Earth Science Seasons Worksheet
Curious about Earth's fascinating seasons? Look no further than our Earth Science Seasons Worksheet! Designed for students and science enthusiasts alike, this comprehensive worksheet delves into the entity of seasons, offering a detailed exploration of the subject's key concepts and principles.
Table of Images 👆
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
What causes the change in seasons on Earth?
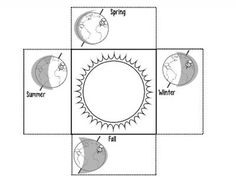
The change in seasons on Earth is caused by the tilt of the Earth's axis as it orbits around the Sun. This tilt results in different regions of the Earth receiving varying amounts of direct sunlight at different times of the year, which in turn leads to the four distinct seasons - spring, summer, autumn, and winter.
How does Earth's tilt impact the seasons?
Earth's tilt on its axis is what causes the change in seasons. As Earth orbits the sun, the tilt causes different parts of the Earth to receive more or less direct sunlight, leading to variations in temperature and daylight hours. When one hemisphere is tilted towards the sun, it experiences summer with longer days and warmer temperatures, while the other hemisphere experiences winter with shorter days and colder temperatures. As Earth continues its orbit, the tilt creates the transitions of spring and autumn.
What is the significance of the solstices and equinoxes?
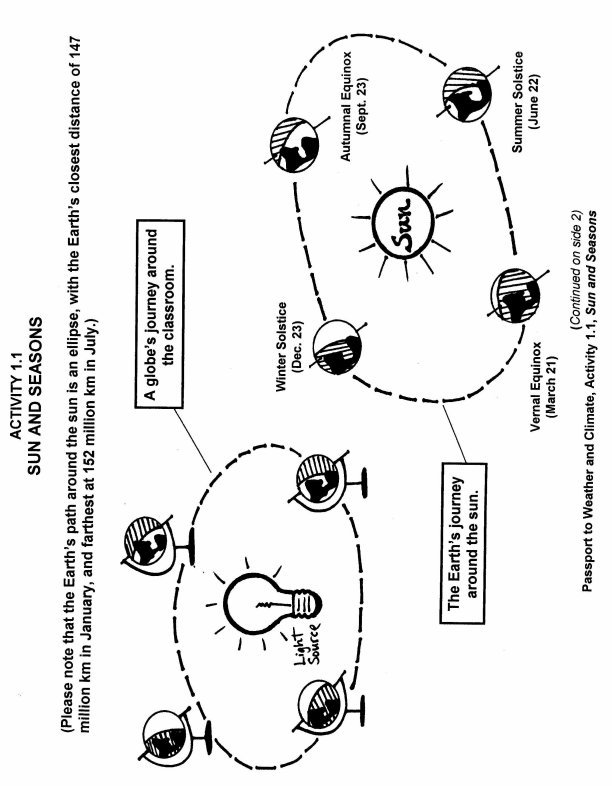
The solstices and equinoxes mark key points in the Earth's orbit around the sun, symbolizing the changing of seasons. The solstices occur when the Earth's axial tilt is either closest to or farthest from the sun, resulting in the longest and shortest days of the year. The equinoxes happen when day and night are roughly equal in length, signaling the beginning of spring or autumn. These celestial events have been significant for cultures throughout history, often tied to agricultural practices, rituals, and festivities that celebrate the cycles of nature.
Why is the Summer Solstice the longest day of the year?
The Summer Solstice is the longest day of the year because it occurs when the Earth's axial tilt is most inclined towards the sun, causing the sun to be at its highest position in the sky and resulting in the most daylight hours for that day in the Northern Hemisphere.
Why is the Winter Solstice the shortest day of the year?
The Winter Solstice is the shortest day of the year because it marks the point when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted furthest away from the sun, resulting in the sun reaching its lowest point in the sky and providing the least amount of daylight. This tilt causes the sun's rays to spread out over a larger surface area, resulting in shorter days and cooler temperatures in the Northern Hemisphere.
How do the tilt and position of Earth's axis affect the intensity of sunlight received in different regions?
The tilt of Earth's axis affects the intensity of sunlight received in different regions by creating the seasons. When a region is tilted towards the Sun, it receives more direct sunlight, leading to warmer temperatures and longer days. Conversely, when a region is tilted away from the Sun, it receives less direct sunlight, resulting in cooler temperatures and shorter days. The position of the Earth's axis also determines which regions receive more or less sunlight throughout the year, influencing the climate patterns in each area.
What is the relationship between the Earth's orbit and the changing seasons?
The Earth's orbit around the sun affects the changing seasons by causing variations in the amount of sunlight that different parts of the Earth receive throughout the year. As the Earth orbits the sun, its tilt relative to the sun remains constant, resulting in different hemispheres being tilted towards or away from the sun at different times. This tilt causes variations in the angle and intensity of sunlight reaching each hemisphere, which in turn leads to the changing seasons as different parts of the Earth receive more or less direct sunlight.
How do the changing seasons affect weather patterns?
The changing seasons affect weather patterns by altering factors such as temperature, precipitation, and humidity. During transitions between seasons, there can be shifts in atmospheric pressure and wind patterns, leading to changes in weather conditions. For example, the summer solstice typically brings warmer temperatures and increased likelihood of thunderstorms, while the winter solstice often ushers in colder temperatures and potential for snow or ice storms. These seasonal variations influence the overall climate and impact local weather patterns.
How do the Northern and Southern Hemispheres experience opposite seasons?
The Northern and Southern Hemispheres experience opposite seasons due to the tilt of the Earth's axis in relation to its orbit around the sun. When one hemisphere is tilted towards the sun, it receives more direct sunlight and experiences summer, while the opposite hemisphere is tilted away from the sun, resulting in less direct sunlight and winter. This tilt causes the length and intensity of daylight to vary, leading to the distinct seasonal changes observed in each hemisphere.
How does the angle of sunlight influence the temperature and climate in different parts of the world during different seasons?
The angle of sunlight influences temperature and climate in different parts of the world during different seasons by determining the amount of solar radiation received at the Earth's surface. When sunlight hits Earth at a more direct angle, such as during summer in the Northern Hemisphere, it delivers more energy per unit area, leading to warmer temperatures. Conversely, when sunlight arrives at a more oblique angle, like during winter in the Northern Hemisphere, it spreads out over a larger area, resulting in cooler temperatures. This variation in solar angle across latitudes and seasons plays a crucial role in shaping regional climates and seasonal temperature patterns worldwide.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments