Light and Sound Worksheets 4th Grade
Are you a 4th-grade teacher or parent in search of engaging and educational resources to help students grasp the concepts of light and sound? Look no further! In this blog post, we are excited to share a variety of worksheets specifically designed to aid in the learning and understanding of these fundamental subjects.
Table of Images 👆
- 2nd Grade Science Sound Worksheets
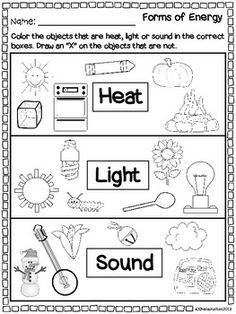
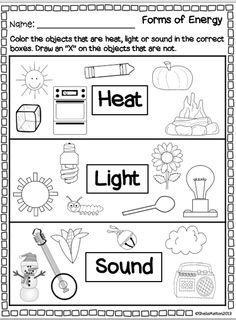
- Forms of Energy Worksheets 2nd Grade
- Light and Sound Science Worksheet First Grade
- 5th Grade Science Worksheets
- Solutions and Mixtures Worksheet 5th Grade
- Printable Science Worksheets
- Types of Energy Word Search
- Native American Symbols Dictionary
- Sound and Light Energy Worksheet
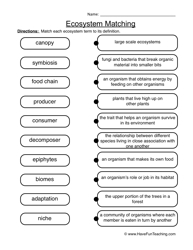
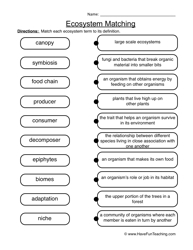
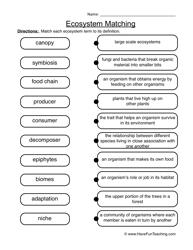
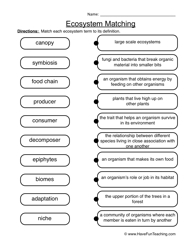
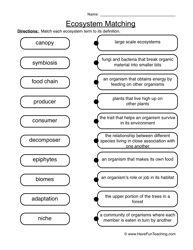
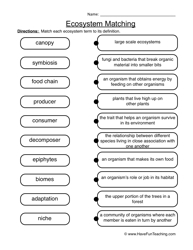
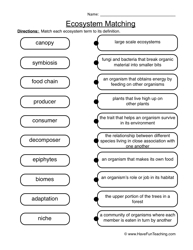
- Ecosystem Worksheet Food Chain
More 4th Grade Worksheets
4th Grade Elapsed Time WorksheetsIrregular Plural Worksheets 4th Grade
Rotational Symmetry Worksheets 4th Grade
Simple Circuit Worksheets 4th Grade
Long Division with Remainders Worksheets 4th Grade
Fourth Grade Reading Comp Worksheets
Reading Response Worksheets 4th Grade
4th Grade Essay Writing Worksheets
Worksheets 4th Grade Narrative Writing
Long Lined Paper Worksheets 4th Grade Essay-Writing
What is light?
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye. It is composed of particles called photons that travel in waves at a constant speed of about 186,282 miles per second in a vacuum. Light plays a crucial role in our daily lives, allowing us to see and providing energy for various processes on Earth.
How does light travel?
Light travels in straight lines known as rays or waves. It moves in a straight line until it strikes a surface, at which point it can reflect, refract, or be absorbed by the material. Light can travel through a vacuum, such as in space, as well as through transparent materials like air, water, and glass, due to its electromagnetic nature.
What are the primary colors of light?
The primary colors of light are red, green, and blue. When combined in varying intensities, these colors can create all the other colors in the visible spectrum of light.
How does light interact with objects?
Light can interact with objects through several processes such as reflection, absorption, transmission, refraction, and scattering. When light hits an object, it can bounce off the surface in reflection, be absorbed by the material, pass through the object in transmission, bend as it enters a different medium in refraction, or spread out in various directions in scattering. The interaction of light with objects determines how we perceive their color, texture, transparency, and other visual properties.
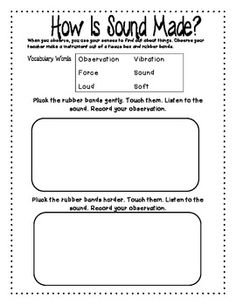
What is sound?
Sound is a form of energy produced by vibrations that travel through a medium, such as air, water, or solids. These vibrations cause changes in air pressure, which the human ear can detect and interpret as different pitches and volumes. Sound is characterized by its frequency (pitch), amplitude (volume), and wave properties, and plays a significant role in communication, music, and many other aspects of our daily lives.
How does sound travel?
Sound travels through a medium, such as air, water, or solids, in the form of vibrations. When an object vibrates, it creates waves of pressure that move through the medium. These waves cause particles in the medium to bump into each other, transferring the energy of the sound wave. As the waves travel, they continue to cause particles to vibrate, transmitting the sound to our ears where we perceive it as sound.
What are the different sources of sound?
Different sources of sound include vibrations of an object, such as a ringing bell or a vibrating vocal cord, as well as the movement of air molecules like those in a musical instrument or a person speaking. Other sources include electronic devices like speakers, sirens, and alarms, which produce sound through the use of technology and electricity. Natural sources such as thunder, wind, and animals also generate sound waves that we hear.
How is sound produced?
Sound is produced when an object vibrates, creating changes in air pressure that travel as sound waves. These waves then enter our ears and are interpreted by our brains as sound. The frequency of the vibrations determines the pitch of the sound, while the amplitude of the vibrations determines the volume.
How is sound measured?
Sound is measured in units called decibels (dB), which quantify the intensity or loudness of a sound wave. Decibels follow a logarithmic scale, meaning that each 10 dB increase represents a tenfold increase in sound intensity. Sound levels are typically measured with a device called a sound level meter, which captures and records sound waves to provide an accurate reading of the noise level in a specific environment.
How does sound interact with different materials?
Sound interacts with different materials in various ways depending on their physical properties such as density, elasticity, and thickness. When sound waves encounter a material, they can be absorbed, reflected, transmitted, diffused, or refracted. Dense and thick materials like concrete tend to reflect sound waves, while soft and porous materials like curtains absorb sound waves. Transparent materials like glass allow sound waves to pass through with little absorption. The interaction of sound with materials ultimately determines the level of sound insulation, transmission, or absorption in a given environment.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments