Electricity Worksheets 4th Grade
Electricity worksheets for 4th grade students offer a comprehensive approach to learning about this important subject. The worksheets provide engaging activities and exercises that focus on key concepts and principles related to electricity. With a strong emphasis on the entity of electricity and its various characteristics, these worksheets are perfect for educators looking to provide their 4th grade students with a thorough understanding of this fascinating topic.
Table of Images 👆
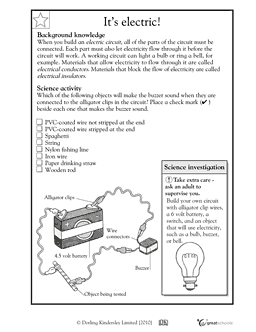
- Electricity Circuit Worksheets 4th Grade
- Science Electricity Worksheets 4th Grade
- Science Electricity Worksheets for 1st Grade
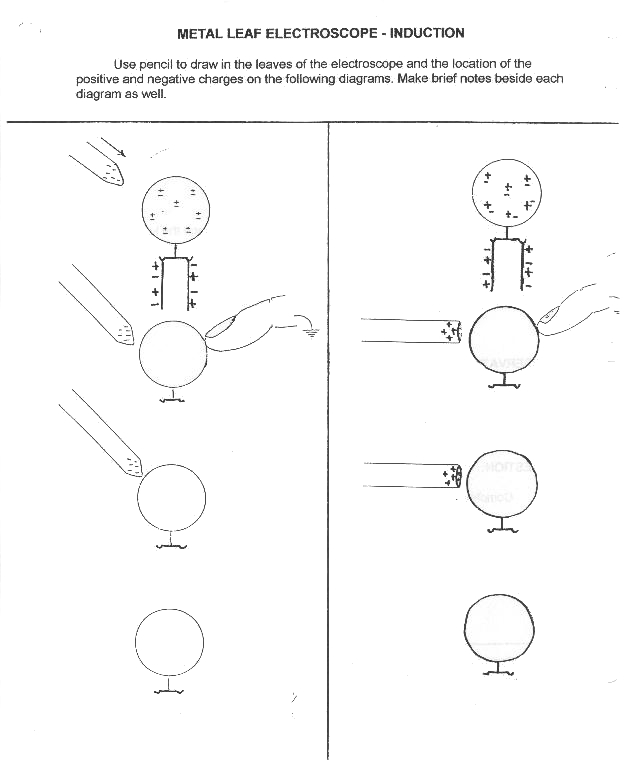
- Static Electricity Worksheet 4th Grade
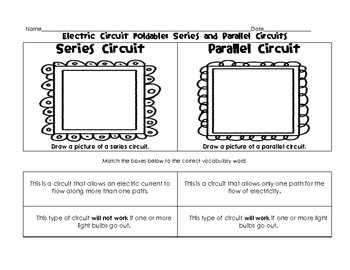
- Series and Parallel Circuits Worksheets
- 2nd Grade Vocabulary Worksheets
- Mimicry and Camouflage Worksheets
- 4th Grade Science Weather Worksheets
- Static Electricity Worksheets
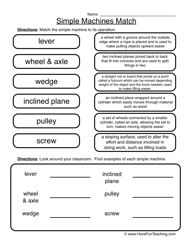
- 1 Simple Machines Worksheet
- Magnetic Attraction Worksheet
More 4th Grade Worksheets
4th Grade Elapsed Time WorksheetsIrregular Plural Worksheets 4th Grade
Rotational Symmetry Worksheets 4th Grade
Simple Circuit Worksheets 4th Grade
Long Division with Remainders Worksheets 4th Grade
Fourth Grade Reading Comp Worksheets
Reading Response Worksheets 4th Grade
4th Grade Essay Writing Worksheets
Worksheets 4th Grade Narrative Writing
Long Lined Paper Worksheets 4th Grade Essay-Writing
What is electricity?
Electricity is a form of energy resulting from the movement of charged particles, such as electrons, through a conductor. It is a fundamental force in nature that powers our modern world, enabling the flow of electrical current through circuits to power devices, lights, and appliances.
What are conductors?
Conductors are materials that allow the flow of electricity or heat through them easily. They typically have a high number of free electrons that can move easily in response to an electric field. Common examples of conductors include metals like copper, aluminum, and gold.
What are insulators?
Insulators are materials that have low conductivity and do not easily allow the flow of electricity or heat through them. These materials are used to prevent the loss or transfer of energy in various applications, such as electrical wiring, building insulation, and thermal protection. Insulators work by blocking the movement of electrons or heat energy, thereby maintaining a barrier between different environments or components.
How is electricity generated?
Electricity is generated through a process called electromagnetic induction, where a magnetic field is used to create an electric current. Most commonly, electricity is generated by spinning turbines attached to magnets within power plants. The spinning motion creates a changing magnetic field, which induces a flow of electrons in wires connected to the turbines, generating electricity that can then be distributed and used to power homes, industries, and various devices.
What is a circuit?
A circuit is a closed loop or pathway that allows electrons to flow and transmit electrical energy from a power source, such as a battery or outlet, to operate electronic devices or systems. It typically consists of components like wires, resistors, capacitors, and switches that are connected together to form a complete path for the electricity to travel.
What is a switch and how does it work in a circuit?
A switch is an electrical component that can be used to complete or break the flow of electricity in a circuit. When the switch is turned on, it creates a closed circuit, allowing current to flow through and power the connected devices. Conversely, when the switch is turned off, it opens the circuit, interrupting the flow of electricity and cutting power to the connected devices. This control over the flow of electricity makes switches essential for turning devices on and off in electrical circuits.
What are the different components of a circuit?
The main components of a circuit are a power source (such as a battery or power supply), conductors (wires) that carry the electric current, resistors that limit the flow of current, capacitors that store and release electrical energy, inductors that resist changes in current flow, switches that control the circuit, diodes that allow current flow in one direction, and transistors that amplify or switch electronic signals. Other components like integrated circuits, sensors, and light-emitting diodes (LEDs) may also be included depending on the specific circuit design and function.
What is resistance and how does it affect the flow of electricity?
Resistance is a measure of how difficult it is for electrical current to flow through a material. It is caused by collisions between moving electrons and atoms in the material. The higher the resistance, the lower the flow of electricity, as it impedes the movement of electrons. This results in a decrease in the current flowing through the circuit, potentially causing a decrease in the overall performance of the electrical system or device.
What is a battery and how does it power a circuit?
A battery is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. It consists of one or more electrochemical cells that store and release electrical energy. When a battery is connected to a circuit, the chemical reactions inside the battery produce a flow of electrons, creating an electric current that powers the circuit. The electrons move from the negative terminal of the battery to the positive terminal, powering the connected devices in the circuit.
What is an electric current and how is it measured?
An electric current is the flow of electric charge through a conductor. It is measured in units called amperes (A), which represent the rate at which electric charge passes through a given point in a circuit. Current can be measured using an ammeter, which is connected in series in the circuit and provides a reading of the flow of electrons through the conductor.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments