High School Biology Meiosis Worksheet
Are you a high school biology student aiming to grasp the intricate process of meiosis? Look no further! Our high school biology meiosis worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of this essential cellular division process. Designed with clarity and precision in mind, this worksheet offers a range of engaging and thought-provoking questions that will deepen your understanding of meiosis and its importance in the natural world.
Table of Images 👆
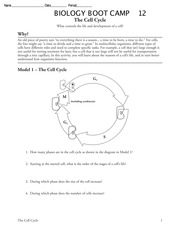
What is meiosis?
Meiosis is a type of cell division that occurs in sexually reproducing organisms, resulting in the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells) with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. It involves two rounds of division, resulting in four daughter cells that are genetically different from each other and the original parent cell.
How does meiosis differ from mitosis?
Meiosis is a type of cell division that results in four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell, allowing for genetic diversity and the formation of gametes. Mitosis, on the other hand, is a process of cell division that results in two daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, and is involved in growth, repair, and asexual reproduction. Meiosis involves two rounds of cell division, resulting in genetic variation through crossing over and independent assortment, while mitosis involves only one round of cell division.
What are the two main stages of meiosis?
The two main stages of meiosis are meiosis I and meiosis II. Meiosis I involves the separation of homologous chromosomes, resulting in two haploid daughter cells, each with a unique combination of genetic material. Meiosis II is similar to mitosis, where sister chromatids are separated, ultimately producing four haploid daughter cells that are genetically different from each other and the parent cell.
What is the purpose of meiosis?
The primary purpose of meiosis is to produce gametes (sperm and egg cells) with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This reduction in chromosome number is essential for sexual reproduction, as it ensures that when the egg is fertilized by a sperm, the resulting zygote will have the correct number of chromosomes. Meiosis also introduces genetic variation through processes such as crossing over and independent assortment, contributing to the diversity of offspring in sexually reproducing organisms.
How many daughter cells are produced at the end of meiosis?
At the end of meiosis, four daughter cells are produced.
How is genetic variation achieved during meiosis?
Genetic variation during meiosis is achieved through the processes of crossing over and independent assortment. Crossing over occurs during prophase I when homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material, creating new combinations of alleles. Independent assortment occurs during metaphase I when homologous pairs line up randomly at the metaphase plate, leading to the random distribution of maternal and paternal chromosomes into daughter cells. These processes result in genetic diversity among offspring, contributing to the overall genetic variation within a population.
What is crossing over and when does it occur during meiosis?
Crossing over is the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis. It occurs during prophase I of meiosis, specifically during the pachytene stage. This process results in genetic variation among offspring by creating new combinations of alleles on the chromosomes.
What is the significance of independent assortment during meiosis?
Independent assortment during meiosis is significant because it leads to genetic variation by producing unique combinations of alleles on different chromosomes. This process occurs during the formation of gametes, where homologous chromosomes align randomly, resulting in the inheritance of different combinations of genes by offspring. This genetic diversity is crucial for the adaptation of organisms to changing environments and plays a key role in evolution.
What is the difference between homologous chromosomes and sister chromatids?
Homologous chromosomes are two chromosomes (one from each parent) that pair up during meiosis and have the same genes at the same loci but potentially different alleles. In contrast, sister chromatids are two identical copies of a single chromosome that are produced during DNA replication in the S phase of the cell cycle and are held together by a centromere. Homologous chromosomes are involved in genetic recombination during meiosis, while sister chromatids are involved in ensuring accurate distribution of genetic material during cell division.
How does meiosis contribute to the formation of gametes?
Meiosis is a type of cell division that leads to the formation of gametes, such as sperm and egg cells. During meiosis, a single cell undergoes two rounds of division, resulting in four new cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. This reduction in chromosome number is essential for sexual reproduction, as it ensures that when the sperm and egg cells combine during fertilization, the resulting zygote will have the correct number of chromosomes. Meiosis also introduces genetic variability through processes such as crossing over and independent assortment, further contributing to the diversity of offspring.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments