Sun Worksheet Earth Science
In the fascinating world of Earth Science, worksheets are invaluable tools that help students grasp the complexities of our planet. Designed to enhance learning and understanding, these worksheets serve as entities that cater to the subject-specific needs of students, providing them with the necessary exercises and activities to reinforce their knowledge of the sun and its role in our solar system.
Table of Images 👆
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
What is the Sun?
The Sun is a star at the center of our solar system, primarily composed of hydrogen and helium. It provides light and heat to the planets, including Earth, through the process of nuclear fusion where hydrogen atoms are converted into helium, releasing vast amounts of energy. Its immense gravity holds the solar system together, determining the orbits of celestial bodies and influencing the conditions that support life on Earth.
How does the Sun generate energy?
The Sun generates energy through nuclear fusion, a process in which hydrogen atoms are converted into helium atoms. In the Sun's core, immense pressure and temperatures trigger nuclear reactions that release a tremendous amount of energy in the form of light and heat. This energy sustains the Sun's luminosity and warmth, making life on Earth possible.
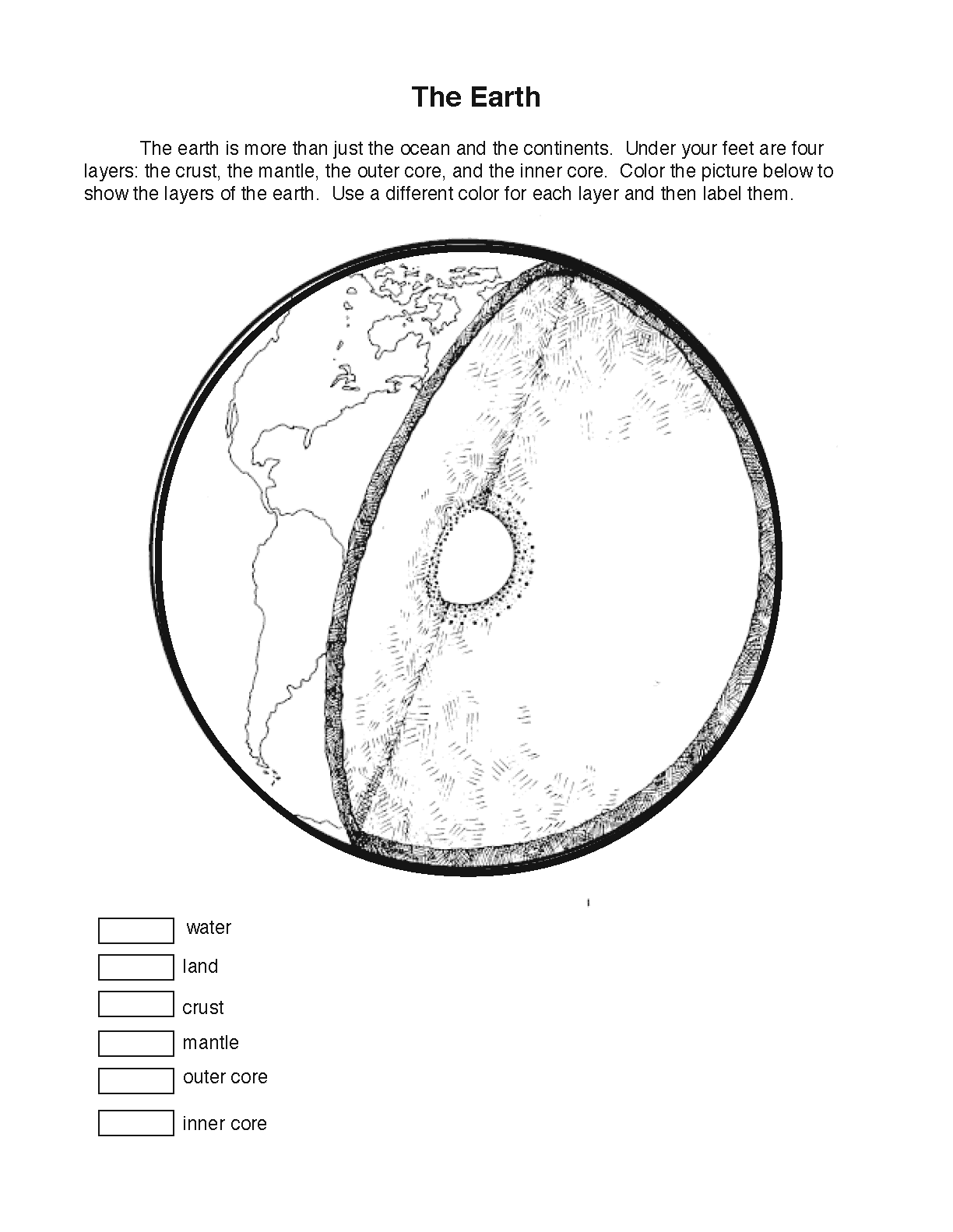
What is the temperature of the Sun's core?
The temperature of the Sun's core is estimated to be around 27 million degrees Fahrenheit (15 million degrees Celsius).
What are sunspots?
Sunspots are areas on the Sun's surface that appear darker and cooler than the surrounding areas due to intense magnetic activity. They typically occur in pairs or groups and are temporary phenomena that can last for days to weeks. Sunspots are associated with strong magnetic fields and often coincide with increased solar activity, such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections.
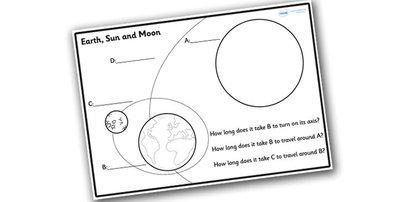
How does the Sun's gravity affect the planets in the solar system?
The Sun's gravity affects the planets in the solar system by holding them in orbit around it. The gravitational force of the Sun is what keeps the planets in their paths and prevents them from drifting off into space. This gravitational pull also determines the speed and shape of their orbits, as well as their distances from the Sun. Essentially, the Sun's gravity is what keeps the entire solar system functioning and maintains the stability of each planet's movement.
How does the Sun's magnetic field create solar flares?
The Sun's magnetic field plays a key role in the creation of solar flares by storing and releasing enormous amounts of energy. When the magnetic field lines become twisted and tangled due to the Sun's rotation, they can suddenly reorganize and release built-up energy in the form of a solar flare. This rapid release of energy results in a burst of intense radiation and particles being ejected from the Sun's surface.
What is the Sun's role in the water cycle on Earth?
The Sun plays a crucial role in the water cycle on Earth by providing the energy needed for evaporation to occur. It heats the Earth's surface, causing water from oceans, lakes, rivers, and other bodies of water to evaporate and form water vapor in the atmosphere. This water vapor then condenses to form clouds and eventually falls back to the Earth as precipitation, such as rain or snow, completing the water cycle.
How does the Sun's energy reach Earth?
The Sun's energy reaches Earth through a process called radiation, in which electromagnetic waves travel through the vacuum of space. These waves include visible light, ultraviolet light, and infrared radiation, which all carry heat and energy from the Sun to Earth. The Sun's energy is essential for driving Earth's climate, weather patterns, and sustaining all forms of life on our planet.
What is the Sun's approximate age?
The Sun is approximately 4.6 billion years old.
How does the Sun's size compare to other stars in the universe?
The Sun is an average-sized star compared to other stars in the universe. It is classified as a yellow dwarf star and is larger than some stars known as red dwarfs, but much smaller than giant stars like Betelgeuse and supergiant stars like Antares. Overall, the Sun falls within the middle range of star sizes in the universe.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments