Science Force and Motion Worksheets
Are you searching for science worksheets that focus specifically on force and motion? Look no further. These informative and engaging worksheets are designed to help students grasp the key concepts of this topic. Whether you are a teacher looking for classroom resources or a parent wanting to supplement your child's learning at home, these worksheets are the perfect entity to reinforce learning and inspire curiosity about the fascinating world of science.
Table of Images 👆
- Force and Motion Worksheets 2nd Grade
- Science Worksheets Push and Pull
- 2nd Grade Science Forces and Motion
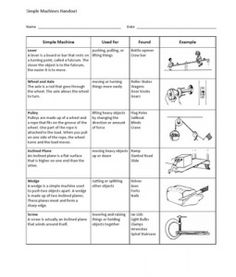
- Science Simple Machines Worksheets
- Push and Pull Worksheets Kindergarten
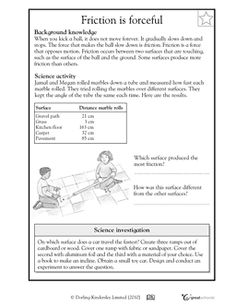
- Force and Friction Worksheets
- Newtons Laws Worksheet
- Newtons Three Laws of Motion Worksheets
- Newtons Laws of Motion Worksheets
- Political Push and Pull Factors
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
What is force?
Force is a physical interaction that causes an object to change its motion or shape. It is typically described as a push or pull exerted by one object on another, and it is measured in units such as Newtons (N). Force is a fundamental concept in physics that governs the movement and behavior of all objects in the universe.
What are the units used to measure force?
The units used to measure force are typically expressed in newtons (N), which is the standard international unit for force. Other common units include pounds (lb) and dynes (dyn) in some systems of measurement.
How is force represented in a free body diagram?
Force is represented in a free body diagram as an arrow pointing in the direction of the force, with the length of the arrow indicating the magnitude of the force. The arrow is labeled with the type of force being applied, such as tension, gravity, friction, or normal force, to clearly depict the forces acting on an object in a given situation.
What is inertia?
Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist changes in its state of motion. This means an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will continue moving at a constant speed and direction unless acted upon by an external force.
What is Newton's first law of motion?
Newton's first law of motion, also known as the law of inertia, states that an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will continue moving in a straight line at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force.
What is friction and how does it affect motion?
Friction is the force that resists the relative motion or tendency of motion between two surfaces in contact. It affects motion by creating resistance that opposes the motion of an object, causing it to slow down or come to a stop. Friction also generates heat and can cause wear and tear on surfaces. Generally, the greater the friction between two surfaces, the more effort is required to move one surface relative to the other.
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
Speed is a scalar quantity that measures how fast an object is moving in a particular direction, while velocity is a vector quantity that measures both the speed and direction of an object's motion. In essence, speed tells you how fast something is going, while velocity tells you how fast something is going and in which direction.
What is Newton's second law of motion?
Newton's second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. Mathematically, it can be expressed as F = ma, where F is the force applied on the object, m is its mass, and a is its acceleration.
How does gravity affect objects on Earth?
Gravity on Earth is a force that pulls objects towards the center of the planet, keeping them grounded. It causes objects to have weight, and influences how they move and interact with one another. The strength of gravity also determines the rate at which objects fall towards the ground when dropped, affecting their speed and acceleration.
How do balanced and unbalanced forces affect an object's motion?
Balanced forces keep an object at rest or moving at a constant velocity, while unbalanced forces cause the object to accelerate in the direction of the stronger force. Balanced forces result in no change in motion, whereas unbalanced forces result in a change in motion by either starting, stopping, or changing the speed or direction of the object.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments