5th Grade Science Weather Worksheets
If you're a 5th grade student studying science and want to reinforce your understanding of weather concepts, worksheets can be a valuable tool. Worksheets provide a structured approach to learning, allowing you to practice and apply what you've learned in a hands-on way. With a range of engaging exercises and activities, these science weather worksheets are designed to help you grasp key concepts and strengthen your knowledge of weather phenomena.
Table of Images 👆
- 5th Grade Science Worksheets
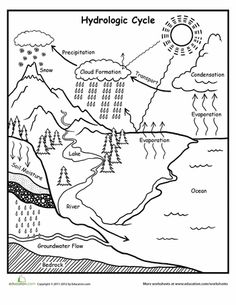
- Earth Water Cycle Worksheets 5th Grade
- 6th Grade Reading Comprehension Worksheets
- Weather Word Search Worksheet
- 5th Grade Worksheets Reading a Weather Map
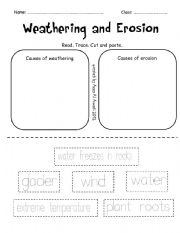
- Weathering and Erosion Worksheet Activity
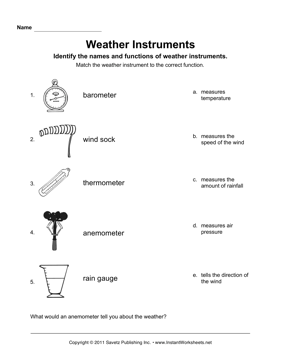
- Weather Instruments Worksheet
- Worksheets Answer Key
- Reading Thermometers Worksheet
- Printable Color by Number Worksheets
More 5th Grade Worksheets
5th Grade Math Worksheets PrintableMultiplication Worksheets for 5th Grade
Constitution Worksheets for 5th Grade
Coordinates Worksheets 5th Grade
United States Worksheets 5th Grade
Free Division Worksheets for 5th Grade
Poetry Terms 5th Grade Worksheets
5th Grade Social Studies Printable Worksheets
What is the water cycle?
The water cycle, also known as the hydrological cycle, is the continuous process by which water moves from the Earth's surface to the atmosphere and back again. It involves processes such as evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and runoff, allowing for the recycling and distribution of water throughout the planet.
What is the difference between weather and climate?
Weather refers to short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific area, such as temperature, humidity, precipitation, and wind. It describes what is happening in the atmosphere at a particular moment or in a short period of time. On the other hand, climate refers to the long-term average of weather patterns in a specific region over an extended period of time, usually decades or centuries. Climate factors in trends, averages, and variations in weather patterns to provide a broader understanding of the typical conditions experienced over time.
How are clouds formed?
Clouds are formed through the process of condensation, where water vapor in the air cools and transforms into tiny water droplets or ice crystals. This usually happens when warm, moist air rises, expands, and cools, causing the water vapor to reach its dew point and condense around tiny particles in the atmosphere, such as dust or pollution. As more water vapor condenses and collects in the air, clouds begin to form and grow in size, eventually leading to precipitation when the droplets become too heavy to stay aloft.
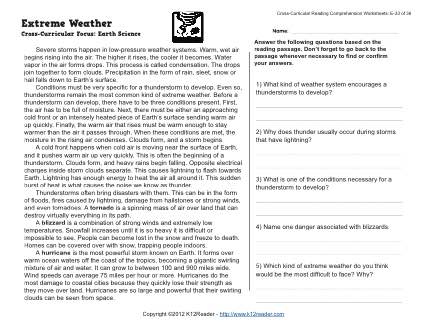
What causes thunder and lightning?
Thunder and lightning are caused by the rapid expansion and contraction of air surrounding a lightning bolt. When a lightning bolt passes through the air, it superheats the air to around 30,000 degrees Celsius, causing it to expand rapidly. This rapid expansion creates a shock wave that we hear as thunder. Lightning itself is an electrical discharge that occurs when positive and negative charges build up in a cloud or between a cloud and the ground, creating a sudden release of energy in the form of a bright flash of light.
Explain the process of evaporation.
Evaporation is the process in which a substance changes from a liquid state to a gaseous state, usually due to an increase in temperature. As heat is applied to the liquid, the kinetic energy of the molecules increases, causing them to move more rapidly and eventually break free from the surface of the liquid. These molecules then enter the surrounding air as vapor. Evaporation is a crucial part of the water cycle, where water evaporates from bodies of water into the atmosphere, contributing to cloud formation and precipitation.
How does air pressure affect weather?
Air pressure plays a significant role in determining weather patterns. High air pressure typically brings fair weather and clear skies, while low pressure often leads to cloudy skies and precipitation. Air moves from areas of high pressure to low pressure, creating wind flows that can influence temperature and humidity levels. Changes in air pressure can indicate the arrival of weather systems such as storms or fronts, making it a critical component in understanding, predicting, and interpreting weather conditions.
What are the different types of precipitation?
The different types of precipitation include rain, snow, sleet, and hail. Rain occurs when water droplets in clouds combine and fall to the ground. Snow forms when water vapor in the atmosphere freezes into ice crystals. Sleet is a mixture of rain and snow or ice pellets that fall to the ground. Hail occurs in strong thunderstorms when updrafts carry raindrops into colder areas of the atmosphere, causing them to freeze and form hailstones that fall to the ground.
What are the four main types of clouds?
The four main types of clouds are cumulus, stratus, cirrus, and nimbus. Cumulus clouds are large, fluffy clouds often associated with fair weather. Stratus clouds are low, flat layers that can bring light rain or drizzle. Cirrus clouds are high, wispy clouds made of ice crystals and often indicate fair weather. Nimbus clouds are dark and dense clouds that bring precipitation, such as rain or snow.
What is the role of the ozone layer in the atmosphere?
The ozone layer in the atmosphere plays a crucial role in protecting life on Earth by absorbing the majority of the sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation, specifically UV-B and UV-C rays. Without the ozone layer, these harmful rays would reach the Earth's surface and cause serious health risks such as skin cancer, cataracts, and damage to plant life. The ozone layer acts as a natural shield, helping to maintain a healthy environment for living organisms to thrive.
Explain the greenhouse effect and its impact on climate change.
The greenhouse effect is a natural process where certain gases in the Earth's atmosphere trap heat from the sun, which helps to keep our planet warm enough to support life. However, human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, have increased the concentration of these greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide and methane, leading to an enhanced greenhouse effect. This excess trapping of heat then causes a warming of the Earth's surface, resulting in climate change. The impacts of climate change include rising temperatures, melting ice caps, sea level rise, extreme weather events, and shifts in ecosystems, all of which have far-reaching consequences for both the environment and human societies.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments