Science Cells Worksheets
Are you in search of engaging and educational resources to reinforce your students' understanding of cells in science? Look no further! Our science cells worksheets are designed to enhance knowledge and comprehension of this fundamental subject. With a focus on providing relevant and concise information, these worksheets are ideally suited for teachers and homeschooling parents who want to engage their students in interactive and insightful learning experiences.
Table of Images 👆
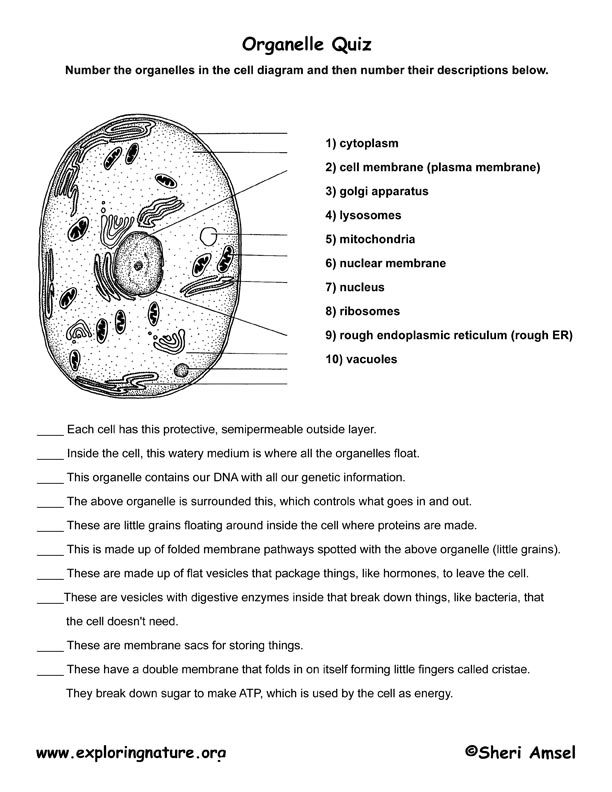
- Cell Organelle Quiz
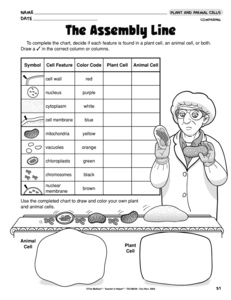
- Plant and Animal Cell Worksheet
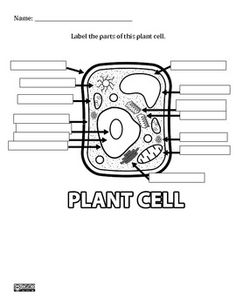
- Plant Cell Diagram Worksheet
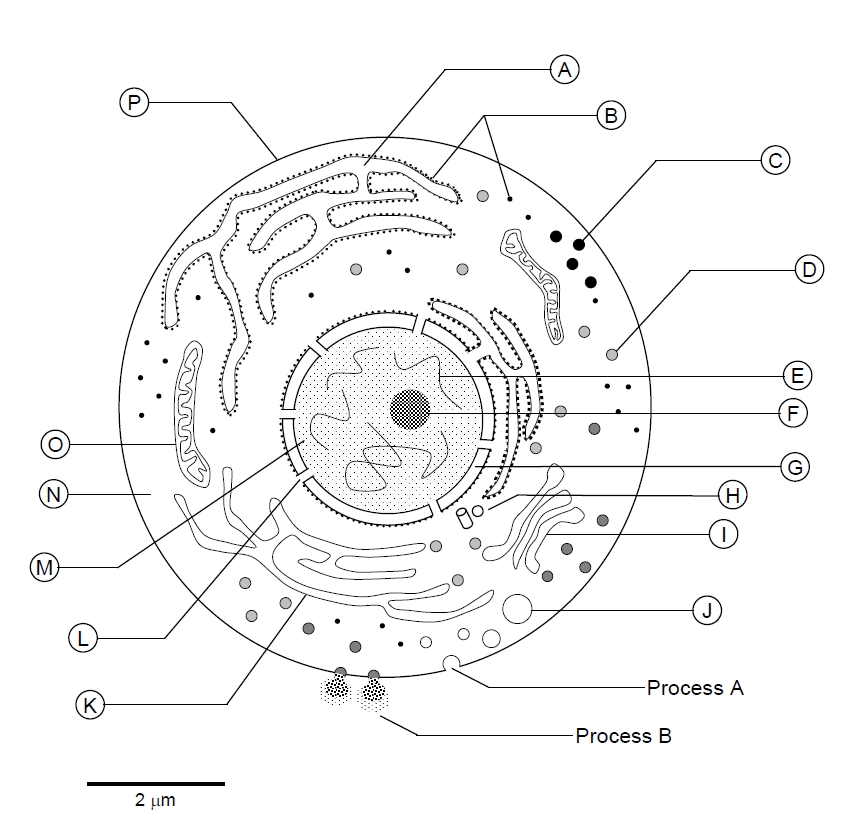
- Cell Diagram Worksheet
- Plant Cell Coloring Page
- Printable Blank Bar Graph Template
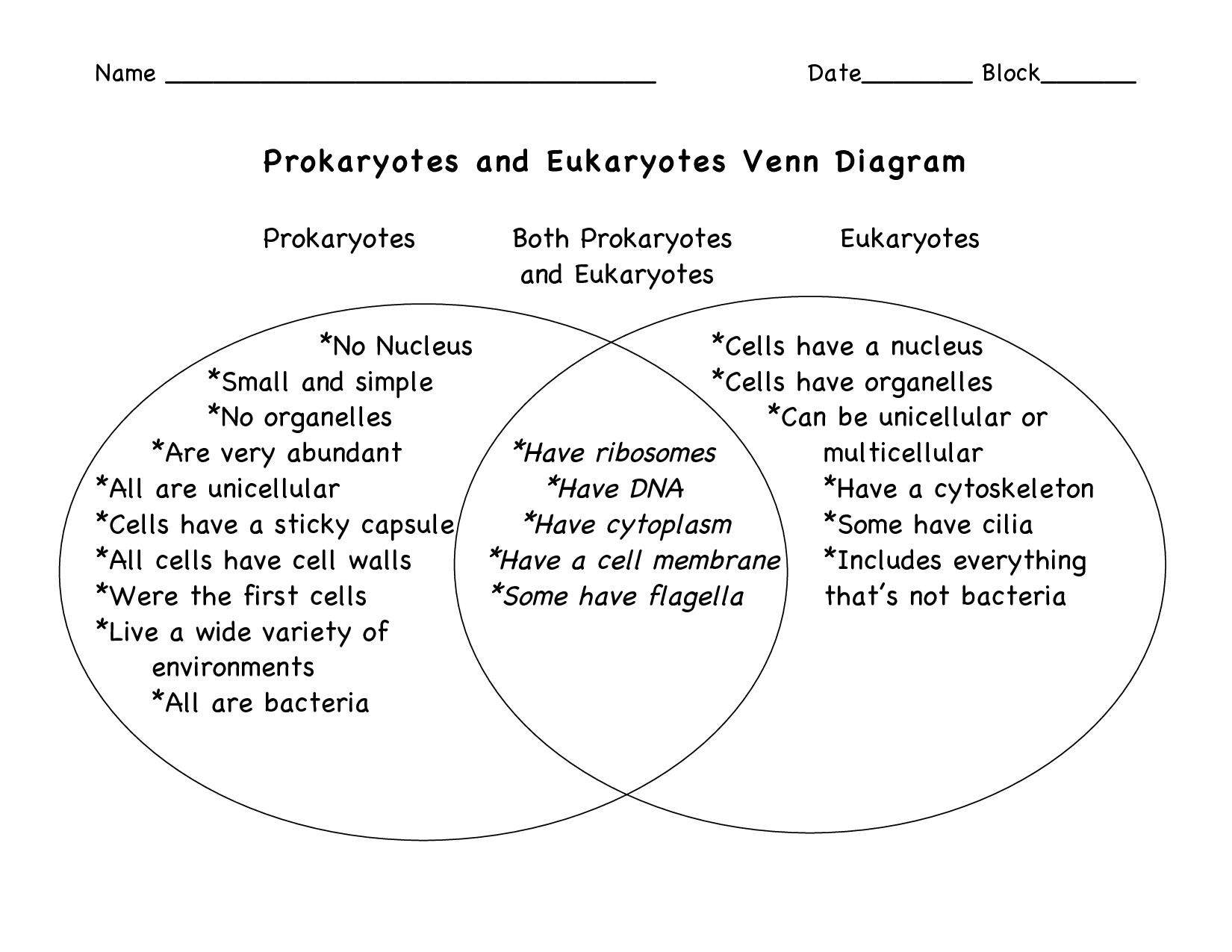
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Venn Diagram
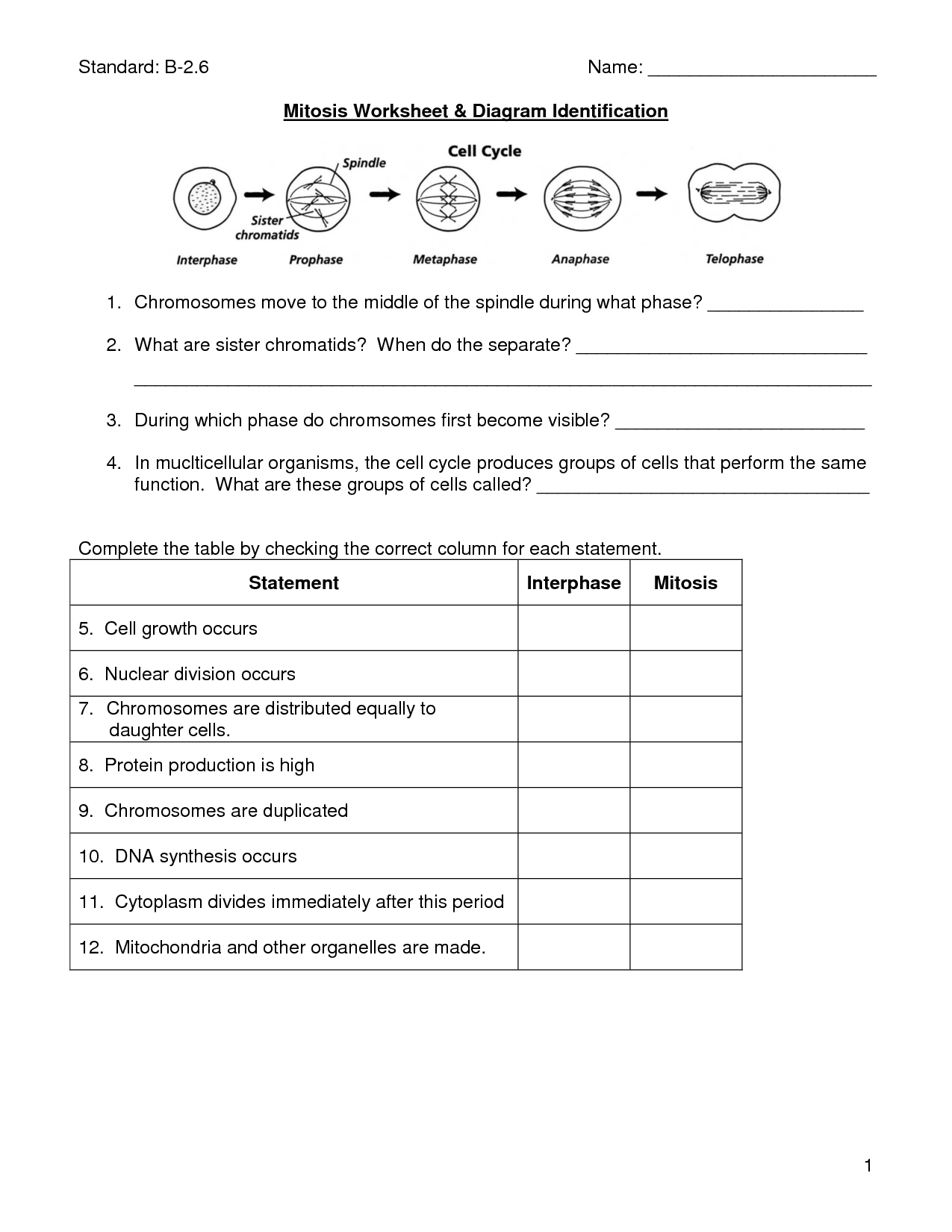
- Diagram Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- 7th Grade Life Science Worksheets
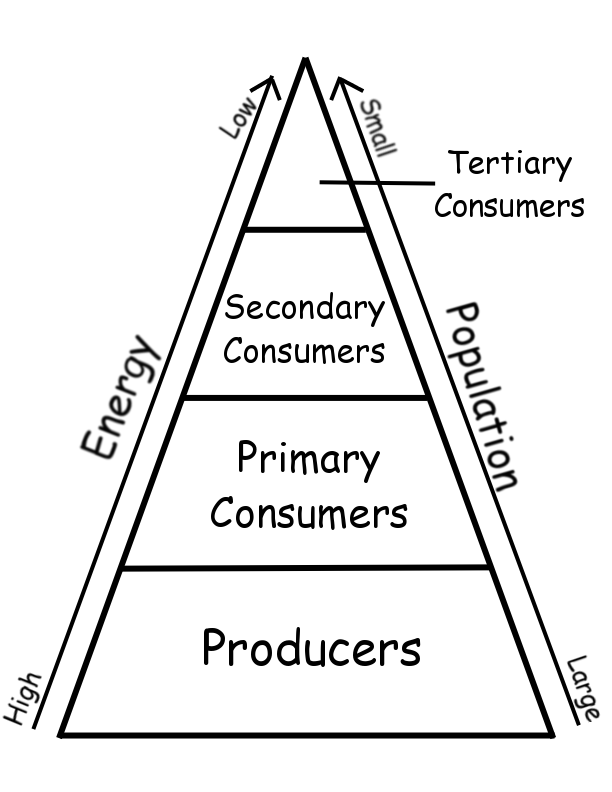
- Science Energy Pyramid
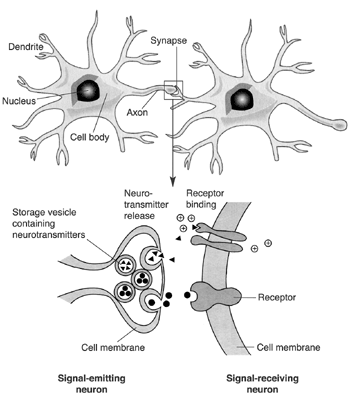
- Nerve Cell Neuron with Synapse
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
What is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms?
The basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms is the cell. Cells are the smallest units of life that can function independently and carry out all necessary biological processes such as growth, reproduction, and metabolism. Each cell is specialized for different functions and together they form tissues, organs, and ultimately whole organisms.
What are the main components of a typical animal cell?
A typical animal cell contains several key components, including the nucleus (which houses the cell's genetic material), the cytoplasm (which contains organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and ribosomes), the cell membrane (which regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell), and various structures like lysosomes (containing enzymes for digestion) and the cytoskeleton (providing structural support and facilitating cell movement). These components work together to ensure the cell functions properly and carries out essential processes for survival.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane functions as a protective barrier that separates the interior of the cell from its external environment, controlling the movement of substances in and out of the cell. It regulates the exchange of nutrients, ions, and waste products to maintain cellular homeostasis, allows for cell recognition and communication, and enables cells to interact with their surroundings. The cell membrane also plays a role in cell signaling, adhesion, and maintaining the structure and shape of the cell.
What is the role of the nucleus in a cell?
The nucleus in a cell serves as the control center, containing the cell's genetic material in the form of DNA. It regulates gene expression, cell growth, and reproduction by allowing certain molecules in and out of the nucleus through its nuclear pores. The nucleus is essential for maintaining the integrity and functioning of the cell by coordinating various cellular activities and processes.
What are mitochondria and what is their function?
Mitochondria are membrane-bound organelles found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Their primary function is to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which serves as the cell's main energy source. Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell due to this vital role in energy production. Additionally, they are involved in numerous other cellular processes such as cell signaling, cell differentiation, and cell cycle control.
What are chloroplasts and where are they found?
Chloroplasts are specialized organelles found in plant cells and some algae. They are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which sunlight is converted into energy-rich molecules to fuel the cell's activities. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that gives plants their characteristic color and allows them to capture light energy for photosynthesis.
What is the function of ribosomes in a cell?
Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis within a cell by translating messenger RNA (mRNA) into functional proteins. They are the site where amino acids are assembled into polypeptide chains according to the instructions coded in the mRNA. This process is crucial for the cell to function properly as proteins are essential for various cellular processes and structures.
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have a defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus. Prokaryotic cells are typically smaller and simpler in structure, with their DNA located in the nucleoid region, while eukaryotic cells are larger, more complex, and contain multiple linear chromosomes within the nucleus. Additionally, eukaryotic cells can be single-celled or multicellular, whereas prokaryotic cells are predominantly single-celled organisms.
What is the role of the endoplasmic reticulum in a cell?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) plays a crucial role in protein and lipid synthesis, modification, and transport within a cell. It is responsible for the folding of proteins, the assembly of lipids, and the transportation of these synthesized molecules to various parts of the cell, including the Golgi apparatus for further processing and distribution. Additionally, the ER is involved in detoxification processes and the regulation of calcium levels in the cell.
How do cells communicate with each other?
Cells communicate with each other through various mechanisms including direct contact through cell junctions, secretion and reception of signaling molecules such as hormones, neurotransmitters, and growth factors, and through cell-to-cell interactions. This communication allows cells to coordinate their activities, respond to external cues, and maintain proper tissue function and homeostasis.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments