing
Long Lined Paper Worksheets 4th Grade Essay-Writing
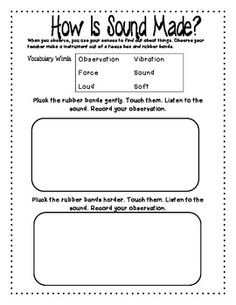
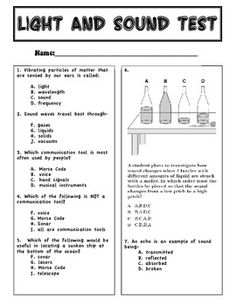
What is a sound wave?
A sound wave is a type of energy vibration that travels through a medium, such as air or water, transferring sound from one point to another. It is created by a source, such as a vibrating object, which causes air particles to move back and forth, producing a series of compressions and rarefactions that propagate as a wave, allowing us to perceive it as sound.
How does sound travel?
Sound travels in the form of waves through a medium, such as air, water, or solids. When an object vibrates, it causes the surrounding molecules in the medium to also vibrate, transferring energy in the form of sound waves. These waves propagate by compressing and rarefying the molecules in the medium, creating areas of high and low pressure that travel through the medium until they reach our ears, where they are detected as sound.
What is amplitude in relation to sound waves?
Amplitude in relation to sound waves is the measure of the strength or intensity of a sound wave, often represented by the height of the wave on a graph. It determines the loudness of a sound, with larger amplitudes corresponding to louder sounds and smaller amplitudes corresponding to quieter sounds.
What is frequency and how does it affect sound?
Frequency is the number of vibrations per second produced by a sound wave, measured in Hertz. In the context of sound, frequency determines the pitch of the sound. Higher frequencies create higher pitches, while lower frequencies produce lower pitches. Additionally, frequency can affect the timbre or quality of a sound, influencing how it is perceived by the listener.
How do different objects produce different sounds?
Different objects produce different sounds based on their physical properties and the way they vibrate when struck or interacted with. The material, size, shape, density, and tension of an object all contribute to the unique sound it creates. Additionally, the frequency, amplitude, and wavelength of the vibrations produced by an object determine the pitch, volume, and timbre of the sound it produces. Ultimately, the combination of these factors results in the distinct sound characteristics of different objects.
What is the difference between pitch and volume?
Pitch refers to the frequency of sound waves, resulting in higher or lower tones, while volume pertains to the amplitude of sound waves, determining the loudness or softness of a sound. In simpler terms, pitch is about how high or low a sound is, while volume is about how loud or soft a sound is.
How does sound change when it travels through different mediums?
Sound changes when it travels through different mediums because the speed of sound varies depending on the density and elasticity of the medium. In denser and more elastic mediums, such as solids, sound travels faster, leading to a higher pitch and clearer tone. In less dense and less elastic mediums, such as gases or liquids, sound travels slower, resulting in a lower pitch and sometimes a muffled or distorted quality. Additionally, the composition of the medium can also affect how sound is transmitted, with different materials absorbing or reflecting sound waves to varying degrees.
How do our ears detect and process sound waves?
Our ears detect and process sound waves through a complex system involving the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. The process begins with the outer ear collecting sound waves and directing them into the ear canal, where they vibrate the eardrum. These vibrations are then transmitted through the middle ear bones to the cochlea in the inner ear, where hair cells convert the vibrations into electrical signals that are sent to the brain via the auditory nerve. The brain then interprets these signals as sound.
What are some examples of echoes and how do they occur?
Examples of echoes include the sound of your voice bouncing back to you when you shout in a mountainside, the reverberation of music inside a cathedral, and the repeated reflection of sonar signals in underwater environments. Echoes occur when sound waves encounter a hard and smooth surface, causing them to bounce back to the source. The distance between the source of the sound and the reflecting surface determines the time it takes for the sound to return as an echo, with larger distances resulting in longer delays between the original sound and the echo.
How can we protect our hearing from loud sounds?
To protect your hearing from loud sounds, you can use earplugs or earmuffs in noisy environments, maintain a safe distance from loud sources, and take breaks from exposure to loud noises. Additionally, keeping the volume at a moderate level when using headphones or earphones and getting regular hearing check-ups can help prevent hearing damage.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


































Comments