Sound Energy Worksheets for 3rd
grade are a great way to engage young learners and reinforce their understanding of this fascinating scientific concept. These worksheets are specifically designed to cater to the needs of 3rd-grade students, ensuring that the content is both age-appropriate and educational. By focusing on the entity of sound energy and its characteristics, these worksheets provide a subject-centric approach that encourages active learning and critical thinking.
Table of Images 👆
More Energy Worksheets
Light and Heat Energy WorksheetsTypes of Energy Transfer Worksheet
Energy Light Heat Sound Worksheets
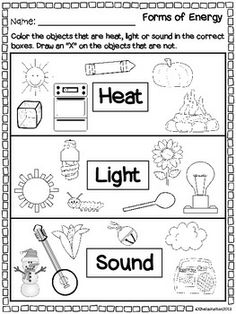
3 Forms of Energy Worksheets
Energy Worksheets for Third Grade
What is sound energy?
Sound energy is a form of mechanical energy that results from the vibration of particles in a medium, such as air, water, or a solid object. When an object vibrates, it creates sound waves that travel through the medium and can be perceived by the human ear. Sound energy is responsible for creating the sensation of hearing and allows us to communicate, detect danger, and experience music and other forms of auditory stimuli.
How is sound energy produced?
Sound energy is produced when an object vibrates, creating pressure waves that travel through a medium, such as air or water. These pressure waves cause the particles in the medium to bump into each other, transmitting the energy of the vibration from one particle to another. When the waves reach our ears, they cause our eardrums to vibrate, and our brains interpret these vibrations as sound.
What is the medium through which sound travels?
Sound travels through a medium, which can be a solid, liquid, or gas. The particles in the medium vibrate as the sound wave passes through, transferring energy and creating the sensation of sound. Without a medium, such as the vacuum of space, sound waves cannot propagate.
How is sound energy detected by our ears?
Sound energy is detected by our ears through a process that involves the outer ear collecting sound waves and sending them to the eardrum, causing the eardrum to vibrate. These vibrations are then transmitted through tiny bones in the middle ear to the cochlea in the inner ear. Inside the cochlea, hair cells convert the vibrations into electrical signals that are sent to the brain via the auditory nerve, where they are perceived as sound.
What is the difference between pitch and volume in sound?
Pitch refers to how high or low a sound is, which is determined by the frequency of the sound waves. Volume, on the other hand, refers to how loud or soft a sound is, which is determined by the amplitude of the sound waves. In simpler terms, pitch is about the "highness" or "lowness" of a sound, while volume is about the "loudness" or "softness" of a sound.
Can sound energy travel through a vacuum?
No, sound energy cannot travel through a vacuum because it requires a medium, such as air, water, or a solid material, to propagate as it relies on the vibration of particles in the medium to transmit energy. In the absence of a medium, like in a vacuum where there are no particles to vibrate, sound waves cannot travel.
What are some examples of objects that produce sound energy?
Examples of objects that produce sound energy include musical instruments like guitars, drums, and pianos, as well as everyday items like alarm clocks, doors creaking, and vehicles honking. Additionally, animals such as birds chirping or dogs barking, and natural phenomena like thunder and waves crashing also generate sound energy.
How does sound travel through different mediums, such as solids, liquids, and gases?
Sound travels through different mediums by creating vibrations that propagate through the particles of the medium. In solids, these particles are closely packed, allowing for faster and more efficient transmission of sound waves. In liquids, the particles are more spread out, which results in a slightly slower transmission of sound. In gases, the particles are even further apart, causing sound waves to travel at a slower speed compared to solids and liquids. Overall, the interaction of sound waves with the particles in each medium determines the speed and efficiency of sound transmission through different mediums.
How does the frequency of a sound wave affect its pitch?
The frequency of a sound wave directly affects its pitch. A higher frequency corresponds to a higher pitch, and a lower frequency corresponds to a lower pitch. This means that the more cycles a sound wave completes per second (measured in Hertz), the higher the pitch of the sound will be perceived by our ears.
How can sound energy be harnessed and used in everyday life?
Sound energy can be harnessed and used in everyday life through technologies like microphones, speakers, and musical instruments. Microphones convert sound into electrical signals that can be amplified and used for communication or recording purposes. Speakers work in reverse, converting electrical signals back into sound waves that can be heard. Musical instruments utilize sound energy to produce music through vibration and resonance. Additionally, sound energy is also utilized in various alarm systems, ultrasound technology, and noise-canceling headphones for everyday use.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



































Comments