Mitosis Notes Worksheet
The Mitosis Notes Worksheet is designed to help students grasp the key concepts and stages involved in cell division. This comprehensive worksheet breaks down the entity and subject of mitosis in a clear and concise manner, making it suitable for biology students at various levels of understanding.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
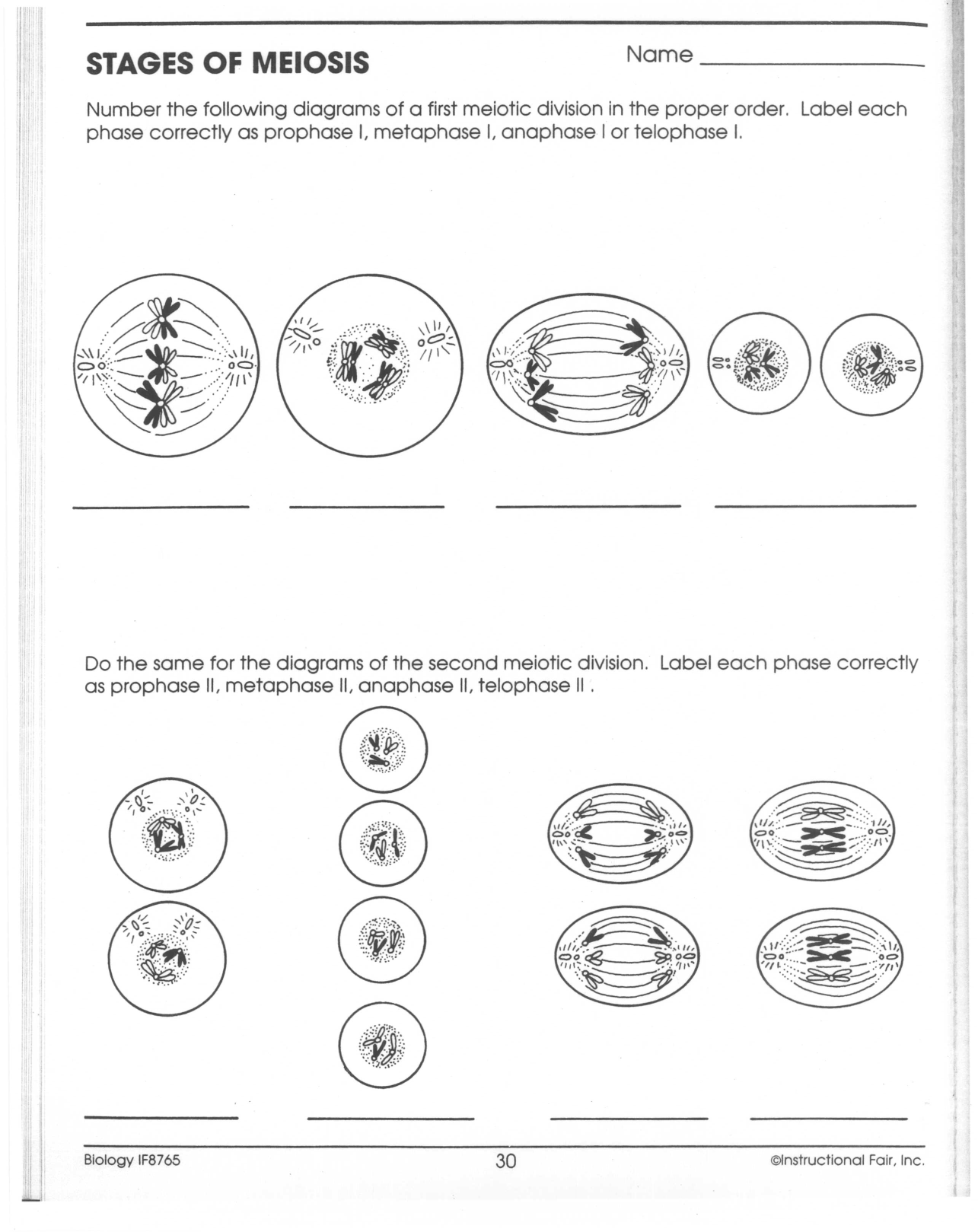
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is mitosis?
Mitosis is a type of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells from a single parent cell. It is a crucial process for growth, development, and repair in multicellular organisms, as well as for asexual reproduction in some single-celled organisms. During mitosis, the cell's nucleus divides, ensuring that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the parent cell's DNA.
What is the purpose of mitosis?
The primary purpose of mitosis is to ensure cell division, leading to the growth, development, and repair of an organism. It maintains the chromosome number by producing two identical daughter cells from a single parent cell. Mitosis plays a crucial role in various biological processes, such as tissue renewal, embryonic development, and wound healing, contributing to the overall maintenance and functioning of an organism.
What are the main stages of mitosis?
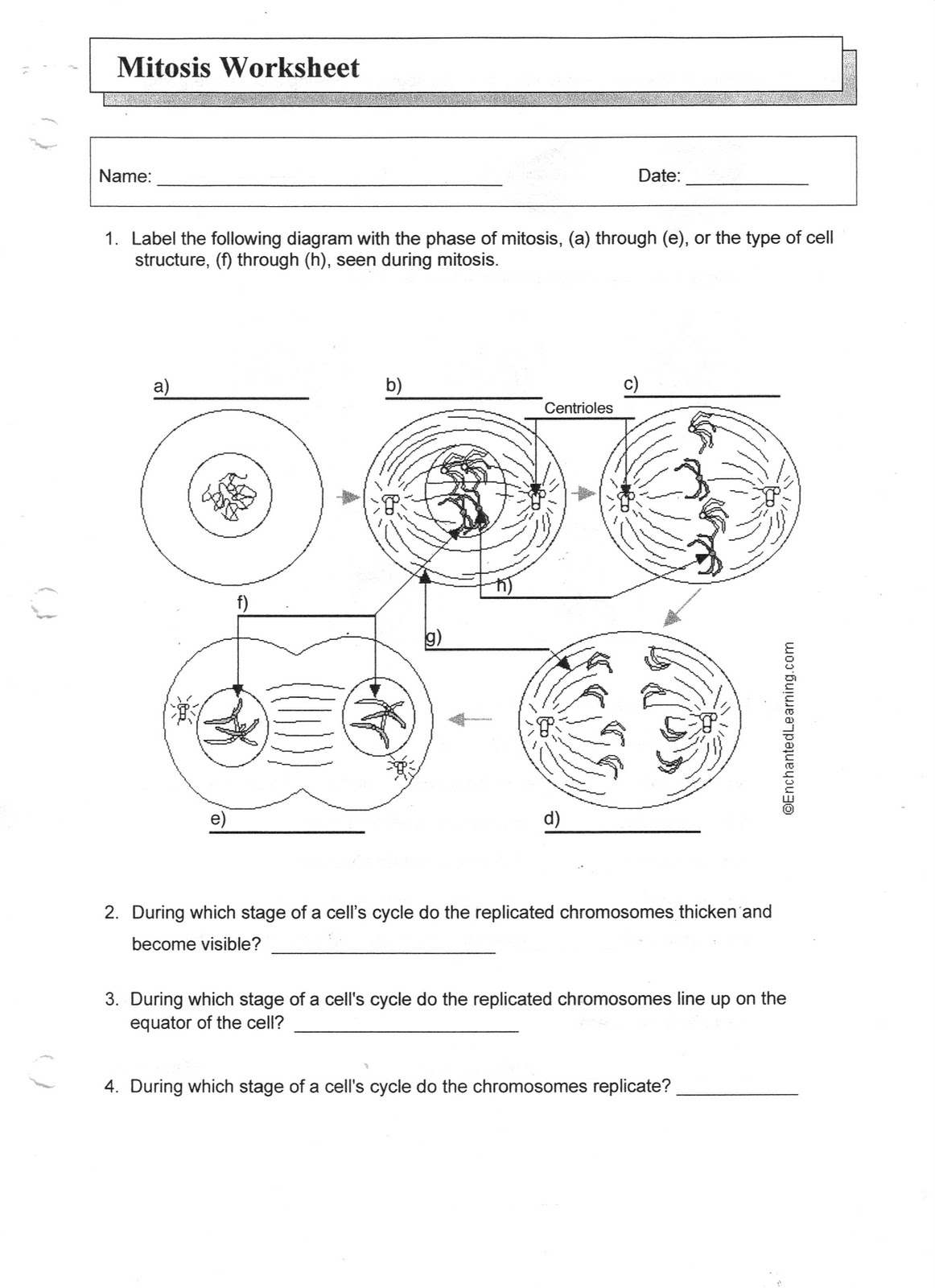
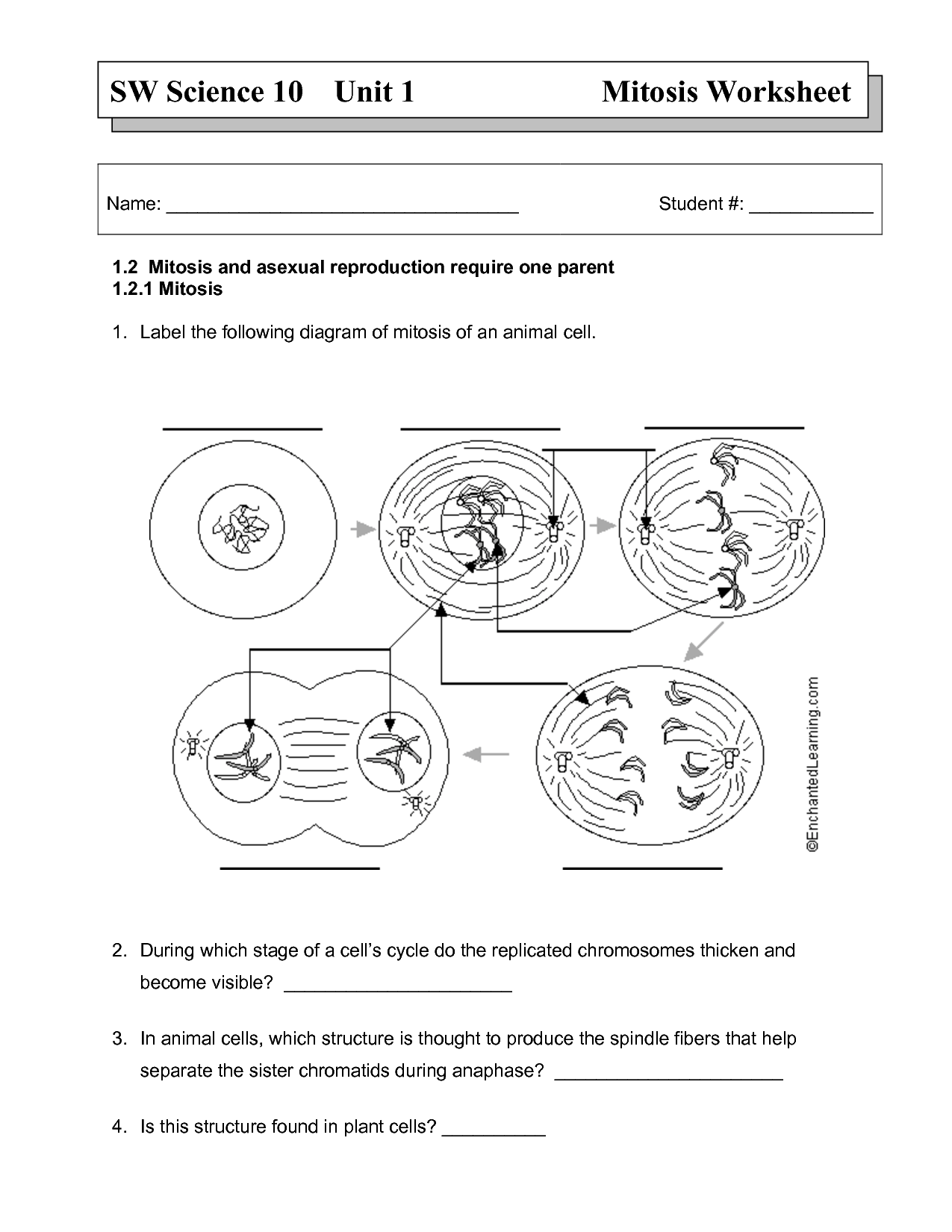
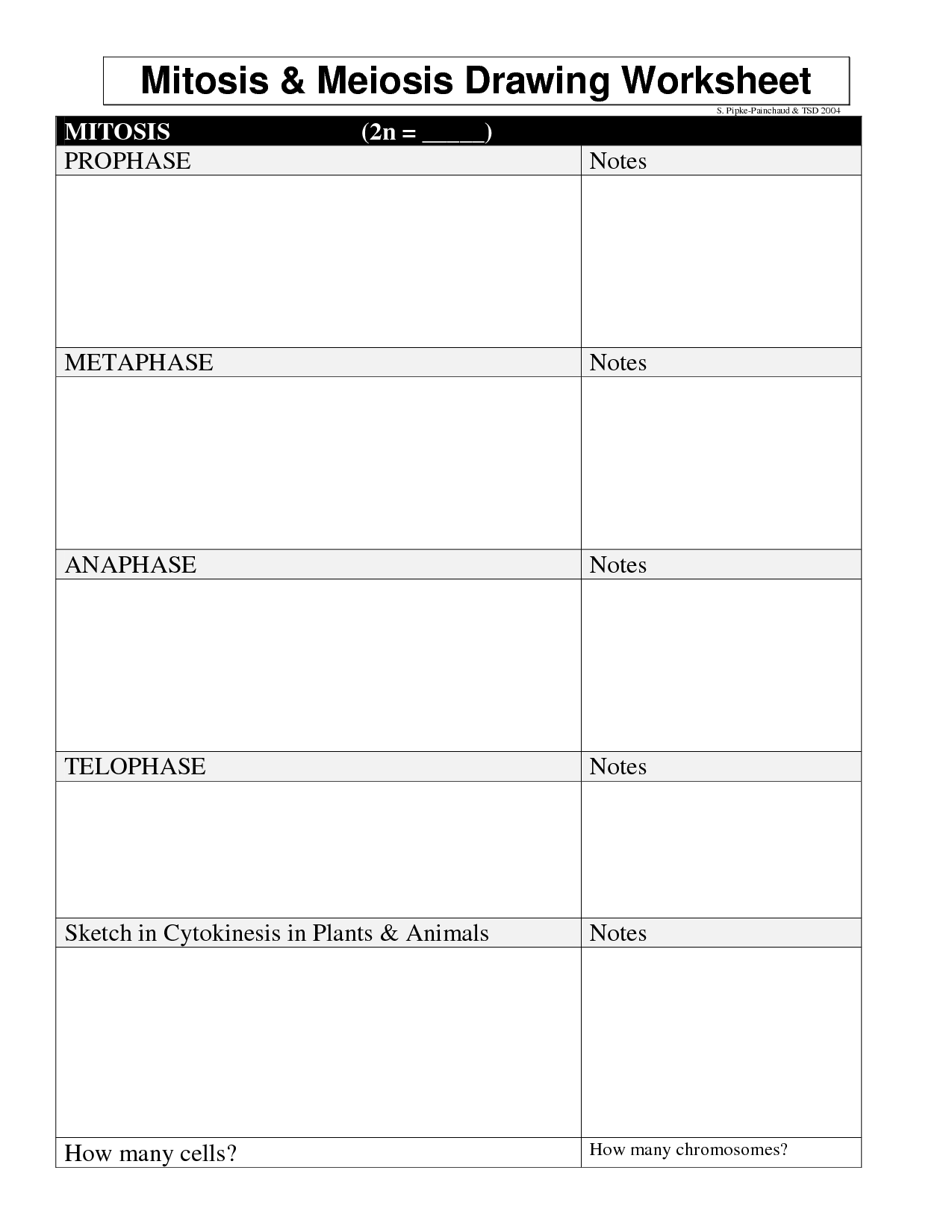
The main stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. In prophase, the chromatin condenses into chromosomes and the nuclear membrane breaks down. Metaphase involves the alignment of chromosomes at the cell's equator. Anaphase sees the separation of sister chromatids towards opposite poles. Finally, in telophase, the chromosomes reach the poles and new nuclear membranes form around them, followed by cytokinesis which splits the cell into two daughter cells.
Describe the process of prophase in mitosis.
Prophase is the first stage of mitosis where the cell prepares for division. During prophase, chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and spindle fibers begin to form. The centrioles move to opposite poles of the cell, and the chromosomes attach to the spindle fibers at their centromeres. Prophase is a critical stage as it sets the stage for the subsequent separation and distribution of chromosomes during mitosis.
Explain the role of the spindle fibers in mitosis.
Spindle fibers are key structures in mitosis that aid in the proper alignment and separation of chromosomes during cell division. They are responsible for attaching to and moving the chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell. By exerting tension on the chromosomes, spindle fibers ensure that each new daughter cell receives the correct number of chromosomes. Without spindle fibers, the process of mitosis would not be able to accurately distribute chromosomes, leading to potential errors in cell division and disruption to the genetic material of the daughter cells.
What happens during metaphase in mitosis?
During metaphase in mitosis, the duplicated chromosomes line up along the metaphase plate, the imaginary line equidistant between the two poles of the cell. The spindle fibers attach to the centromeres of each chromosome, ensuring they are correctly aligned and ready to be separated during anaphase. This alignment is crucial for ensuring that each daughter cell receives an accurate and complete set of chromosomes.
How does anaphase differ from other stages of mitosis?
Anaphase is the stage of mitosis where sister chromatids are pulled apart and move towards opposite poles of the cell, while other stages of mitosis involve processes like prophase where chromosomes condense, metaphase where chromosomes align at the equator of the cell, and telophase where the nuclear envelope reforms. Anaphase specifically marks the moment when genetic material is separated into two sets that will become the nuclei of the two daughter cells, making it a crucial and distinct phase of cell division.
Describe the process of telophase in mitosis.
During telophase, the chromosomes at opposite ends of the cell begin to de-condense and form two distinct nuclei. The nuclear envelope reappears around each set of chromosomes, creating two separate nuclei. The spindle fibers disassemble, and the nucleoli reappear. This phase effectively marks the end of mitosis, and the cell is now prepared for cytokinesis, the final stage of cell division where the cytoplasm is divided into two daughter cells.
What is cytokinesis and when does it occur in relation to mitosis?
Cytokinesis is the process by which the cytoplasm of a cell is divided into two daughter cells following nuclear division (mitosis in eukaryotes). Cytokinesis occurs after the completion of the mitotic phase, specifically after telophase, which is the final stage of mitosis. During cytokinesis, the cell membrane pinches in or a new cell wall forms, separating the two newly formed nuclei and creating two separate daughter cells.
What are some examples of where mitosis occurs in the human body?
Mitosis occurs in various tissues and organs in the human body such as the skin, liver, bone marrow, and stomach lining. Skin cells constantly undergo mitosis to replace old or damaged cells, while liver cells undergo mitosis to regenerate and repair the liver after injury. Bone marrow cells undergo mitosis to produce new blood cells, and cells in the stomach lining undergo mitosis to replenish and maintain the integrity of the stomach epithelium.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments