Classifying Animals Worksheets Preschool
Preschool is an exciting time for little learners to explore the world around them, including the fascinating world of animals. Our classifying animals worksheets are designed specifically for preschoolers to learn about different types of animals and their characteristics. These engaging worksheets feature various animals that will capture the attention and curiosity of young minds. By organizing animals into different categories, children can develop their understanding of important science concepts such as classifying and categorizing. With our classifying animals worksheets, preschoolers can embark on a fun and educational journey to discover the diverse animal kingdom.
Table of Images 👆
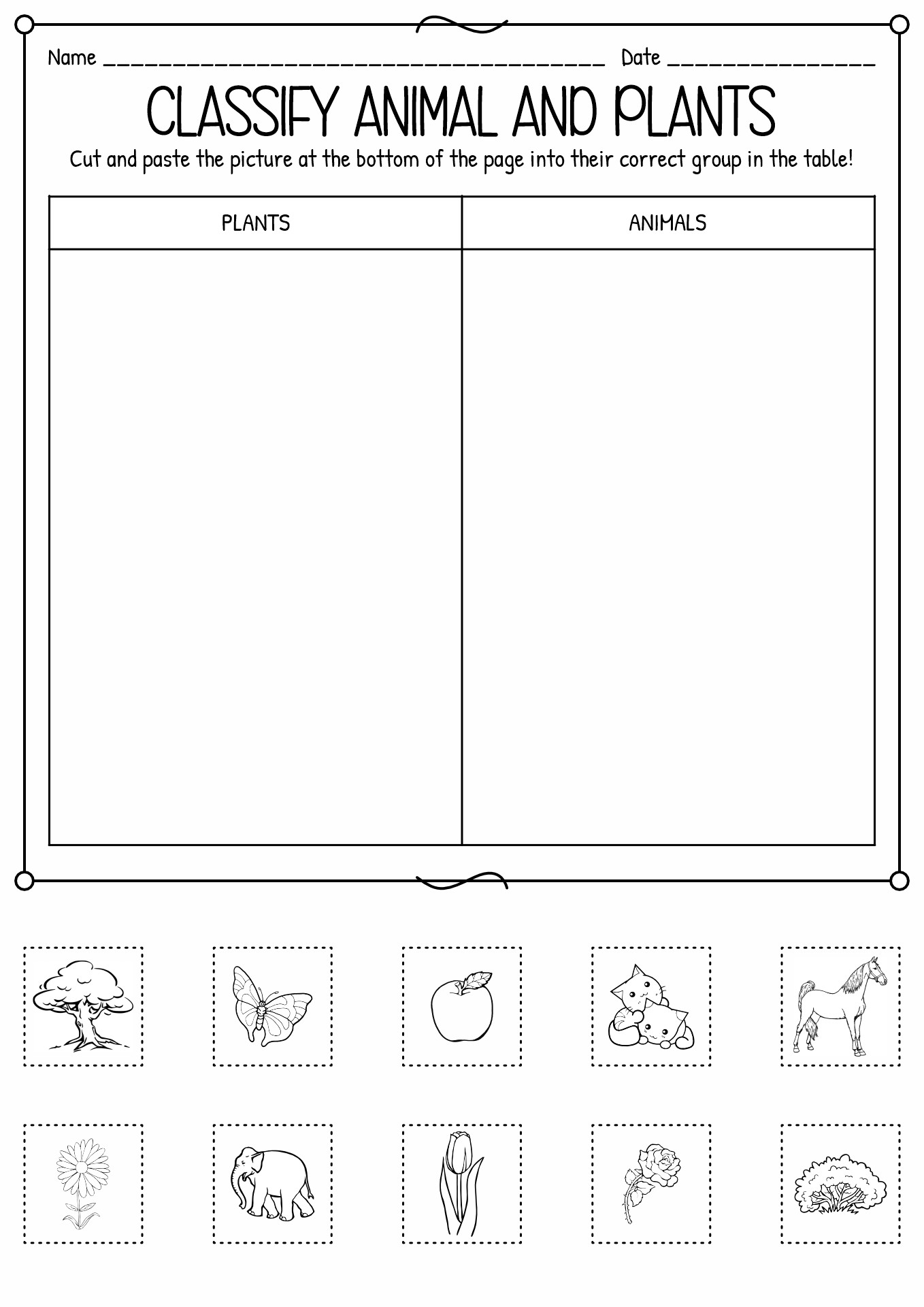
- Classifying Plants and Animals Worksheets
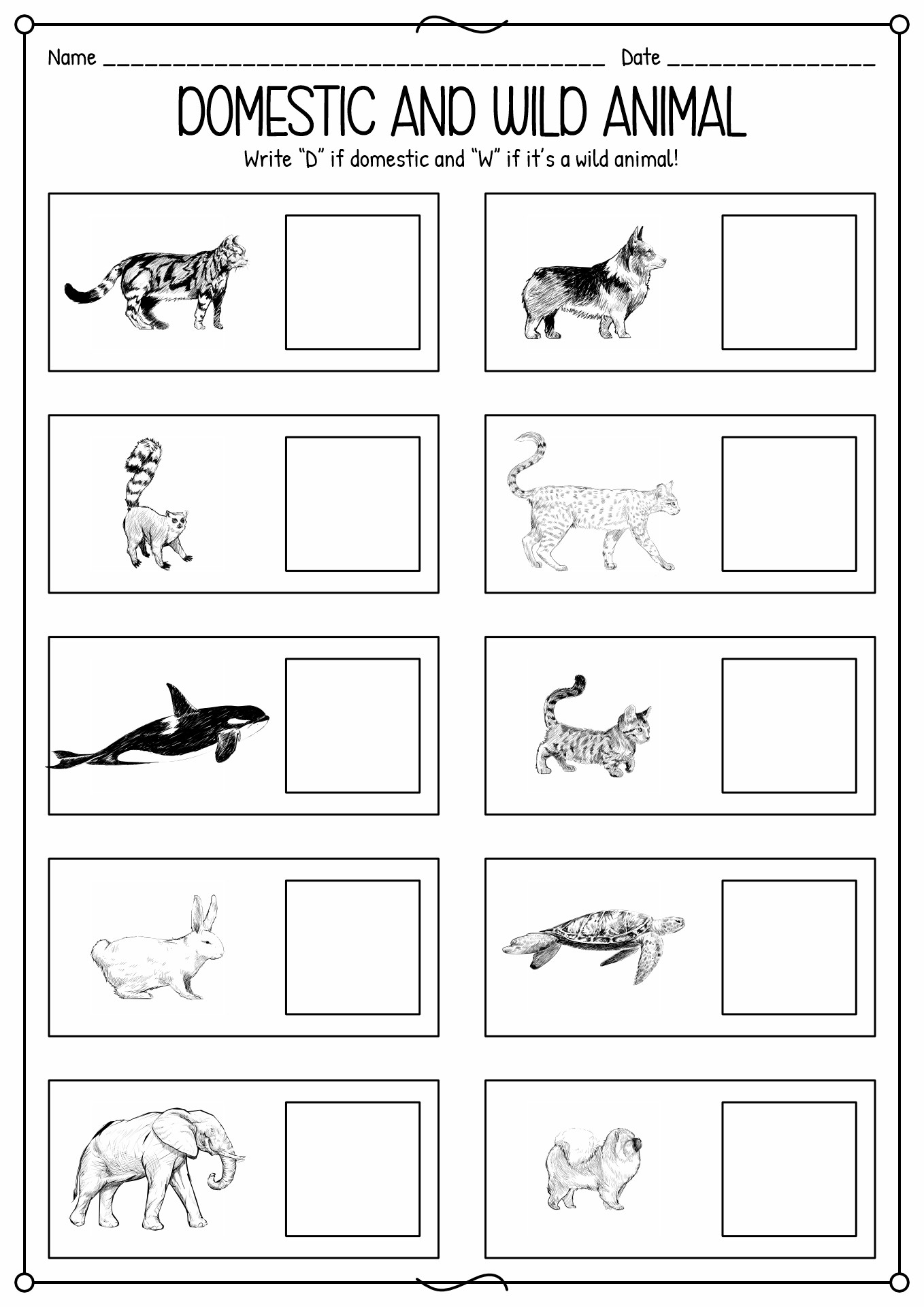
- Domestic and Wild Animals Worksheet
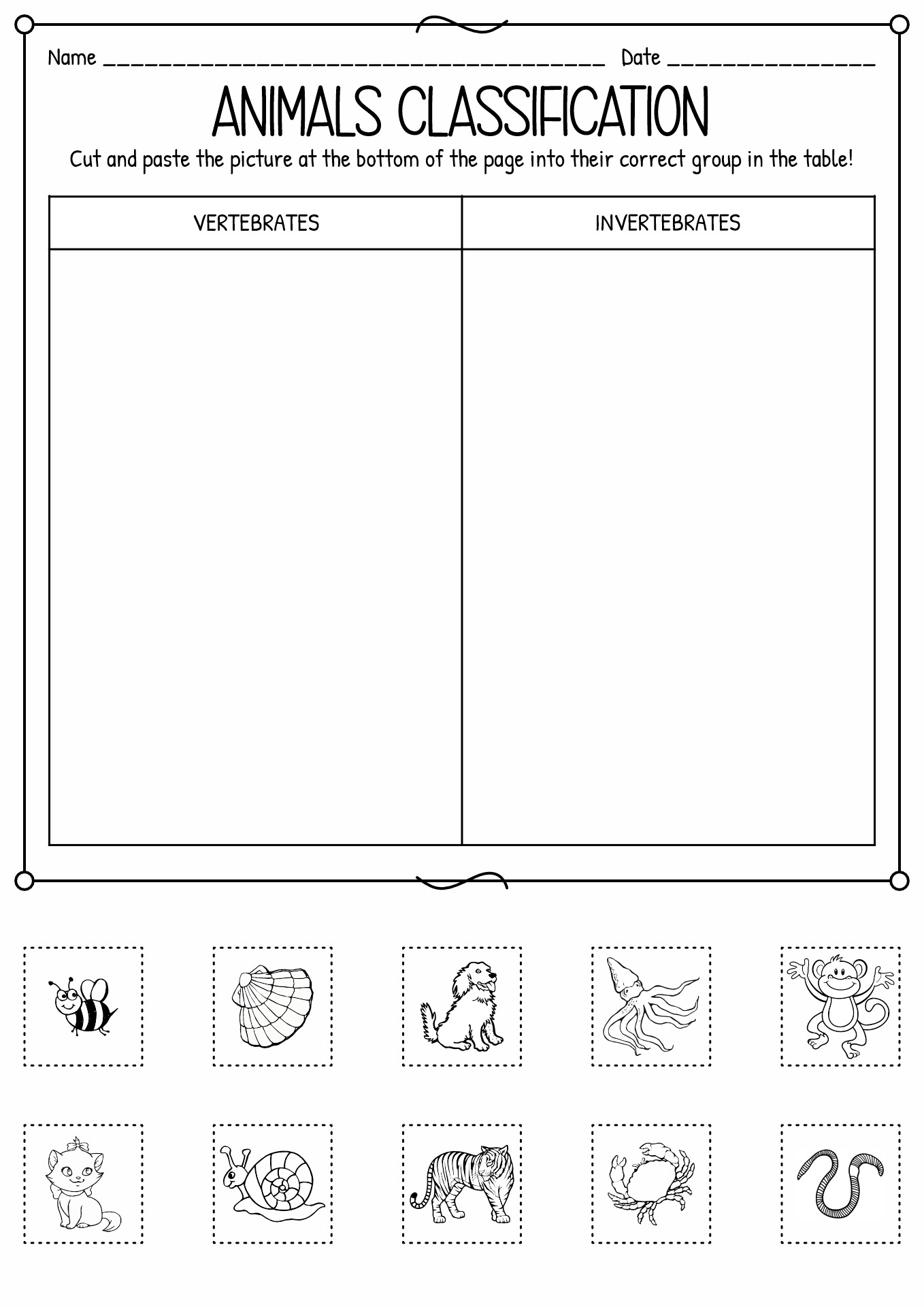
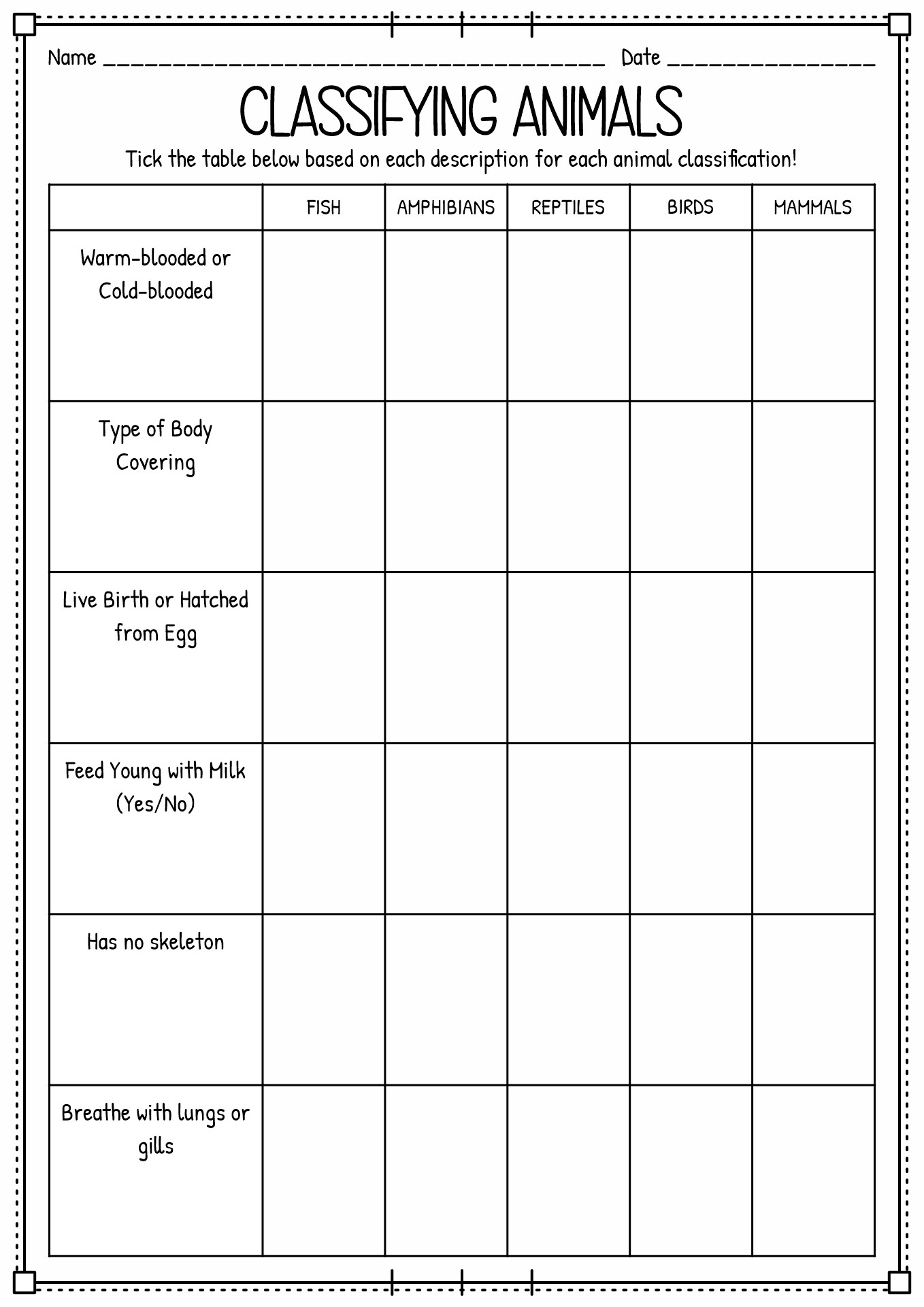
- Cut and Paste Animal Classification Vertebrate Worksheets
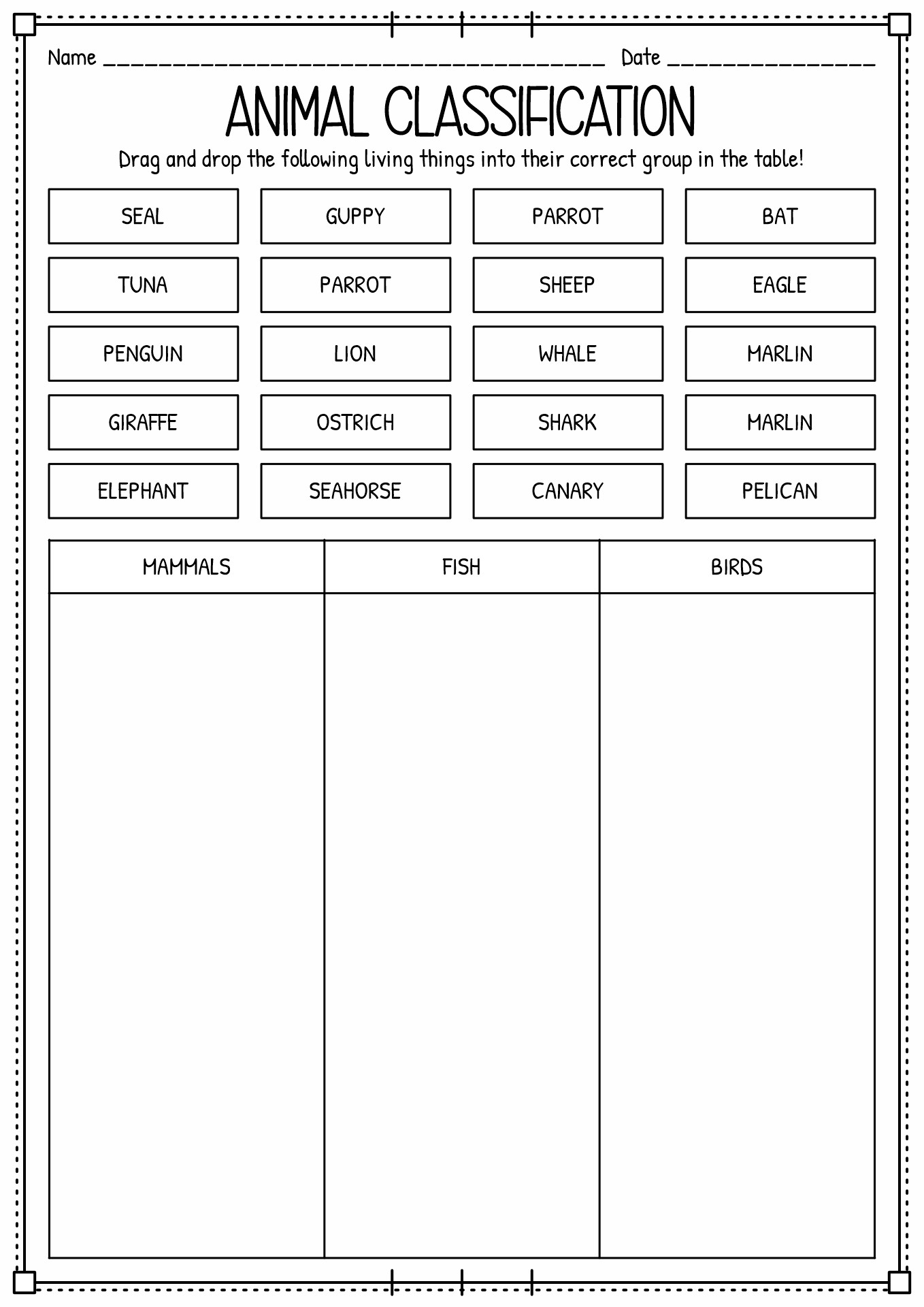
- Animal Classification Worksheet
- Animal Kingdom Classification Worksheet
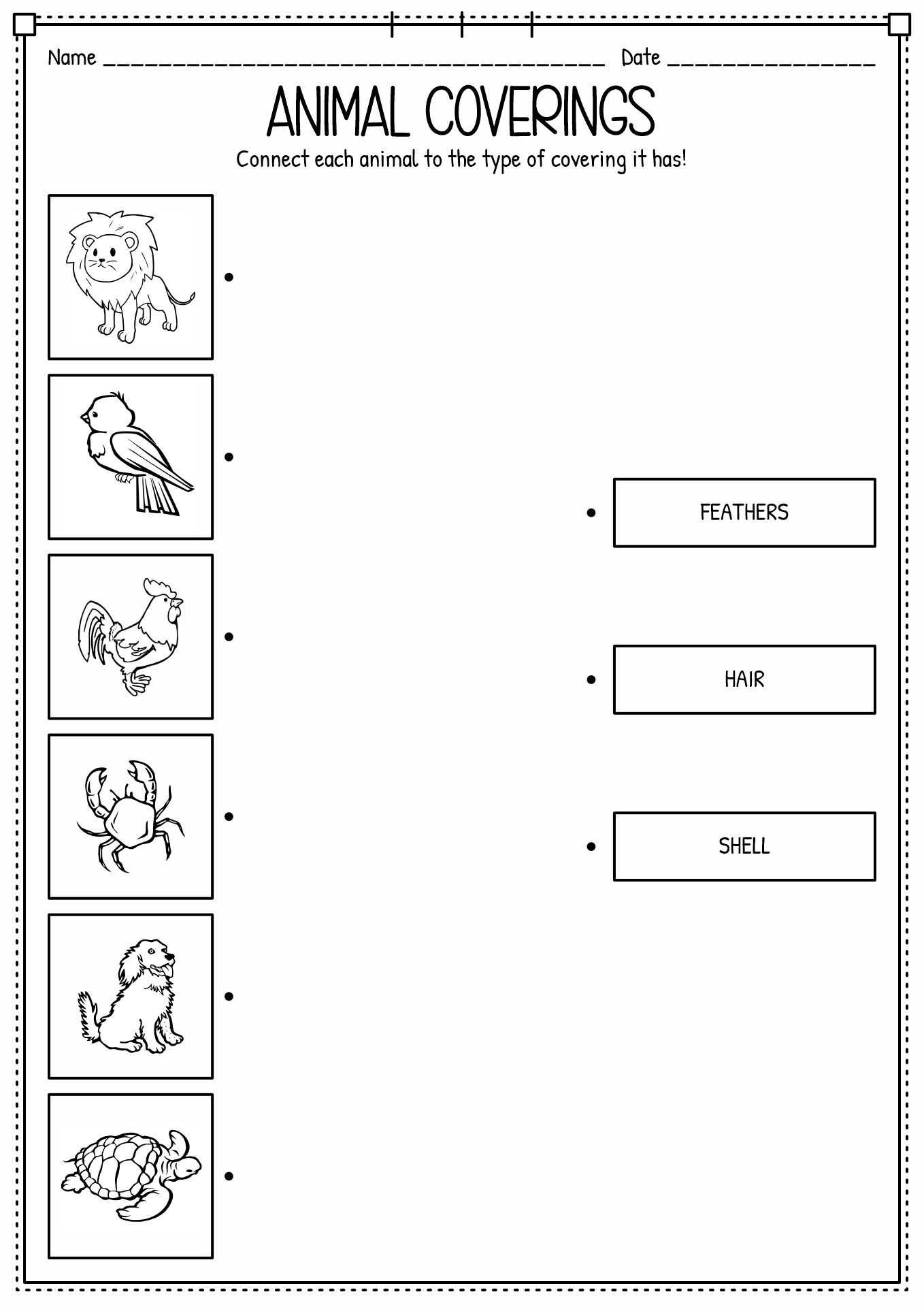
- Animal Coverings Worksheets for Kindergarten
- Endangered Animals Worksheets
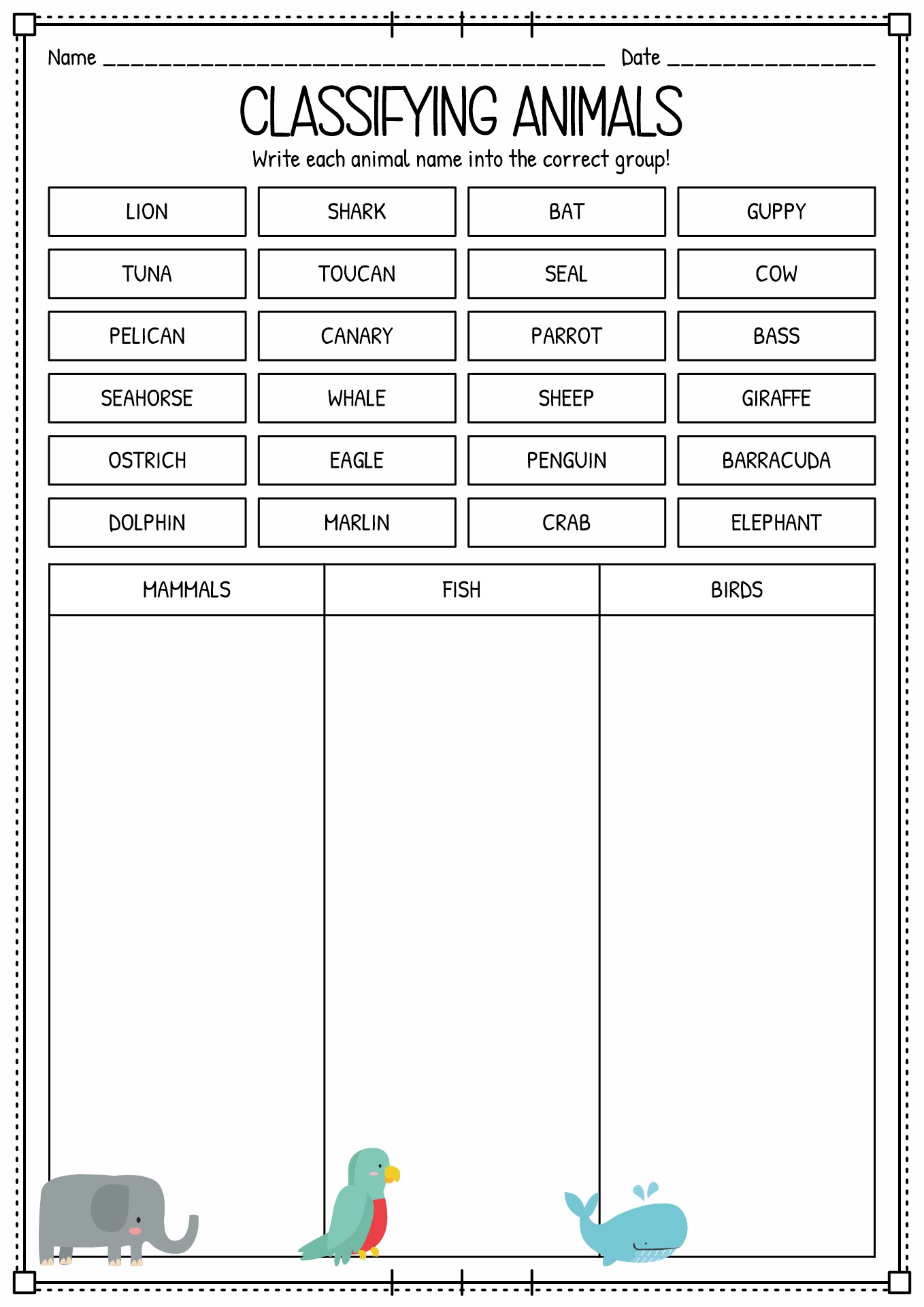
- Classifying Animals Worksheets
- First Grade Animal Classification Worksheets
- Classification of Living Organisms Worksheet
- Elementary Animal Classification Worksheet
- Animal Classification Worksheet Middle School
- Animal Cut and Paste Activities
- 3rd Grade Animal Worksheets
- Animal Classification Worksheet

Teaching preschoolers about animal classification can be engaging with our Classifying Animals Worksheets Preschool, where educational materials come to life.
More Preschool Worksheets
Writing Practice Worksheets for Preschool12 Free Printable Number Tracing Preschool Worksheets
Pre Writing Worksheets for Preschool
Spring Worksheets for Preschool
Clothing Printable Worksheets for Preschoolers
Penguin Preschool Worksheets
Getting to Know Yourself Worksheet Preschool Printable
Preschool All About Me Worksheets Printables
Preschool Valentine Worksheets to Print
Classifying Animals Worksheets Preschool
Get familiar with the animal through these Classifying Animals Worksheets Preschool!
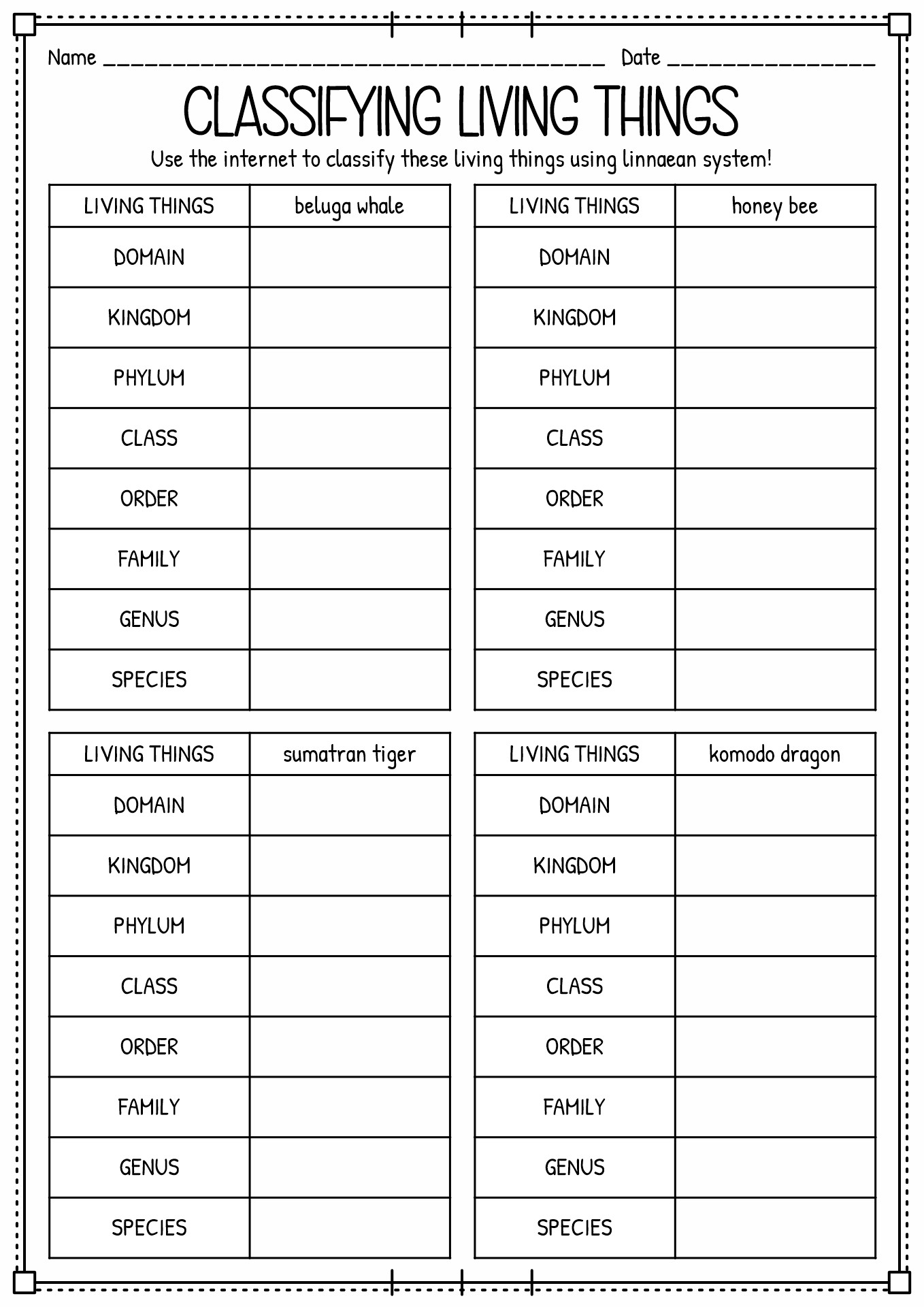
Summary: Animal classification means grouping animals according to their characteristics. There are some types of animal classification. There are seven classifications of animals in biology, domain, kingdom, phylum or division, class, order, family, genus, and species. The kingdom classification of animals is also known as Animalia. This grouping will help the scientist to make breakthroughs that will benefit the nature and environment.
What is the Purpose of Animal Classification?
In biology, animal classification means grouping animals according to their features. There are some types of animal classification. There are seven classifications of animals in biology, domain, kingdom, phylum or division, class, order, family, genus, and species. The purpose of animal classification is to help the scientist discover their behaviour and characteristics. This grouping will help the scientist to make breakthroughs that will benefit the nature and environment.
How to Explain Animal Kingdom?
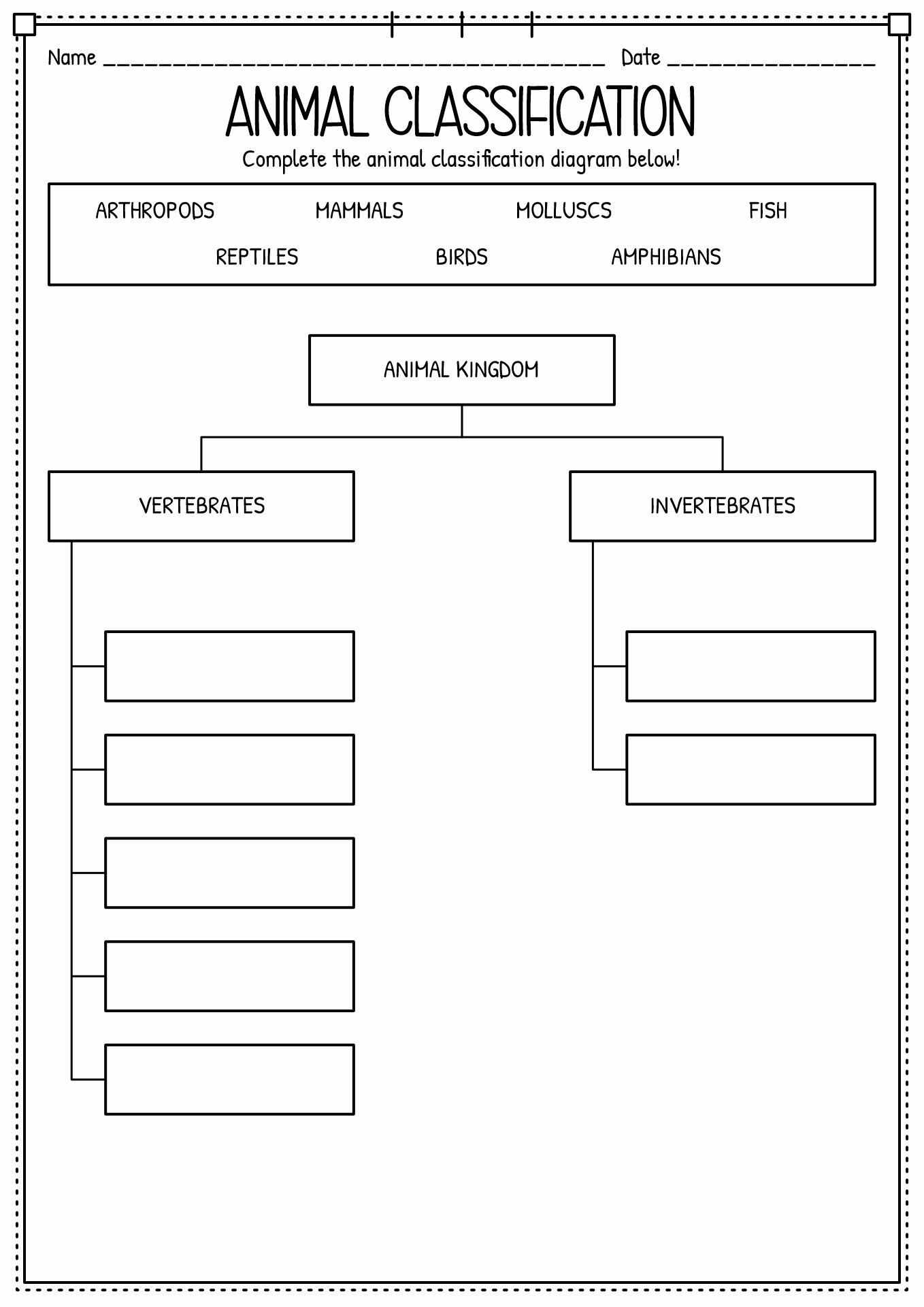
The kingdom classification of animals is also known as Animalia. Animalia is the largest out of five other kingdoms on Planet Earth (Protozoa, Chromista, Plantae, Fungi, and Animalia). It is a classification where the biologist divides the animals into some groups based on their characteristics. Kingdom is in the second highest classification in taxonomy ranks, below the domain. There are billions of animals inside the animal kingdom. There are some sub-categories to define animal groupings, such as division, class, order, family, genus and species. Each category fits similar organisms (physically, anatomically or behaviourally).
A living thing can be considered an animal if it is a eukaryotic multicellular. Animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, can move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of cells (blastula) during embryonic growth. Animalia consists of two classifications, vertebrates (chordates) and invertebrates (non-chordates). It is based on the notochord (flexible rod cartilage). Vertebrates include birds, fish, mammals, reptiles and amphibians. Meanwhile, invertebrates consist of porifera, cnidaria, Annelida, Mollusca, Platyhelminthes, Echinodermata, and Arthropoda (crustacea, Arachnida, insects and Myriapoda).
How to Spot the Differences between Vertebrates and Invertebrates?
Do you know that 97% of animals on Earth are invertebrates? The primary differences between vertebrate and invertebrate animals are the existence of the backbone. Vertebrates have spines, and invertebrate does not. As invertebrates do not have an internal skeletal system, they sometimes have an external skeleton that shields their soft and frail body called an exoskeleton. Invertebrates can reproduce extremely fast, unlike many vertebrates, which take years to develop. Vertebrate animals, on the other hand, have a spine that grows from a notochord they have as an embryo. They also have specified internal systems (complex respiratory structures), a completed circulatory system and sensory organs that make the nervous system. Due to their backbone, many vertebrates have a larger physique than invertebrates. They also tend to move faster because of their spines. Below is the table of differences between vertebrates and invertebrates:
|
Vertebrate |
Invertebrate |
|
They have a backbone and internal skeleton. |
Lack of backbone and internal skeleton. |
|
They lack an exoskeleton. |
They have an exoskeleton. |
|
Open circulatory system. |
Closed circulatory system. |
|
Most of them have compound eyes. |
They do not have compound eyes. |
|
Radial or bilateral body symmetry |
Bilateral body symmetry only. |
|
There are three nutrition modes (Autotrophic, Parasitic and Heterotropic). |
Only has one mode of nutrition (Heterotrophic) |
|
Examples of vertebrates: Mammals (cats, dogs, whales), reptiles (snakes, crocodiles, turtles), aves (chicken, duck, owl), and amphibious (frog, toad, newt). |
Examples of invertebrates: are an octopus, sea urchin, worm, sponge, rotifer, spider, nematode, leech, mollusc, annelid, snails, slug, insect, starfish, and sea cucumber. |
What are Endangered Animals?
Endangered animals are a type of creature that is risked by extinction. Species become threatened with complete elimination for two main reasons: habitat loss or genetic divergence. A loss of habitat or place for a living can happen in a natural way, as the dinosaurs went from the Earth 65 million years ago. Human activity can also be the reason for the animal to lose their place. The never-ending growth of housing, industry and agriculture decreases the area for the animals to live. When the animal loses their home, it will have difficulty having a life, which causes extinction. Similar to habitat loss, genetic loss can also happen naturally and is affected by human actions. The natural cause happens when the animal fails to adapt to the new environment. Human action can also direct a loss of genetic variation. Overhunting and overfishing have diminished the inhabitants of numerous animals.
Why is Learning About Animals Important?
Introducing animals to children is essential as it will help them to understand the nature around them. The awareness and interest in animals can guide children to develop empathy at a young age and improve more positive classroom relationships, and social-emotional growth. As children have knowledge of animals, they understand the differences and similarities, and needs and compassion and empathy for the animals can develop. It will also serve as the foundation for their biology and science studies in school.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments
Printable images for classifying animals worksheets in preschool are valuable tools that engage young learners, allowing them to visually categorize different species and develop their cognitive skills in a fun and interactive way.
These classifying animal worksheets for preschoolers are a helpful way to introduce early science concepts in a fun and engaging format.
These printable animal classification worksheets for preschoolers are a helpful educational tool, offering a visual aid to help children build their knowledge and understanding of different animal species.
Printable animal classification worksheets for preschool provide an engaging and interactive way for young children to learn about different animals, helping them develop their observational and critical thinking skills.
These Classifying Animals Worksheets for preschool are an excellent tool to foster curiosity and learning about animals in an engaging way. The clear and simple format makes it easy for young learners to understand and enjoy the classification process. Highly recommended resource!