Printable Worksheets About Magnets
Are you interested in learning more about magnets and how they work? Look no further! We have a wide variety of printable worksheets that cover various aspects of magnets, perfect for students or anyone curious about this fascinating subject.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is a magnet?
A magnet is an object that produces a magnetic field around itself. This field attracts certain materials such as iron and produces a force that can either attract or repel other magnets. Magnets have two poles, north and south, with opposite poles attracting each other and like poles repelling each other.
How are magnets classified?
Magnets are classified based on their material composition and behavior with respect to magnetism. There are three main categories of magnets: ferromagnetic materials, which are naturally magnetic like iron, nickel, and cobalt; paramagnetic materials, which become weakly magnetized in the presence of an external magnetic field; and diamagnetic materials, which are weakly repelled by a magnetic field. Additionally, magnets can also be classified as permanent magnets, which retain their magnetism once magnetized, or temporary magnets, which only exhibit magnetism when placed in a magnetic field.
What are the properties of magnets?
Magnets have several key properties, including the ability to attract certain materials such as iron, nickel, and cobalt, the ability to repel other magnets of the same polarity, the creation of a magnetic field that extends around them, the capacity to align with Earth's magnetic field, and the ability to induce an electric current when moving near a conductor.
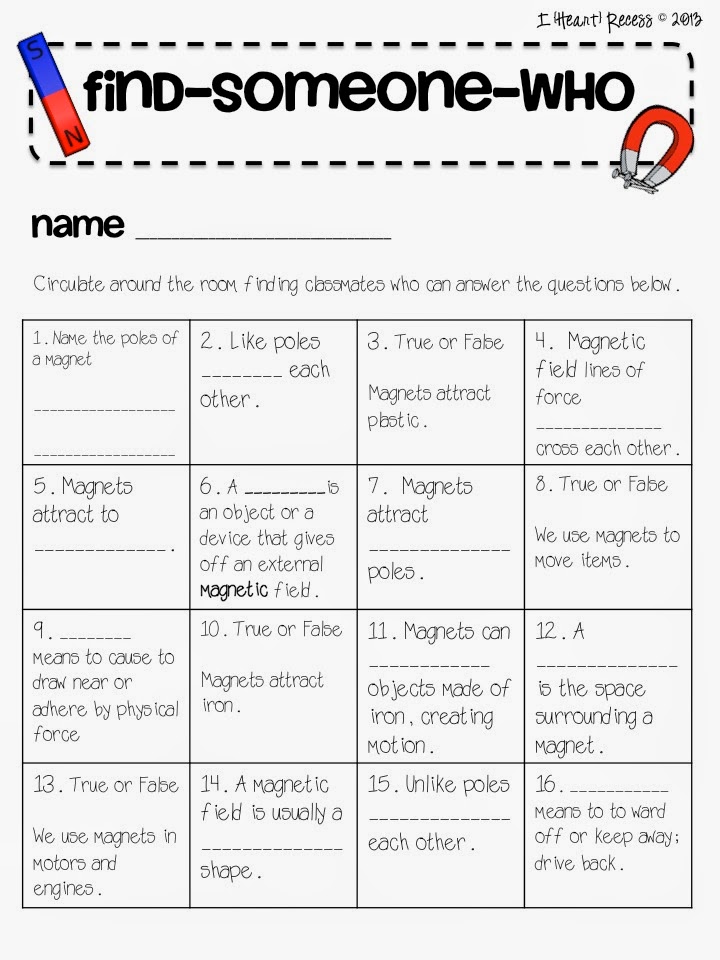
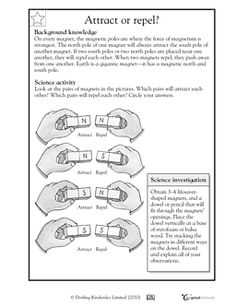
What are the poles of a magnet?
The poles of a magnet refer to the regions where the magnetic field is strongest - the North and South poles. The North pole of a magnet is attracted to the South pole of another magnet, while the North pole repels another North pole. This creates the magnetic attraction and repulsion that we observe with magnets.
How do magnets attract or repel each other?
Magnets attract or repel each other due to the alignment of their magnetic fields. When the north pole of one magnet is brought close to the south pole of another magnet, they will attract each other because opposite poles attract. Conversely, if the north pole of one magnet is brought close to the north pole of another magnet, they will repel each other because like poles repel. This interaction is governed by the fundamental properties of magnetism and the behavior of magnetic fields.
How can the strength of a magnet be increased or decreased?
The strength of a magnet can be increased by exposing it to a stronger magnetic field, aligning the magnetic domains in the material by hammering or heating it, or adding more magnetic material to it. On the other hand, the strength of a magnet can be decreased by subjecting it to a demagnetizing process, heating it above its Curie temperature, or by physically damaging the material to disrupt its magnetic properties.
What are magnetic fields?
Magnetic fields are physical phenomena created by moving electric charges that exert forces on other nearby moving charges. These fields can attract or repel certain materials and are the basis for the operation of magnets and electric motors. Magnets have north and south poles that point in the direction of the magnetic field lines, which form loops around the magnet. These fields play a vital role in various natural and man-made processes, from guiding compass needles to enabling technologies like MRI machines.
What are some everyday applications of magnets?
Some everyday applications of magnets include MRI machines for medical imaging, magnetic compasses for navigation, refrigerator magnets for holding notes or photos, magnetic strips on credit cards for data storage, and speakers and headphones for audio output. Magnets are also used in electric motors, generators, and transformers, as well as in various industrial applications such as separating metals in recycling facilities and in magnetic levitation transportation systems.
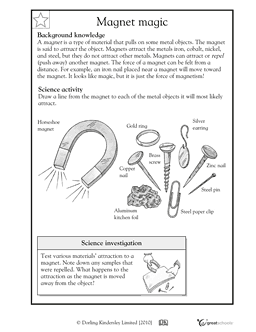
How do magnets interact with different materials?
Magnets interact differently with different materials based on their magnetic properties. Ferromagnetic materials like iron, nickel, and cobalt are strongly attracted to magnets and can become magnetized themselves. Paramagnetic materials are weakly attracted to magnets but do not retain magnetization. Diamagnetic materials, such as copper and gold, are weakly repelled by magnets. The interaction between a magnet and a material is determined by the material's atomic structure and magnetic susceptibility.
What are some safety precautions to take when using magnets?
When using magnets, some safety precautions to take include keeping them away from electronic devices as they may cause damage, avoiding placing them near pacemakers or other medical devices, handling them carefully to prevent pinching or crushing injuries, and storing them in a secure location away from small children who may accidentally ingest them. Additionally, strong magnets should be kept separate from each other to prevent them from snapping together and causing injuries.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments