Work and Energy Worksheet 1
The Work and Energy Worksheet 1 is designed for students who are studying the concepts of work and energy. This worksheet serves as a valuable resource for practicing and applying these principles.
Table of Images 👆
- Chemistry Stoichiometry Worksheet Answer Key
- Potential Kinetic Energy Worksheet
- Ohms Law Worksheet Answers
- Sound and Light Energy Worksheet
- 4th Grade Science Worksheets
- Earth Science Worksheets Answers
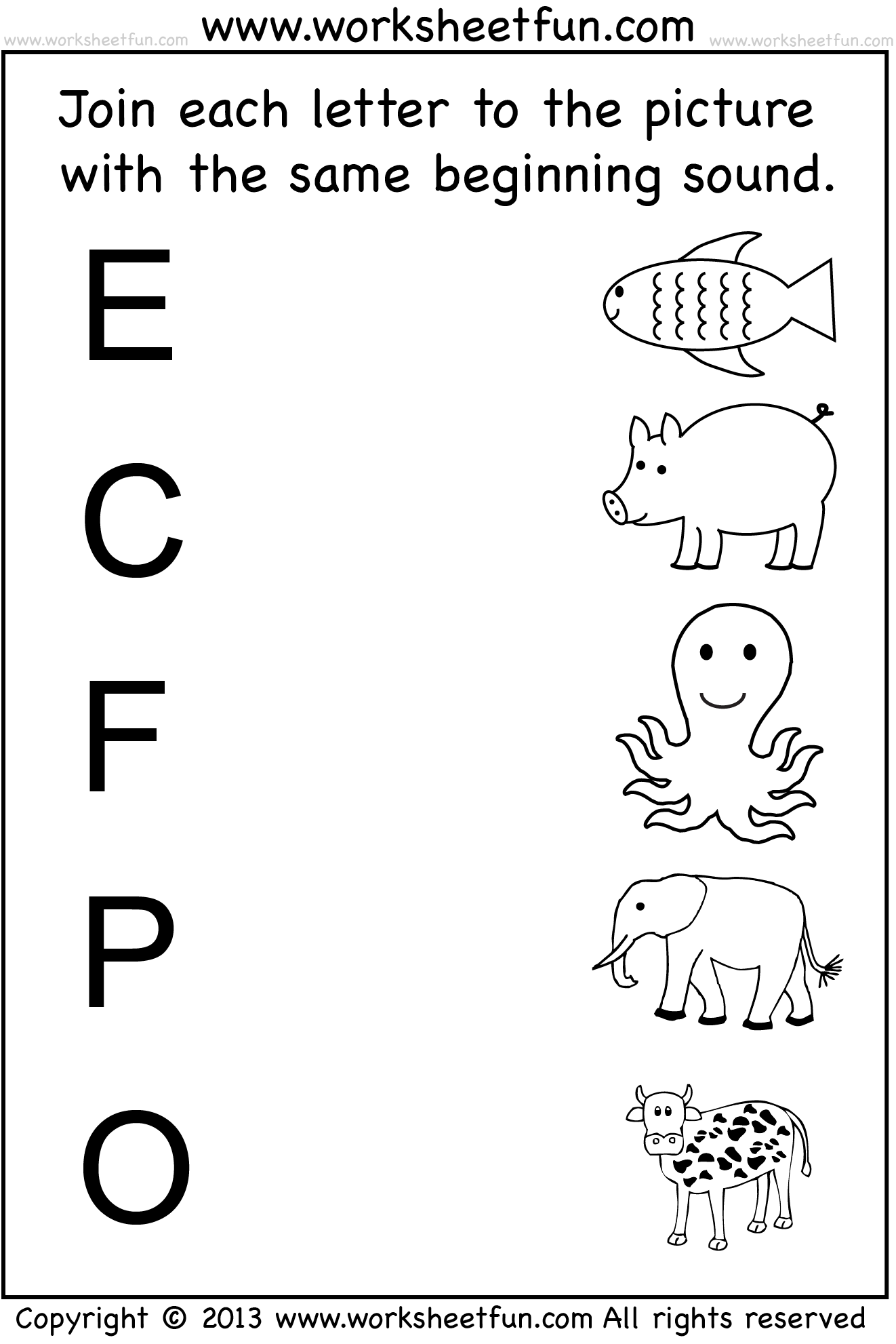
- Free Kindergarten Beginning Sounds Worksheets
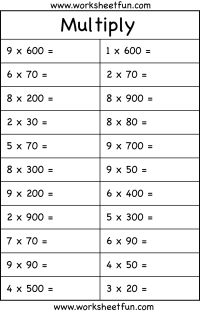
- Printable Multiplication Worksheets for 4th Grade Math
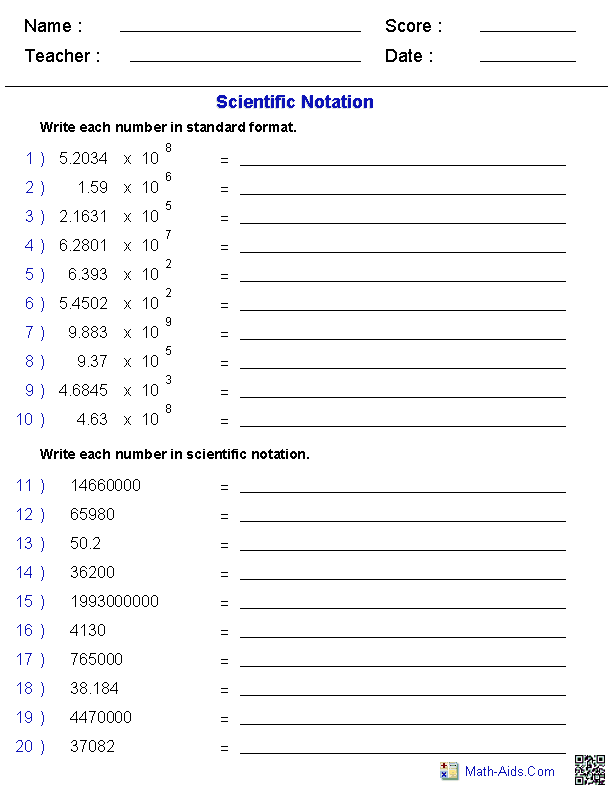
- Scientific Notation Worksheet
- Mindfulness Activity Worksheets
More Energy Worksheets
Light and Heat Energy WorksheetsTypes of Energy Transfer Worksheet
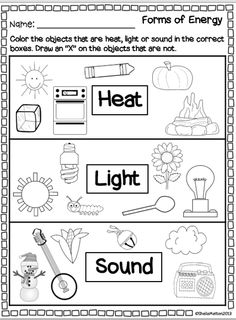
Energy Light Heat Sound Worksheets
3 Forms of Energy Worksheets
Energy Worksheets for Third Grade
What is the definition of work?
Work can be defined as the physical or mental effort exerted to achieve a specific result or to produce or accomplish something. It involves the use of energy to move an object over a distance or to apply force to achieve a task. Work is measured in units such as joules or calories and is a fundamental concept in physics and everyday life.
How is work calculated?
Work is calculated by multiplying the force applied to an object by the distance over which the force is applied. The formula for work is W = F * d, where W is work, F is the force, and d is the distance. This formula allows us to quantify the amount of energy transferred when a force is applied to move an object over a certain distance.
What are the units of work?
The units of work are typically measured in joules (J) or foot-pounds (ft-lb) in the International System of Units (SI) or the British imperial system, respectively. Work is the product of force applied over a distance in the direction of the force, and it represents the transfer of energy to or from an object.
What is the work-energy principle?
The work-energy principle states that the work done on an object is equal to the change in its kinetic energy. In other words, the work-energy principle explains that the work done to accelerate an object is converted into its kinetic energy. This principle is a fundamental concept in physics and is commonly used to analyze and understand the motion of objects.
What is the definition of energy?
Energy is the capacity of a system to do work or produce heat. It can exist in various forms, such as kinetic energy (energy of motion), potential energy (stored energy), thermal energy (heat energy), and electromagnetic energy (light energy). Energy plays a fundamental role in all physical processes and is pivotal for sustaining life and driving various activities in the universe.
What are the different types of energy?
The different types of energy include kinetic energy (energy of motion), potential energy (stored energy), thermal energy (heat energy), chemical energy (energy stored in chemical bonds), electrical energy (energy from moving electric charge), nuclear energy (energy stored in the nucleus of an atom), and radiant energy (energy that travels in waves, such as light and sound).
How is mechanical energy defined?
Mechanical energy is defined as the sum of potential energy, which is energy stored due to the position or configuration of an object, and kinetic energy, which is the energy possessed by an object due to its motion. In simpler terms, mechanical energy encompasses the energy associated with both the movement of an object and the forces acting upon it.
What is the law of conservation of energy?
The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. This means that the total energy in a closed system remains constant over time, with energy being transferred and converted between different forms, such as kinetic, potential, thermal, or chemical energy.
How is power related to work?
Power is directly related to work, as power is the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred. The formula for power is P = W/t, where P is power, W is work, and t is time. In other words, the more power an object or system has, the faster it can perform work or transfer energy. Thus, power and work are intricately linked in the context of physical systems and energy transformations.
What is the unit of power?
The unit of power is the watt (W), named after James Watt, which is a derived unit in the International System of Units (SI).
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments