Science Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Heat Energy Worksheets with Answers are a great tool to help students grasp the fundamental concepts of heat energy. These worksheets provide a clear and concise way to test understanding, reinforce learning, and assess knowledge on this specific subject. By using these worksheets, students will learn various energy and heat concepts such as thermal energy, phase changes, heat transfer, specific heat, and heat capacity. Whether you are a teacher looking for supplementary resources or a parent wanting to support your child's learning of heat energy at home, these heat energy worksheets will engage and challenge students, helping them excel in science.
Table of Images 👆
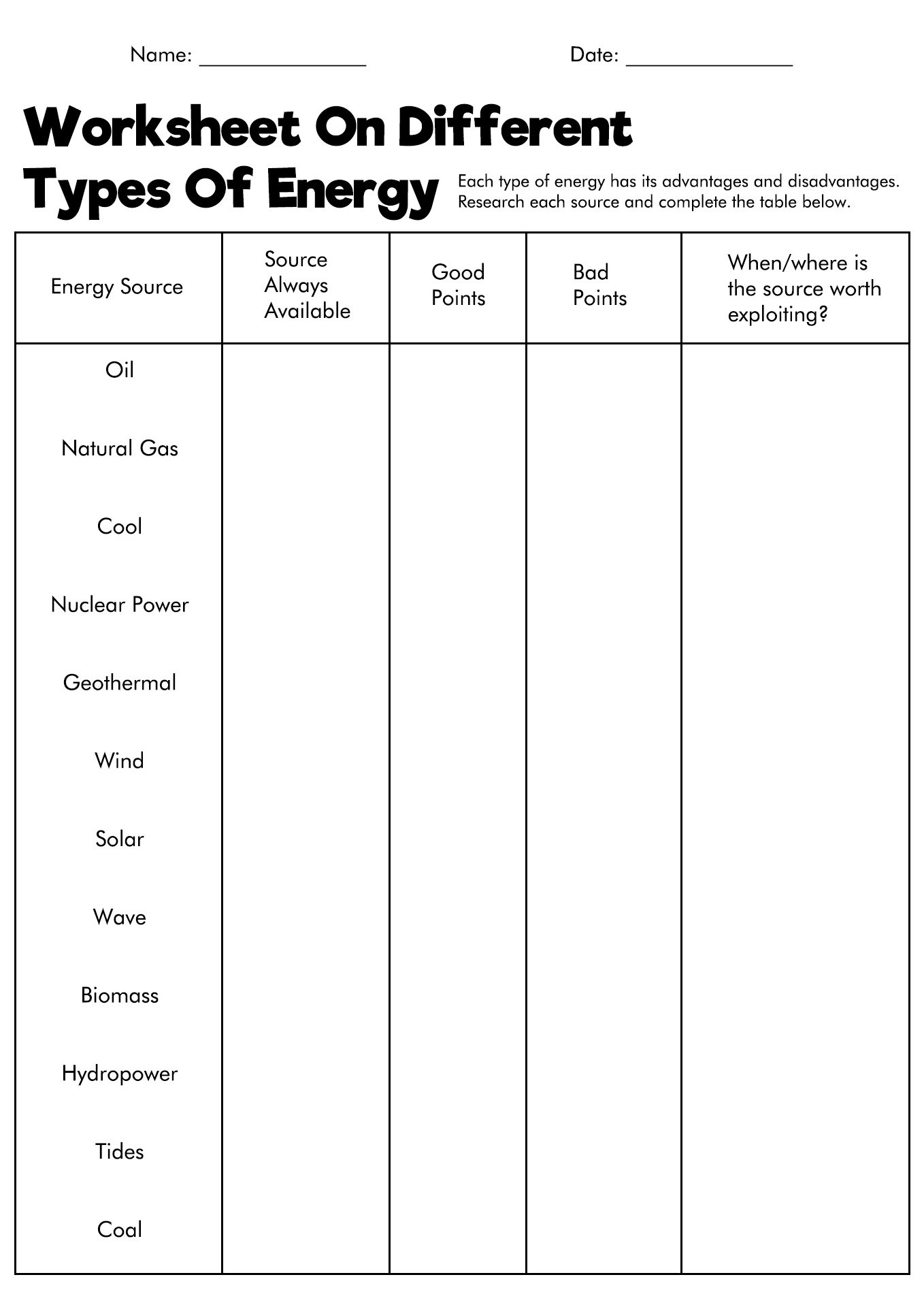
- Forms of Energy Worksheet Answers
- Heat Energy Transfer Worksheet
- Heat Energy Transfer Worksheet
- Heat and Thermal Energy Worksheet Answers
- Specific Heat Capacity Worksheet
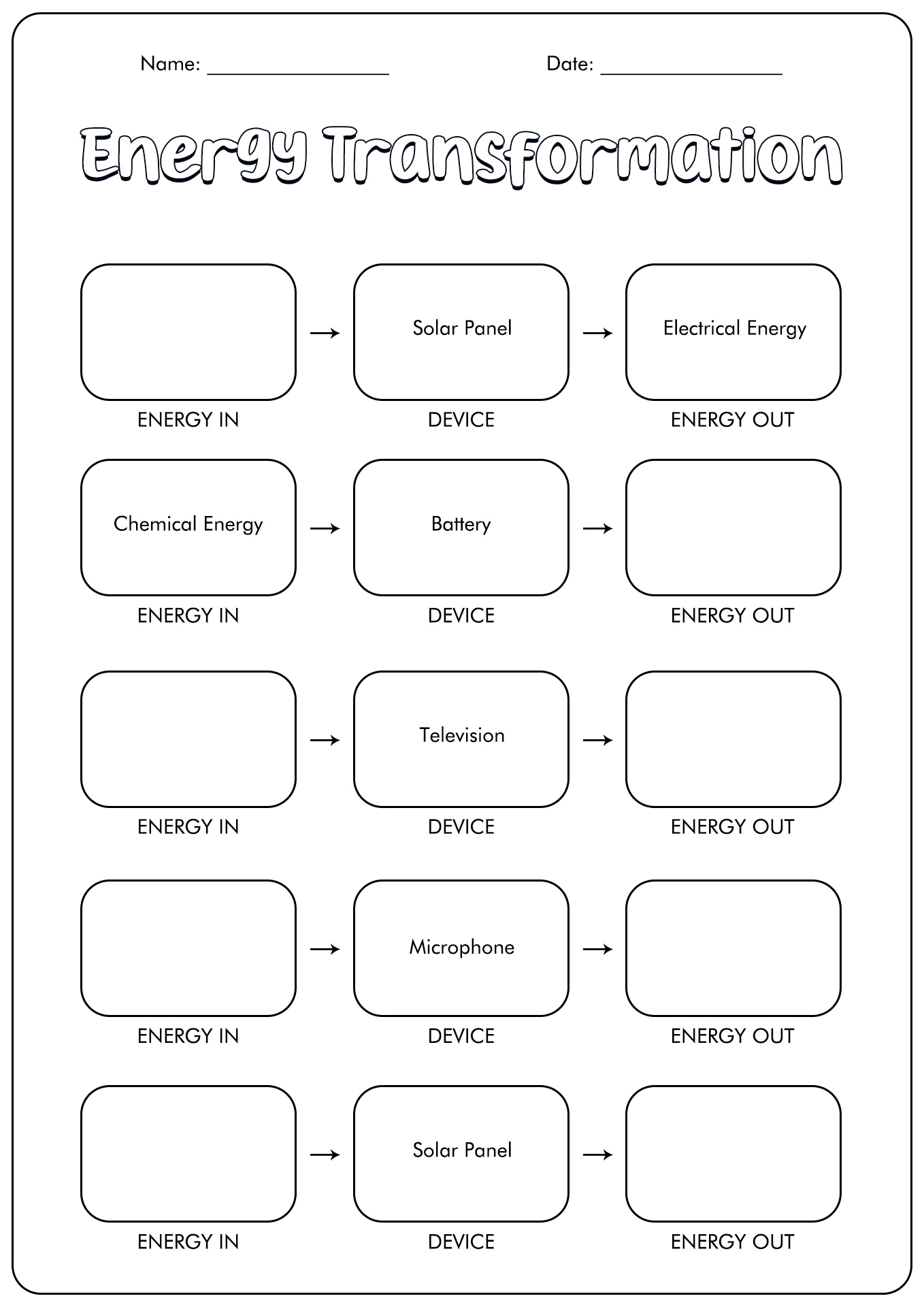
- 6th Grade Energy Transformation Worksheet
- Thermal Energy Worksheet Heat and Temperature
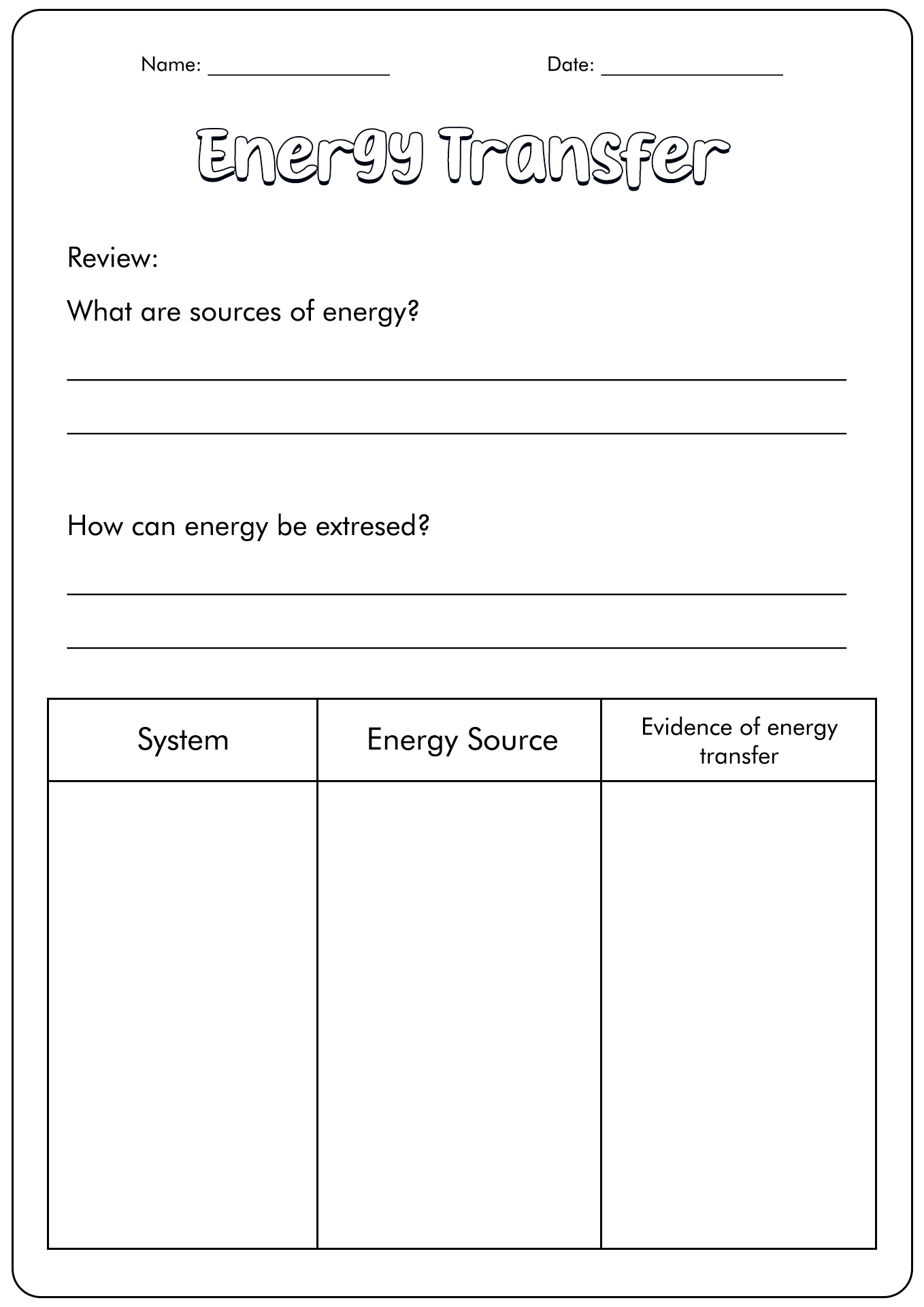
- Energy Transfer Worksheets
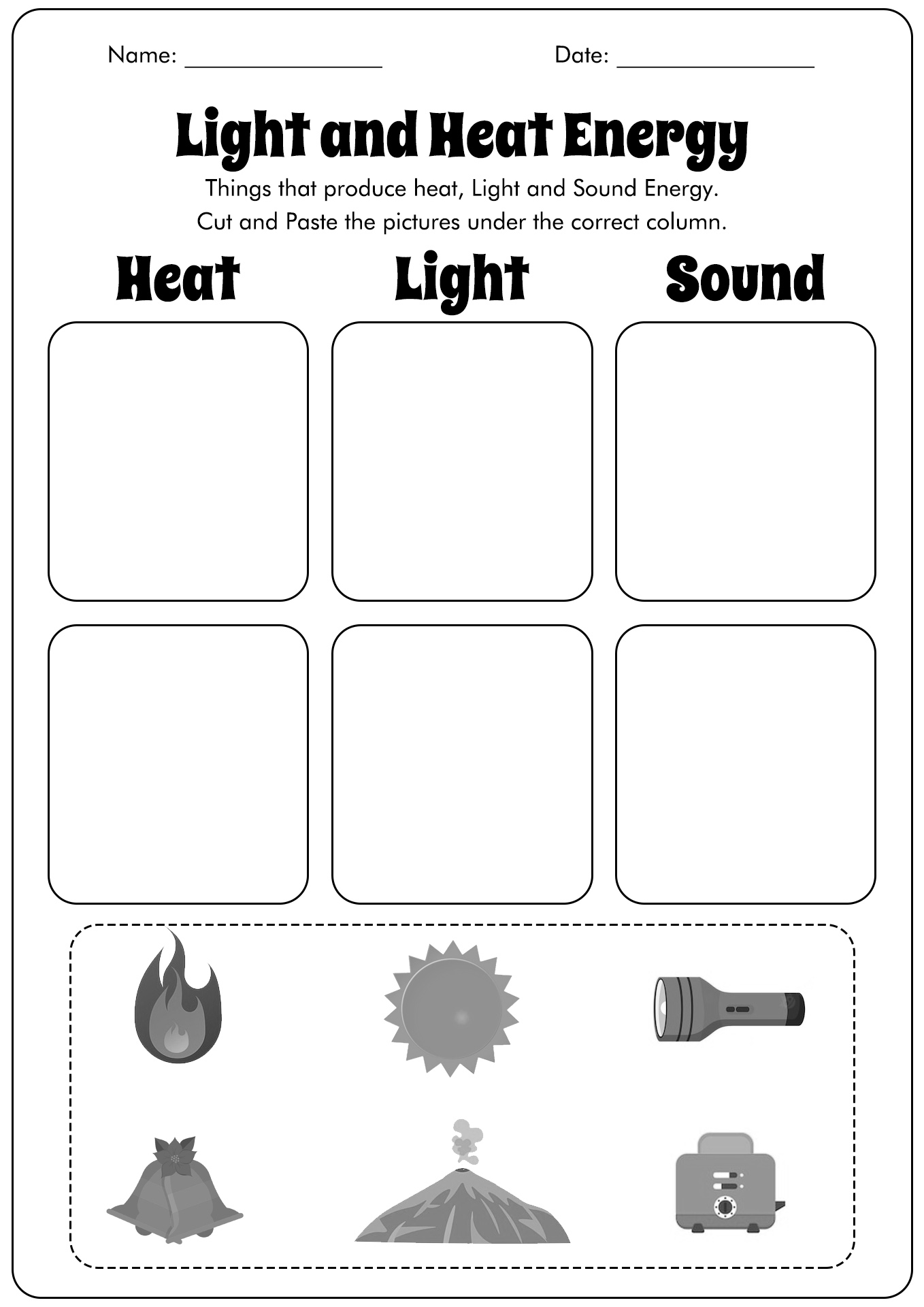
- Light and Heat Energy Worksheets
- Thermal Energy Transfer Worksheet
- Energy Word Search Worksheet

Understanding heat energy is crucial in science education, and with our Science Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer, you can enhance your educational resources.
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
1st Grade Life Science Worksheets
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
Feel the heat with these Science Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
What is Energy?
Energy is a common term that we hear every day and everywhere. However, what is energy? Many experts agree that it is a difficult question to answer. There are many types of answers to this question.
So, what is energy? According to the American Petroleum Institute (API), energy is the capability of a system to run. The system can be in a vehicle, human, or natural forces. Energy will cause the vehicle to move, the human to grow, and nature to flourish.
We cannot see energy with our eyes, but we can sense and feel it. It has many forms (kinetic, gravitational, chemical, elastic, nuclear, electrical, and radical). In science, we can measure energy in various units, such as joules, calories, kilowatt-hours, electron volts, quads, and more.
How Many Types of Energy?
In physics, energy is the allotment for doing work. Energy has many forms. The popular ones are potential, kinetic, thermal, chemical, electrical, nuclear, and more. Every form of energy is related to movement.
For example, any item has kinetic energy when it is in motion. Humans cannot make, build, or produce energy. However, they can transform from one form into another.
The transformation is known as energy conservation. This conservation means energy can shift from one type to a different one. Below is the table of types of energy:
|
Type of Energy |
Physical Manifestation |
|
Kinetic |
Motion |
|
Gravitational |
The height on top of an allusion level. |
|
Elastic |
The result of push and pull power. |
|
Chemical |
The reaction of an element causes heat. |
|
Nuclear |
The reaction of a nucleus results in heat. |
|
Temperature |
Extreme temperature |
|
Electrical |
Voltage and current. |
|
Radiant |
Electromagnetic waves. |
What is Heat Energy?
Heat is one of the energy types. It transferred intensity from one object to another because of the temperature differences. The impact of this transfer is the escalation temperature on the cold object and the lessening on the hot one.
Hence, the definition of heat is the energy flow from a warm matter to a colder one. The source of heat is everywhere; even our body has it.
Based on the Science Learning Hub of New Zealand, every object has heat energy. The movement of some minuscule particles, such as molecules or ions (in the form of liquid, solid, or gases), results in heat. Meanwhile, the warmth is transferable.
For example, when we put ice cubes into a hot cup of tea, the ice will melt because the heat from the tea is transferred to the ice cubes. This transfer will also affect the hot tea as it becomes warm or even cold because of the low temperature of the ice cubes.
How Many Sources of Heat Energy?
Heat energy can be the fuel of a work. It is one of the essential types of energy for daily human life. We use it for cooking, ironing, heating food, and drying hair. There are plenty of sources of high-temperature energy:
- Sun: The bright sun is the largest source of energy for all organisms on Earth. It keeps life on this planet thriving for millions of years.
- Earth: The heat energy from the Earth is known as geothermal energy. We can find it in the spring or underground rocks.
- Air: The air consists of heat pumps for commercial and residential purposes.
- Burning Fuels: Burning fuels have a substance that could release heat energy if burned. Some examples of this source are wood, kerosene, diesel, coal, charcoal, oil, and more.
- Electricity: We can transfer the electrical energy to be heated with a device, such as a rice cooker, iron, or hair dryer.
How is Heat Energy Transmitted?
When an object's temperature rises, the particle inside will gain more energy. The excess can be transferred to other particles with lower temperatures. In the case of fast-moving particles bumping into slow-moving ones, it will send the power. This transaction will make the pace of slow particles faster.
The process will keep repeating until it reaches the thermal equilibrium. When a solid object receives heat sufficiently, there will be an increase of energy in the particle. It will erase the bond that ties the elements. Hence, a solid object (ice cubes) can transform into liquid (water), and the liquid (water) can transform into a gas (evaporate).
- Convection: Convection is the heat transfer process because of the movement of the particles in the object. It usually occurs in liquid or gas elements. The warm air is less solid than cold air, causing the warm air to move up and the cool air to replace them. The cold air turns warm, and the same cycle happens again.
- Conduction: Conduction is a heat transfer from one solid object to another. The transmission can happen when two pieces of stuff touch each other. An example of conduction is when putting a pan on top of a burning stove. The heat from the stove will affect the pan and make it hot.
- Radiation: Radiation is a heat transmission process in which the temperature goes through a place with no molecules. It is an example of electromagnetic energy. We can feel the heat without direct contact with the object. An example of radiation is when we feel the sun or campfire warm.
What is Science Heat Energy Worksheet with Answer?
Science Heat Energy Worksheet with Answer is a worksheet designed for students to understand various heat concepts. They can explain and describe types of heat energy through those worksheets. Not only that, but they can also learn about other terms like temperature and insulation. Those things are related to heat theory.
Because those worksheets are very important for students' knowledge development, teachers and parents should use these worksheets are the main science learning tool.
Energy is the capability of a system to run. Heat is the energy flow from a warm matter to a colder one. It is one of the essential types of energy for daily human life.
To learn about heat energy and all of its concepts, students can use Science Heat Energy Worksheets with answers. These worksheets will help students to understand how heat energy is transmitted such as convection, conduction, and radiation.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments
Printable images for science heat energy worksheets with answer provides an interactive and visual learning experience, making complex concepts easier to grasp, while enabling students to self-assess their understanding and reinforce knowledge through immediate feedback.
These printable science heat energy worksheets with answer provide students with an interactive and engaging way to learn about the principles of heat energy, enabling them to grasp complex concepts easily and self-assess their understanding.
Printable images: science heat energy worksheets with answers. Enhance learning by providing clear visual aids and easy access to accurate solutions, promoting understanding and retention of key concepts.
Great resource for reinforcing concepts of heat energy in a concise and easy-to-understand format. The included answer key is a helpful tool for checking understanding. Highly recommend!
This printable resource on Science Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer is a valuable tool for enhancing students' understanding of this topic. It provides clear explanations and engaging activities that promote critical thinking. Highly recommended!