Electricity Worksheets for 4th Grade
Are you a 4th-grade teacher or parent looking for engaging and informative resources to teach your child or students about electricity? Look no further! In this blog post, we will explore a range of electricity worksheets specifically designed for 4th graders. These worksheets will cover various topics related to electricity, helping young learners grasp the fundamentals of this fascinating subject in an interactive and comprehensive manner.
Table of Images 👆
- Electrical Circuits Worksheets
- Conductors and Insulators Worksheet 4th
- Electrical Circuit Diagram Worksheet
- Electricity Circuit Worksheets 4th Grade
- Ohms Law Worksheet Answers
- Circuit Symbols Worksheet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers
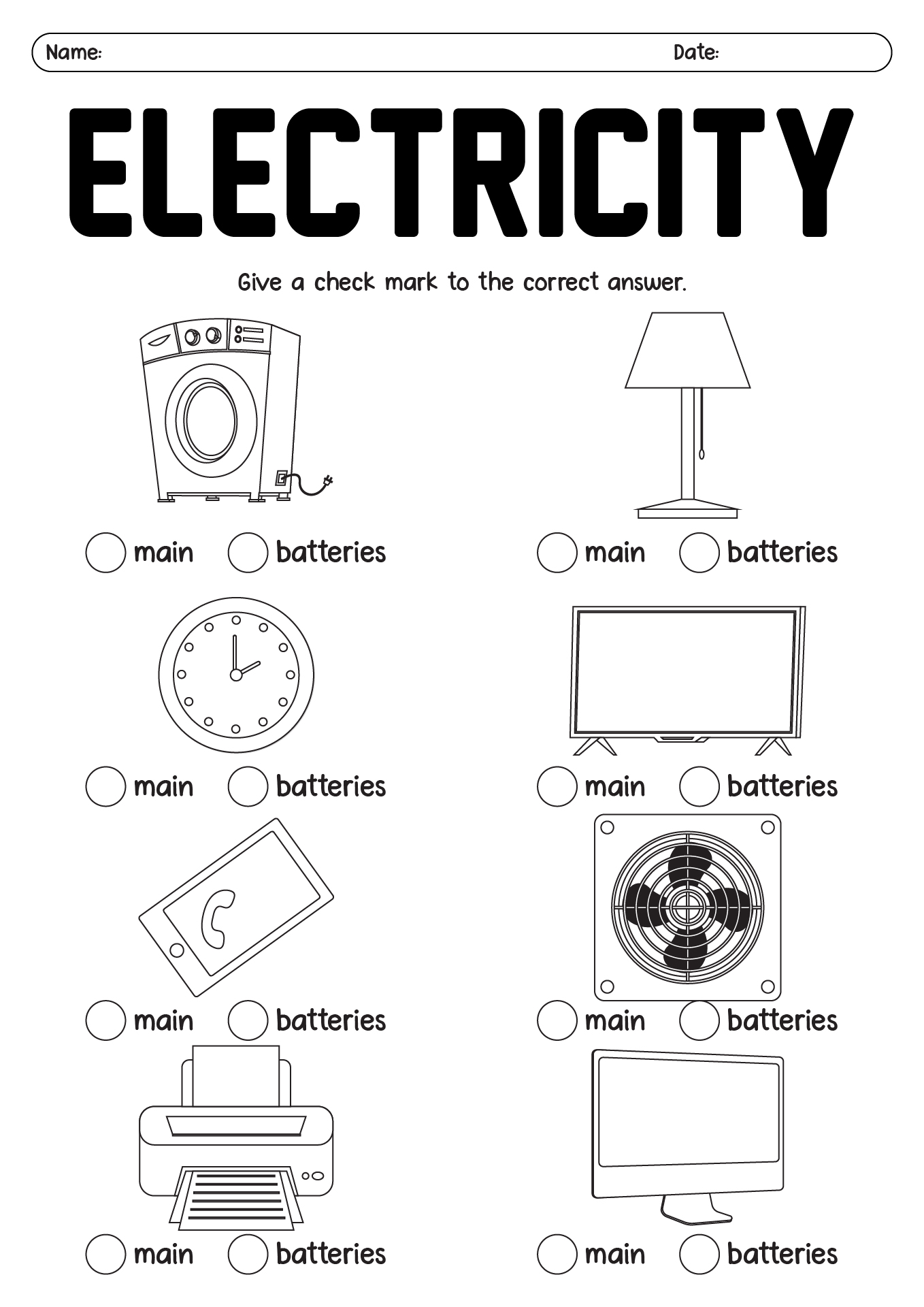
- Electricity Basics Worksheet for 4th Grade Students
- 4th Grade Electricity Science Worksheets
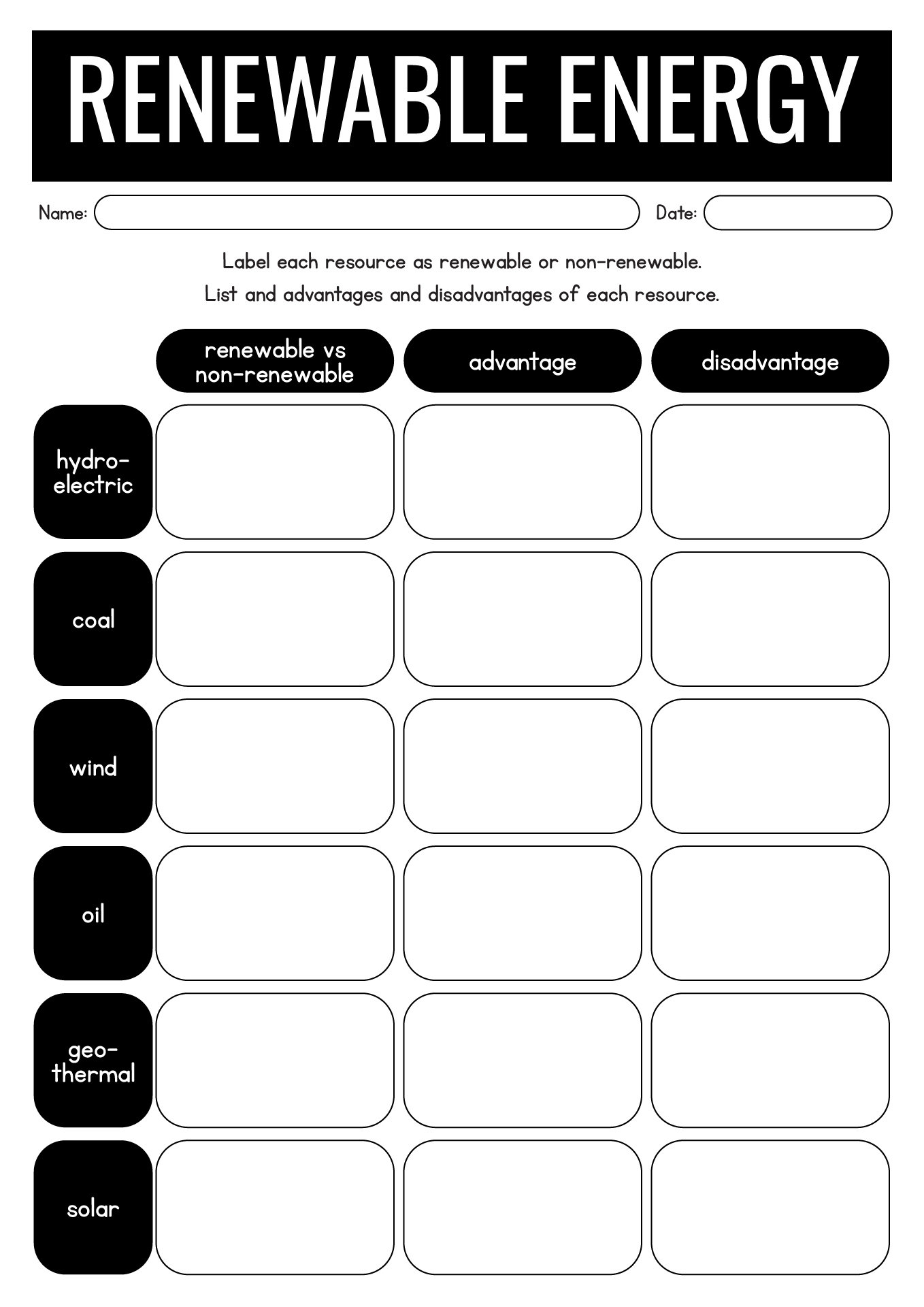
- Renewable Energy Activities for Fourth Graders
- Electricity Worksheets For Fourth Graders
- Science Worksheets On Electricity For 4th Grade
- Electricity Learning Sheets For Grade Four

More 4th Grade Worksheets
4th Grade Elapsed Time WorksheetsIrregular Plural Worksheets 4th Grade
Writing 4th Grade Reading Worksheets
Rotational Symmetry Worksheets 4th Grade
Simple Circuit Worksheets 4th Grade
Fourth Grade Reading Comprehension Worksheets
Long Division with Remainders Worksheets 4th Grade
4th Grade Spelling Worksheets Printable
Printable Adjective Worksheets 4th Grade
Fourth Grade Reading Comp Worksheets
Are you looking for engaging and educational resources to help your 4th-grade students learn about electricity? Look no further! Electricity worksheets for 4th grade are a fantastic way to introduce young learners to the basics of electricity in a fun and interactive way.
In the 4th grade, students start to delve deeper into scientific concepts, including electricity. By introducing electricity worksheets in 4th grade, students can grasp the basics of circuits, conductors, insulators, and more. So, these worksheets provide a hands-on approach to learning and allow students to explore and experiment with electricity in a safe and controlled environment.
That’s why you should introduce these electricity worksheets in your classroom today and spark your students' interest in science!
Explore our electricity worksheets for 4th grade students to enhance their understanding of basic electrical concepts in a fun and engaging way!
What are Electricity Worksheets for 4th Grade?
Before diving into the specifics of electricity worksheets for 4th graders, it's important to have a basic understanding of what electricity is. Electricity happens when electric charges travel through a conductor, such as a metal wire. It can power our homes, light up our rooms, and keep our devices running. Teaching students about electricity at a young age can help them develop a strong foundation in science and technology.
Specifically, when it comes to teaching electricity to 4th-grade students, electricity worksheets can be incredibly beneficial. These worksheets are designed to engage young learners and help them grasp the fundamental principles of electricity in a fun and interactive way.
Teachers can incorporate electricity worksheets into their lesson plans in a variety of ways. They can use worksheets as homework assignments, in-class activities, or even as part of a science fair project. By making use of worksheets, teachers can cater to different learning styles and engage students in a more meaningful way.
What Can Students Learn from Electricity Worksheets for 4th Grade?
Through electricity worksheets for 4th grade, students can learn a variety of important concepts related to electricity. Some of the key topics covered in these worksheets may include:
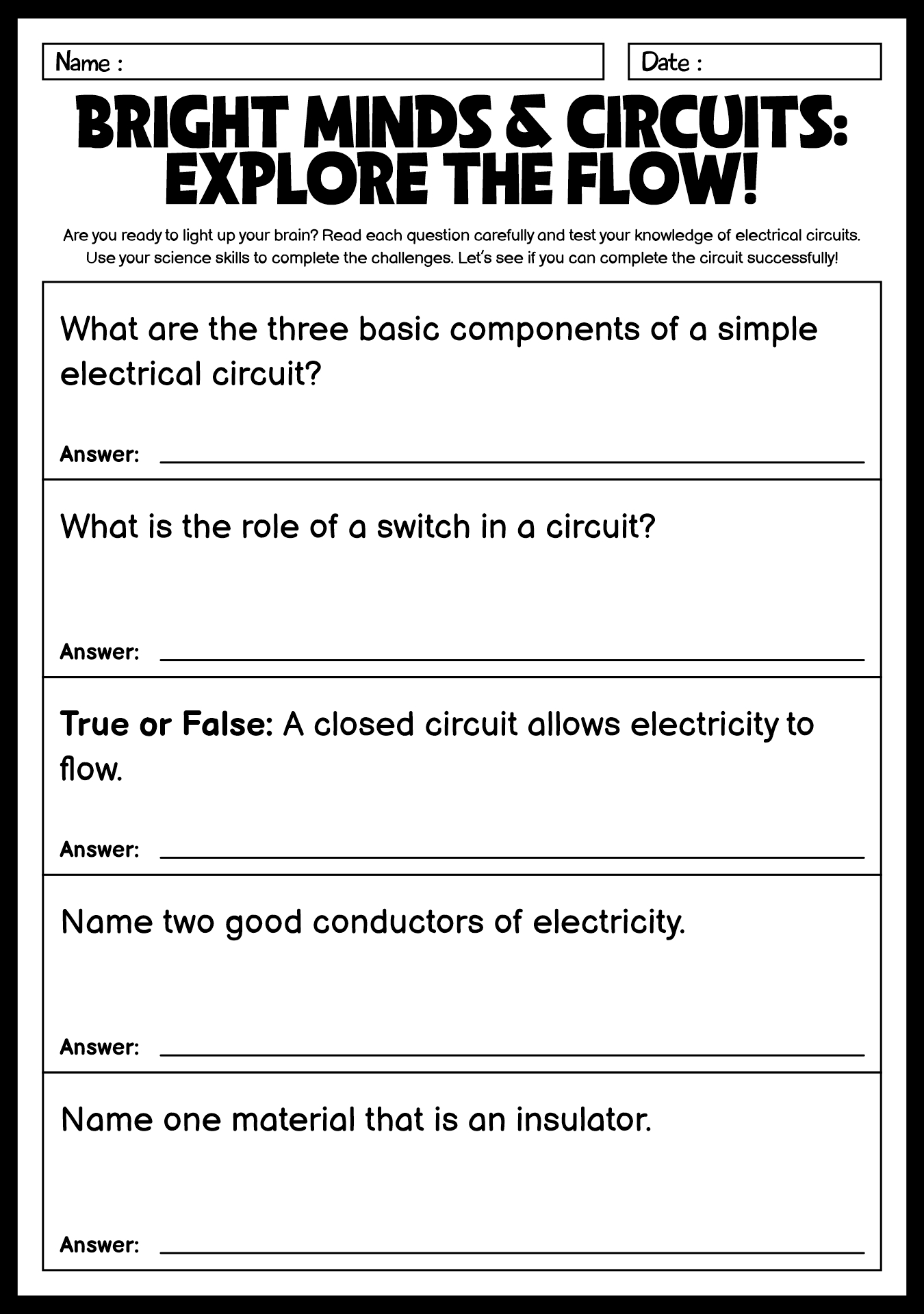
- Types of Circuits: Students can learn about different types of circuits, such as parallel and series circuits, and how electricity flows through them.
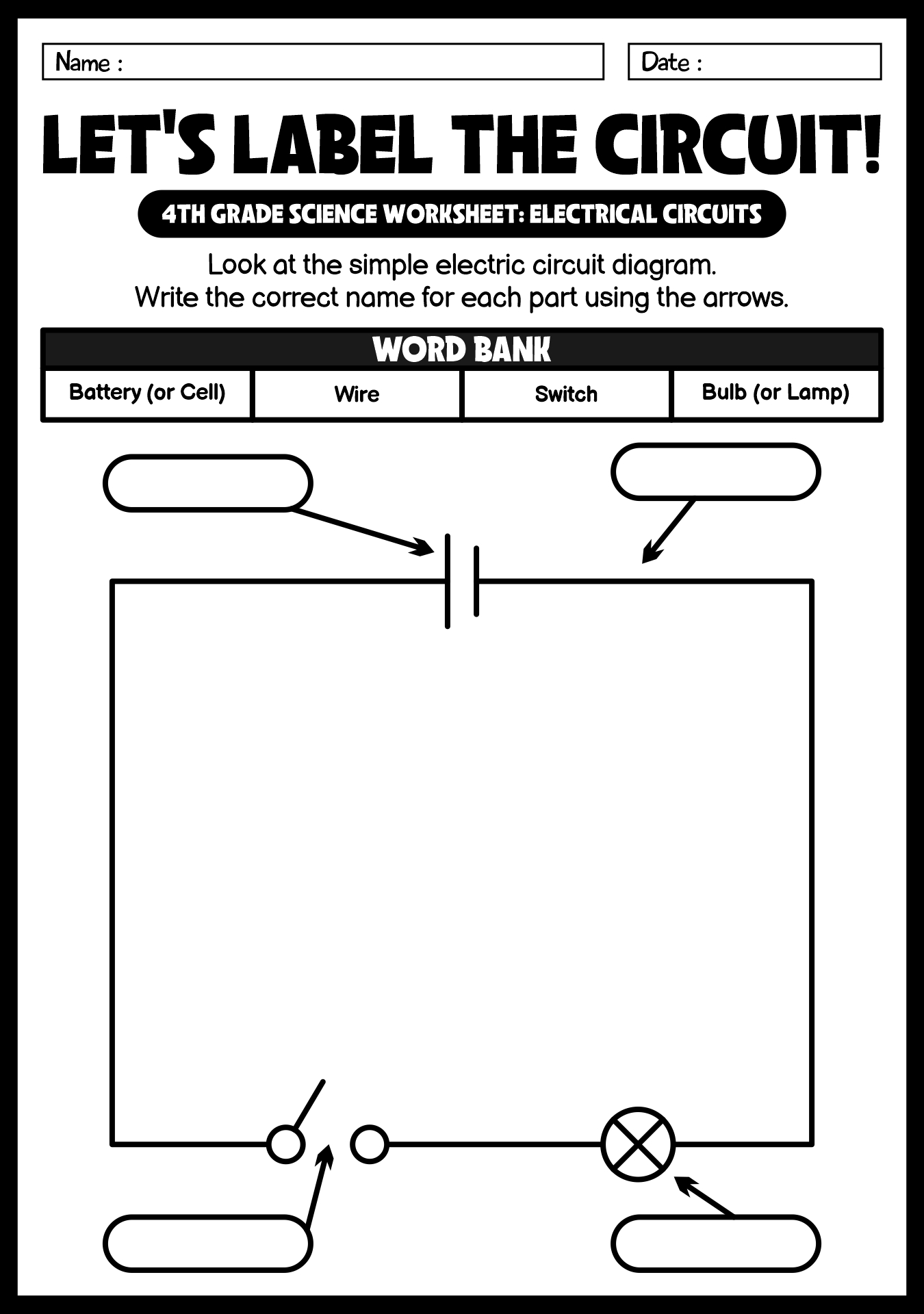
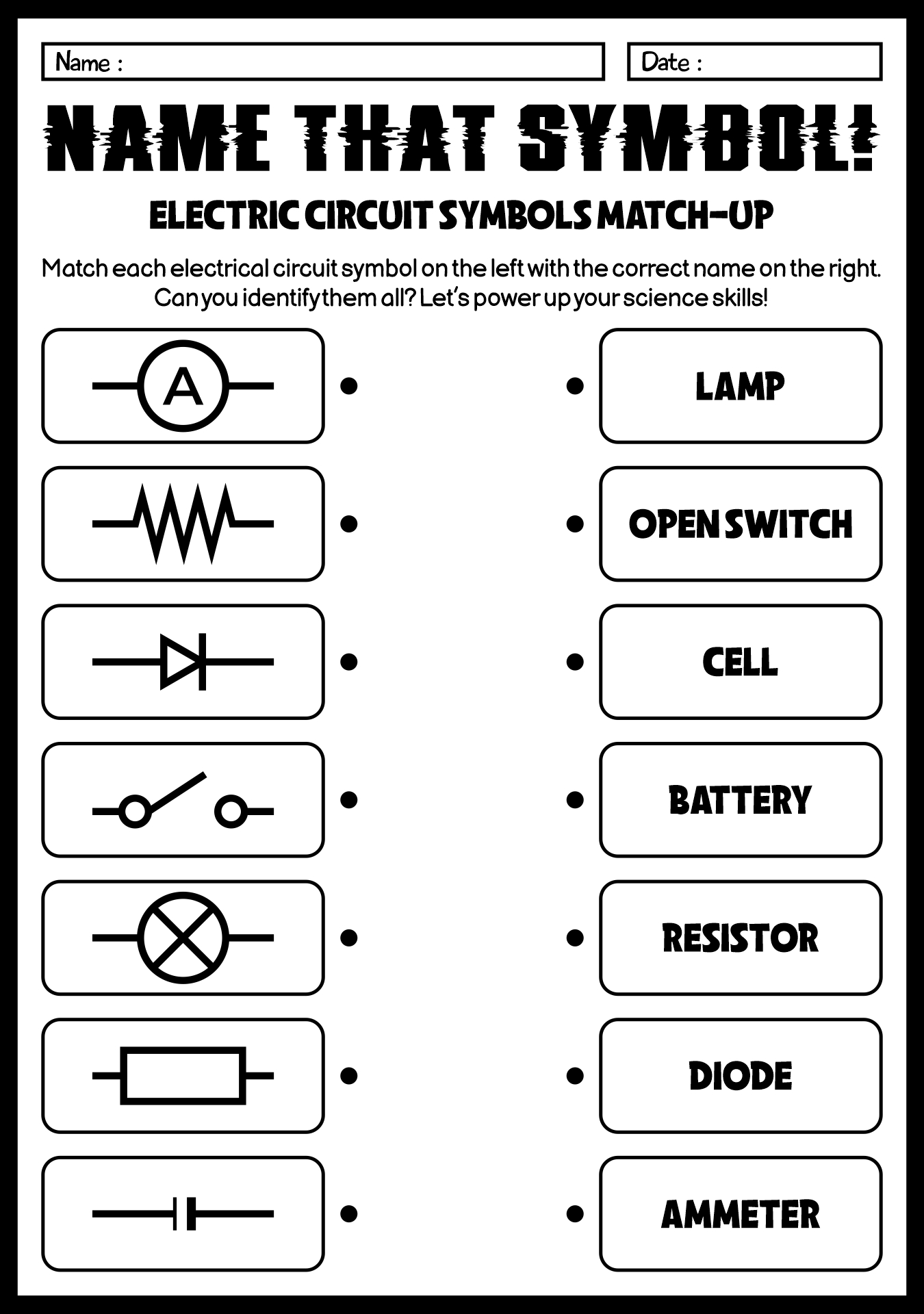
- Electrical Symbols: Worksheets may include lessons on common electrical symbols used in circuit diagrams, helping students understand how to read and interpret these diagrams.
- Safety Precautions: Students can also learn about important safety precautions to take when working with electricity, such as never touching exposed wires and always unplugging devices before working on them.
Can Your Students Identify Conductors and Insulators with These Electricity Worksheets for 4th Grade?
Of course! To start, it's essential to explain to your students what conductors and insulators are. Materials that let electricity pass through easily are called conductors, such as copper, water, and other metals. Unlike conductors, insulators stop electricity from passing through them. Examples include rubber, plastic, and wood.
Understanding the difference between conductors and insulators is crucial for students as it helps them comprehend how electricity works in everyday life. By identifying conductors and insulators, students can apply this knowledge to real-world scenarios, such as electrical safety, circuit design, and energy efficiency.
One way to incorporate these concepts into your lesson plans is by using electricity worksheets specifically designed for fourth-grade students. These worksheets typically include activities such as identifying conductors and insulators, matching objects to their corresponding category, and completing circuits to test conductivity.
Here, we also give you some tips for effective implementation:
- Introduce the concept of conductors and insulators with real-life examples
- Use visual aids such as diagrams and illustrations to enhance comprehension
- Encourage group work and collaboration on worksheet activities
- Provide feedback and review student responses to ensure understanding
Can These Electricity Worksheets for 4th Grade Improve Scientific Thinking?
Yes! Electricity is a fundamental concept in the field of science and technology. By learning about electricity through these worksheets, students can gain insight into how circuits work, how energy is transferred, and the importance of safety when dealing with electrical currents. These concepts not only enhance their scientific knowledge but also prepare them for future learning in more advanced STEM subjects.
So, electricity worksheets for 4th grade students can indeed improve their scientific thinking in several ways. By engaging in hands-on activities and experiments related to electricity, students can develop a deeper understanding of scientific concepts, enhance their critical thinking skills, and apply their knowledge to real-world situations. These worksheets serve as valuable tools to supplement traditional classroom instruction and provide students with a well-rounded approach to learning.
What Real-World Applications are Found in These Electricity Worksheets for 4th Grade?
Now, let's explore some of the real-world applications that can be found in 4th-grade electricity worksheets!
- Circuit Building: One common activity in electricity worksheets is circuit building. Students are given a set of components, such as batteries, wires, and light bulbs, and are asked to create a circuit that lights up the bulb. This hands-on activity helps students understand how circuits work and how electricity flows through them.
- Energy Conservation: Another important concept covered in electricity worksheets is energy conservation. Students learn about the importance of saving energy and ways to reduce electricity usage in their daily lives. This practical knowledge can help students become more conscious of their energy consumption habits.
- Electrical Safety: Never forget, safety comes first when handling anything electrical! Electricity worksheets often include information on how to stay safe around electrical devices and what to do in case of an emergency. Raising awareness about electrical safety among students is a crucial step in avoiding accidents.
Overall, our electricity worksheets for 4th grade are a valuable tool for teaching children about the wonders of electricity in a fun and engaging way. By using these worksheets, you can help your child develop a strong foundation in science and technology while fostering a love for learning. So, start exploring electricity worksheets with your 4th grader today!
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments