Food Chain Worksheets for 5th Grade
Food chain worksheets are a valuable educational resource designed for 5th-grade students to enhance their understanding of how energy and nutrients flow through different organisms in an ecosystem. These worksheets provide an engaging way for young learners to grasp the concept of food chains and learn about the interdependence between plants and animals in nature.
Table of Images 👆
More 5th Grade Worksheets
5th Grade Math Worksheets PrintableMultiplication Worksheets for 5th Grade
Constitution Worksheets for 5th Grade
Coordinates Worksheets 5th Grade
United States Worksheets 5th Grade
Free Division Worksheets for 5th Grade
Poetry Terms 5th Grade Worksheets
5th Grade Social Studies Printable Worksheets
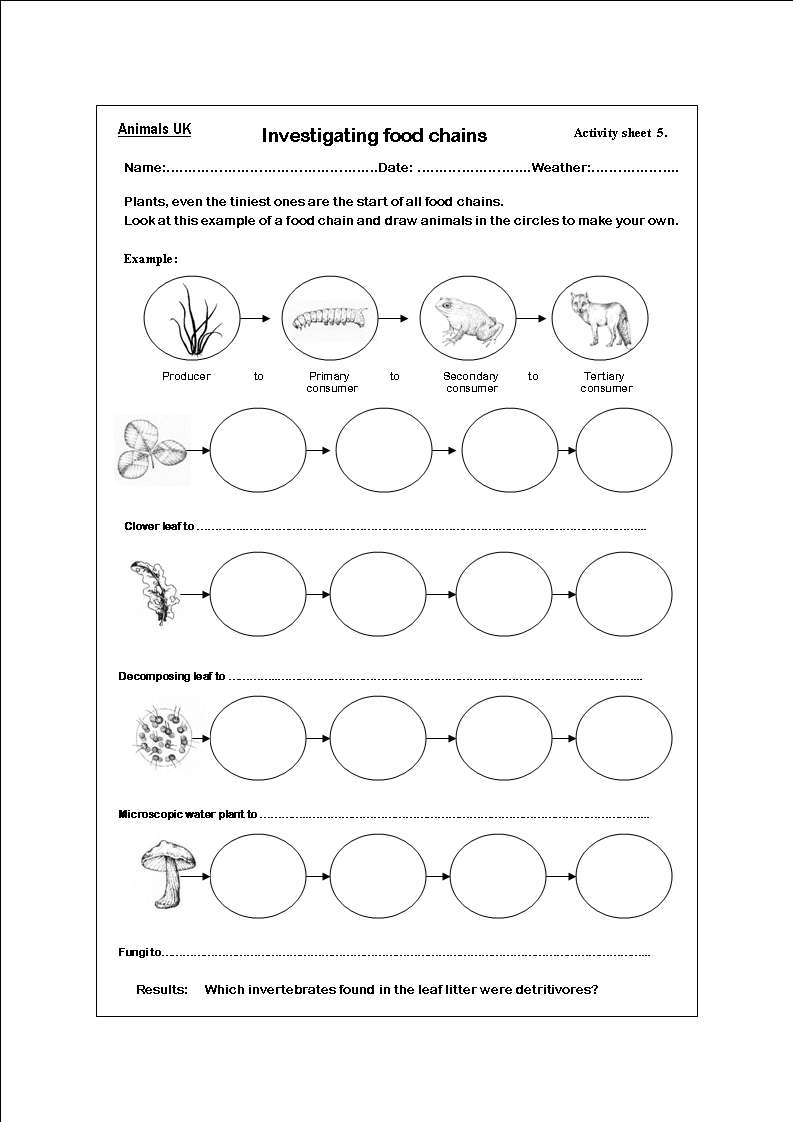
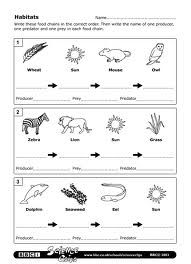
What is a food chain?
A food chain is a sequence of organisms in an ecosystem where each organism is the food source for the next organism in the chain. It represents the transfer of energy and nutrients as one organism consumes another. Each level in a food chain is called a trophic level, with producers at the base followed by primary consumers, secondary consumers, and so on, up to apex predators.
What are producers in a food chain?
Producers in a food chain are organisms, usually plants or autotrophic microorganisms, that produce their own energy through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. They are the foundation of any ecosystem as they convert sunlight, water, and nutrients into food energy that can be consumed by other organisms in the ecosystem.
What are consumers in a food chain?
Consumers in a food chain are organisms that obtain their energy by consuming other organisms. They are divided into primary consumers (herbivores that eat plants), secondary consumers (carnivores that eat herbivores), and tertiary consumers (carnivores that eat other carnivores). Consumers play a crucial role in maintaining the balance and energy flow within ecosystems by transferring energy and nutrients through their consumption of other organisms.
Name an example of a herbivore in a food chain.
A rabbit is an example of a herbivore in a food chain. They primarily feed on plants, such as grasses, clover, and vegetables, making them an important consumer in many ecosystems.
Name an example of a carnivore in a food chain.
A lion is an example of a carnivore in a food chain.
Name an example of an omnivore in a food chain.
A bear is an example of an omnivore in a food chain, as it consumes both plants and animals as part of its diet.
What is a primary consumer in a food chain?
A primary consumer in a food chain is an organism that consumes producers (plants or algae) directly for energy. These organisms are herbivores that eat plants or algae as their primary source of food, forming the second trophic level in the food chain.
What is a secondary consumer in a food chain?
A secondary consumer in a food chain is an organism that feeds on primary consumers, which are herbivores that eat plants. Secondary consumers are carnivores that obtain energy and nutrients by consuming other animals. They play a crucial role in controlling the populations of primary consumers and maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.
What is a tertiary consumer in a food chain?
A tertiary consumer in a food chain is an organism that consumes secondary consumers, which in turn feed on primary consumers (plants or herbivores). Tertiary consumers are typically apex predators that are at the top of the food chain and have few or no natural predators themselves.
How does energy flow through a food chain?
Energy flows through a food chain starting from producers, such as plants, which convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. Herbivores then consume these plants, transferring the energy up the chain. Carnivores further consume the herbivores, continuing the energy transfer. At each step, energy is lost as heat, waste, and by metabolic processes, so each subsequent trophic level receives less energy. This flow of energy through a food chain supports the organisms within the ecosystem and ultimately contributes to the overall balance of energy in the ecosystem.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments