Chemistry Mole Practice Worksheet
For those seeking extra practice with mole calculations in chemistry, a mole practice worksheet can be a valuable resource. This handy tool provides exercises and problems specifically designed to strengthen your understanding and mastery of this fundamental concept in chemistry. Whether you are a high school student preparing for an exam or a college student reviewing for a midterm, a mole practice worksheet can help solidify your understanding of this key topic.
Table of Images 👆
- Mole Calculation Worksheet Answer Key
- Mass to Mole Stoichiometry Worksheet Answer Key
- Mole Conversion Worksheet Answers
- Mole Chemistry Worksheet Answers
- Moles Molecules and Grams Worksheet
- Chemistry Stoichiometry Worksheet Answer Key
- Chemistry Worksheet Answer Keys
- Average Atomic Mass and Isotopes Worksheet Answer Key
- Empirical Formula Worksheet Answer Key
- Mole Conversion Worksheet Answer Key
- Chemistry pH and Poh Calculations Worksheet Answers
- Balancing Chemical Equations Worksheet 2 Answer Key
- Balancing Chemical Equations Worksheet
More Chemistry Worksheets
What is the formula for converting moles to particles?
The formula for converting moles to particles is to multiply the number of moles by Avogadro's number, which is approximately 6.022 x 10^23 particles/mole. This formula helps you determine the number of particles present in a given number of moles of a substance.
How do you convert moles to grams for a specific element or compound?
To convert moles to grams for a specific element or compound, you need to use the molar mass of the substance. First, determine the molar mass by adding up the atomic masses of each atom in the chemical formula. Then, multiply the number of moles by the molar mass to get the number of grams. This conversion is done using the formula: grams = moles x molar mass.
What is the equation for determining the number of moles from grams?
To determine the number of moles from grams, you can use the equation: moles = mass (in grams) / molar mass (in g/mol). This equation helps you convert the mass of a substance into its corresponding amount in moles by considering the molar mass of the substance.
How do you calculate the molar mass of a compound?
To calculate the molar mass of a compound, add up the atomic masses of all the elements in the compound based on the chemical formula. The atomic masses can be found on the periodic table. Multiply the atomic mass of each element by the number of atoms of that element in the compound. Then, sum up all the weighted atomic masses to get the molar mass of the compound, which is typically expressed in grams per mole (g/mol).
What is Avogadro's number and what does it represent?
Avogadro's number is approximately 6.022 x 10^23, and it represents the number of atoms, molecules, ions, or other elementary entities in one mole of a substance. This constant is crucial in chemistry for relating the mass or volume of a substance to the number of particles it contains, allowing for precise measurements and calculations in chemical reactions and other processes.
How do you determine the empirical formula from a molecular formula?
To determine the empirical formula from a molecular formula, you need to find the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in the compound. To do this, divide the subscripts in the molecular formula by the greatest common factor to get the empirical formula. For example, if the molecular formula is C6H12O6, the greatest common factor is 6, so dividing each subscript by 6 gives the empirical formula CH2O.
What is the difference between a balanced equation and an unbalanced equation?
A balanced equation has an equal number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation, showing that the law of conservation of mass is obeyed. An unbalanced equation, on the other hand, has a different number of atoms of each element on both sides, indicating that mass is not conserved. Balancing an equation involves adjusting coefficients to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides, allowing for an accurate representation of the chemical reaction.
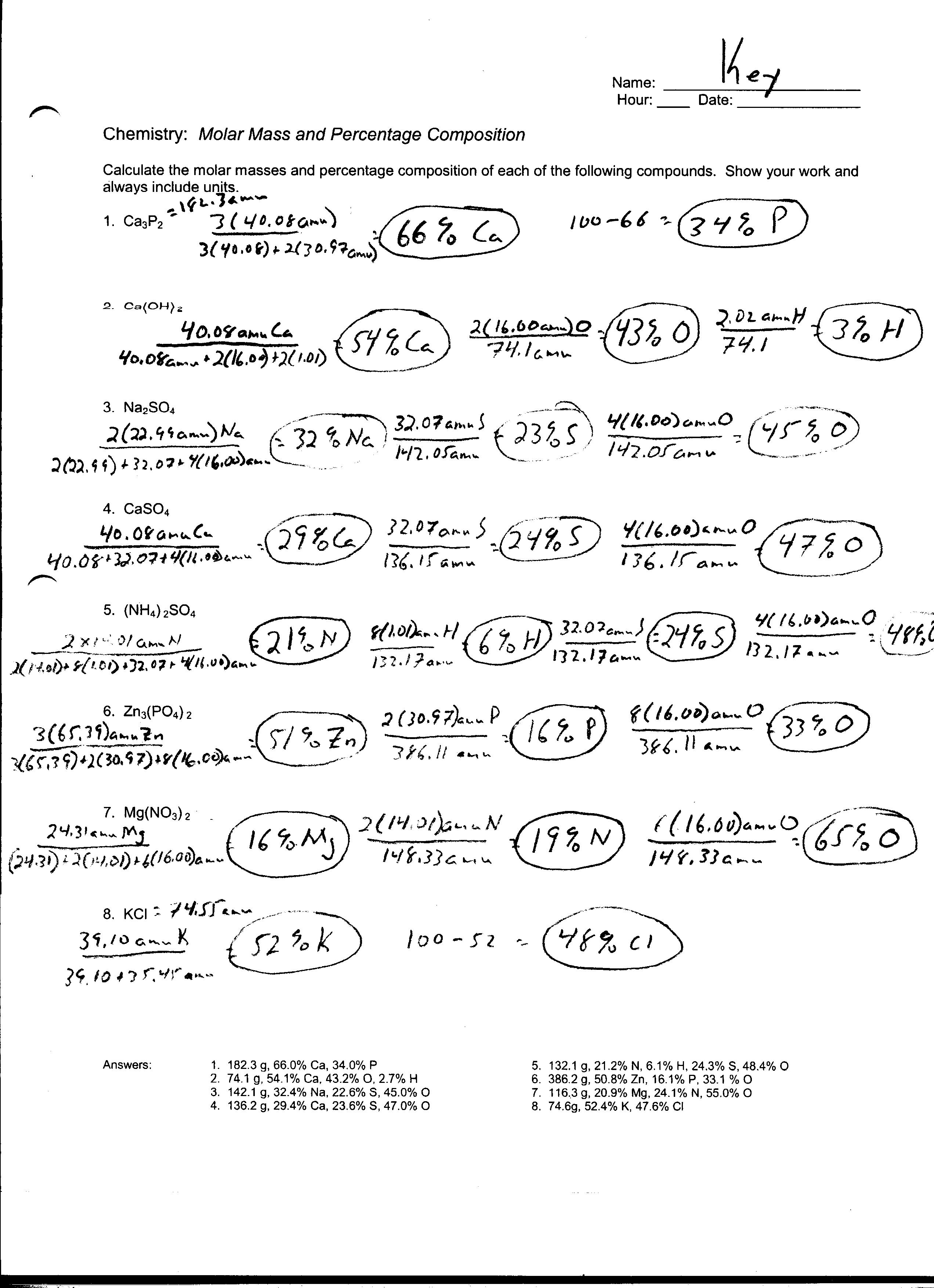
How do you calculate the percent composition of an element in a compound?
To calculate the percent composition of an element in a compound, you first determine the molar mass of the element and the compound. Then, divide the molar mass of the specific element by the molar mass of the compound and multiply the result by 100 to get the percentage. This calculation gives you the percentage of that specific element's contribution to the total mass of the compound.
What is the difference between a limiting reactant and an excess reactant?
A limiting reactant is the substance that is completely consumed in a chemical reaction, thereby limiting the amount of product that can be formed. On the other hand, an excess reactant is the substance that is present in excess quantity and remains after the limiting reactant is completely used up. It does not determine the amount of product formed but is present in surplus.
How do you calculate the theoretical yield of a reaction?
To calculate the theoretical yield of a reaction, you first need to determine the balanced chemical equation for the reaction. Then, identify the limiting reactant by comparing the mole ratios of the reactants in the balanced equation to the actual amounts of reactants used. Calculate the theoretical yield by multiplying the amount of limiting reactant used by the stoichiometry factor in the balanced equation that relates the limiting reactant to the product. This will give you the maximum amount of product that can be obtained in the reaction under ideal conditions.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments