Worksheets Physical Science Electricity
If you're a teacher or parent in need of engaging and effective educational materials for teaching physical science, specifically electricity, then worksheets can be a valuable tool. Worksheets provide a structured and organized way to reinforce learning and help students solidify their understanding of this complex subject matter.
Table of Images 👆
- Science Worksheets Energy Transformation
- Physical Science Worksheets
- Heat and Thermal Energy Worksheet
- Physical Science Worksheets and Answers
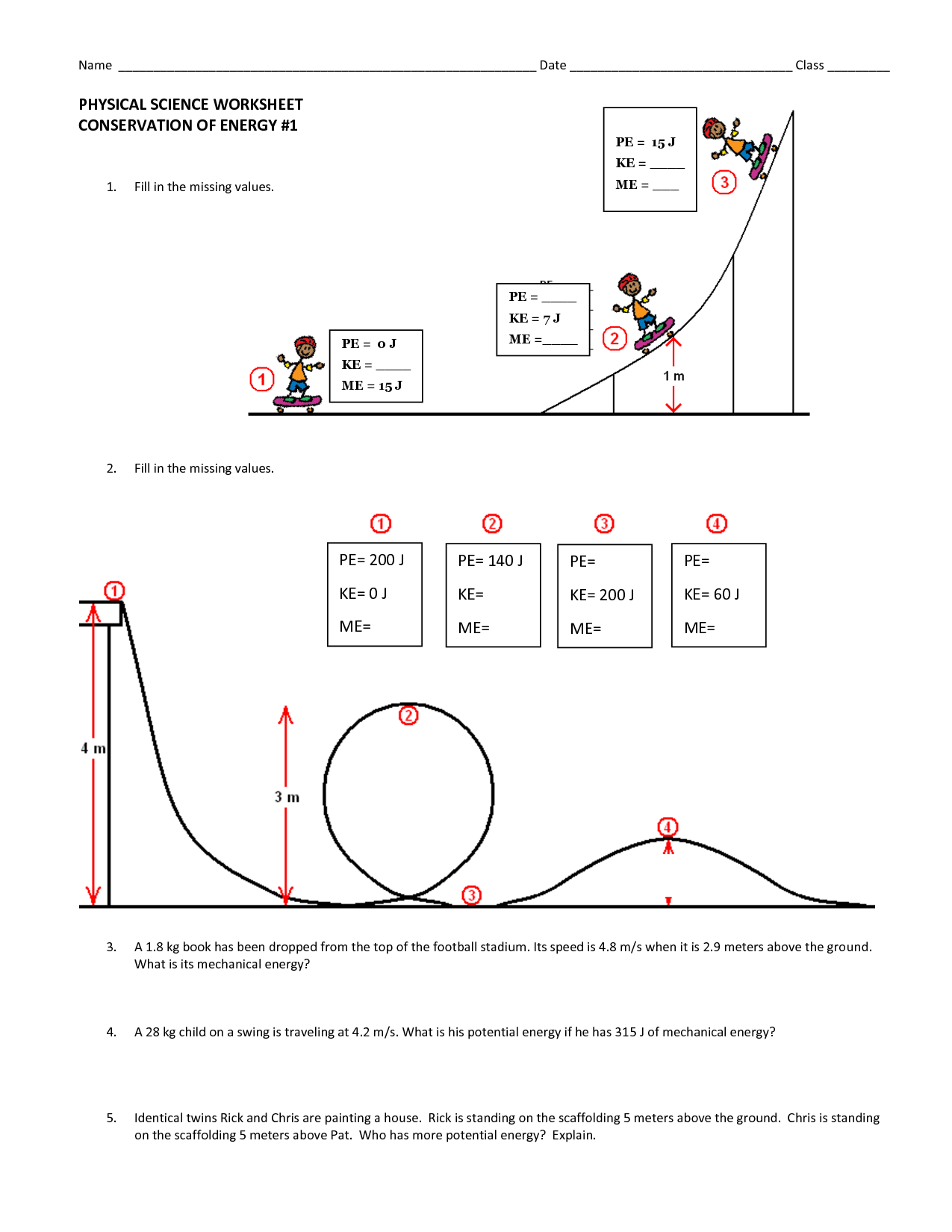
- Physical Science Conservation of Energy Worksheet 2
- Potential and Kinetic Energy Worksheet Key
- First Grade Worksheets Science Sound Energy
- Physical Science Newtons Laws Worksheet Answer Key
- Physical Science Electricity and Magnetism Worksheet
- Work and Power Worksheet Answers
- Electricity Circuit Worksheets 4th Grade
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
What is electricity?
Electricity is a form of energy resulting from the existence of charged particles, such as electrons or protons. It can flow through conductors like wires and is used to power various devices and systems by moving electrons along a path. Electricity is a crucial aspect of modern life, serving as the foundation for a wide range of technological advancements and innovations.
What is an electric circuit?
An electric circuit is a closed loop through which an electric current can flow. It typically consists of components such as a power source (such as a battery), conductors (such as wires), resistors, switches, and other devices that manipulate the flow of electricity. The circuit allows electricity to move from the power source through the components and back to the source in a continuous loop, enabling the transfer of energy to operate various electrical devices and systems.
What is an electric current?
An electric current is the flow of electric charge through a conducting medium such as a wire. The movement of electrons, or other charged particles, creates a flow of electricity that can be used to power various devices and systems. It is measured in amperes (A) and plays a crucial role in the operation of electrical circuits and equipment.
What are conductors and insulators?
Conductors are materials that allow the flow of electrical currents, such as metals like copper and aluminum. Insulators, on the other hand, are materials that do not allow the flow of electrical currents, such as rubber or plastic. Conductors have high electrical conductivity and low resistance, while insulators have high resistance and low conductivity.
What are the three main components of an electric circuit?
The three main components of an electric circuit are a voltage source (such as a battery), a load (such as a light bulb or motor), and conductive wires or traces that connect the voltage source to the load, completing the circuit and allowing electricity to flow.
What is voltage?
Voltage is a measure of the electric potential difference between two points in an electric circuit. It is the force that pushes electric charges (such as electrons) through a conductor, creating the flow of electricity. Voltage is measured in volts (V) and is a key factor in determining the performance and behavior of electrical and electronic devices.
What is resistance?
Resistance is the opposition that a material or electronic component offers to the flow of electric current. It is measured in ohms and is essential in controlling the flow of electricity in circuits, determining how much current will pass through a component for a given voltage. Resistance can be intentional, used in components like resistors to limit current, or can be unwanted, such as in wires where it can lead to energy loss in the form of heat.
How does a switch control the flow of electricity in a circuit?
A switch controls the flow of electricity in a circuit by opening or closing a pathway for the electric current to travel. When the switch is closed, it completes the circuit, allowing the electricity to flow through and power the connected devices or components. Conversely, when the switch is open, it interrupts the flow of electricity, cutting off the power supply to the circuit. This mechanism gives users the ability to turn devices on or off, effectively controlling the flow of electricity in the circuit.
What are the differences between series and parallel circuits?
In a series circuit, the components are arranged in a single path where the same current flows through each component one after another, while in a parallel circuit, the components are connected in multiple paths, allowing current to flow through each component simultaneously. In a series circuit, the total resistance is equal to the sum of the individual resistances, while in a parallel circuit, the total resistance is less than the individual resistances. Additionally, in a series circuit, if one component fails, it will interrupt the entire circuit, whereas in a parallel circuit, if one component fails, the other components will still function independently.
How does an electric motor work?
An electric motor works by converting electrical energy into mechanical energy through the interaction of electromagnetic fields. When an electric current flows through a wire wrapped around a coil (the armature) within a magnetic field created by permanent magnets or electromagnets, a force is exerted on the coil causing it to rotate. This rotational motion is then transferred to a shaft connected to the motor's load, such as a fan or a pump, resulting in mechanical work being performed.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments