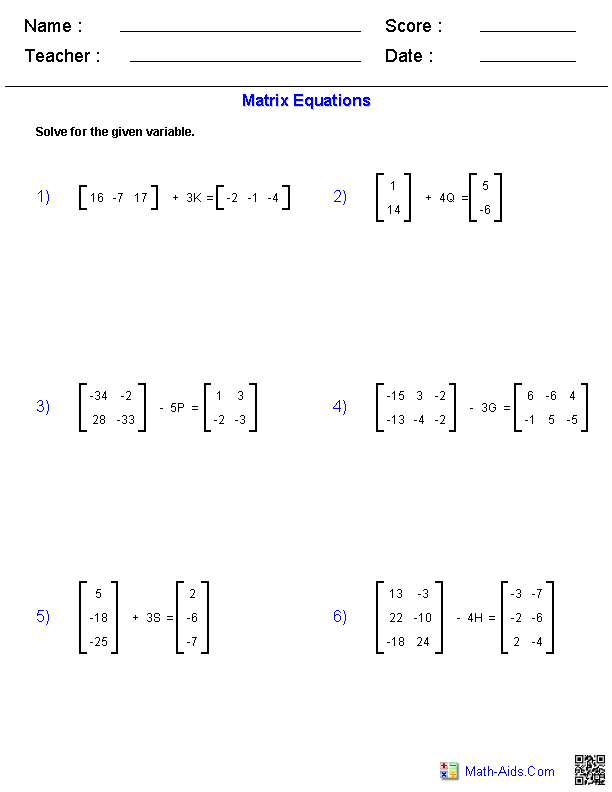
Matrix Inverse Worksheet
Are you struggling with understanding how to find the inverse of a matrix? Look no further! This blog post is designed to help beginners in linear algebra navigate the process of finding the inverse of a matrix through a carefully crafted worksheet. By providing step-by-step instructions and examples, this resource aims to empower students to confidently tackle matrix inversion problems.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What does it mean for a matrix to be invertible?
A matrix is said to be invertible if it has an inverse matrix that, when multiplied with the original matrix, results in the identity matrix. In other words, for a matrix A to be invertible, there must exist another matrix B such that A * B = B * A = I, where I represents the identity matrix.
How do you find the inverse of a 2x2 matrix?
To find the inverse of a 2x2 matrix \(\begin{pmatrix} a & b \\ c & d \end{pmatrix}\), first calculate the determinant as ad - bc. Then, swap the positions of a and d, change the signs of b and c, and divide the entire matrix by the determinant. So, the inverse of the matrix would be \(\frac{1}{ad - bc} \begin{pmatrix} d & -b \\ -c & a \end{pmatrix}\).
Are all square matrices invertible?
Not all square matrices are invertible. A square matrix is invertible if and only if its determinant is non-zero. If the determinant is zero, the matrix is singular and does not have an inverse.
Can a matrix have more than one inverse?
No, a matrix can have at most one inverse. If a matrix has more than one inverse, it would violate the fundamental property of inverses, which states that for any matrix A, there exists at most one matrix B such that AB = BA = I, where I is the identity matrix.
What is the product of a matrix and its inverse?
The product of a matrix and its inverse is the identity matrix.
Is the inverse of a matrix always symmetric?
No, the inverse of a matrix is not always symmetric. While some special types of matrices (such as symmetric matrices) may have symmetric inverses, in general, the inverse of a matrix does not have to be symmetric. The symmetry property of a matrix is independent of its invertibility.
Can a matrix with all zero entries have an inverse?
No, a matrix with all zero entries cannot have an inverse. In order for a matrix to have an inverse, it must be a square matrix and have a non-zero determinant. Since a matrix with all zero entries would have a determinant of zero, it is not invertible.
What is the significance of the determinant when finding a matrix's inverse?
The determinant of a matrix is significant when finding its inverse because a matrix is invertible if and only if its determinant is not zero. In other words, a matrix has an inverse only if it is non-singular, which means that the determinant is a key factor in determining whether a matrix can be inverted or not. If the determinant is zero, the matrix is singular and does not have an inverse.
How does the row reduction method help in finding the inverse of a matrix?
The row reduction method, also known as Gaussian elimination, helps in finding the inverse of a matrix by transforming the given matrix into reduced row-echelon form through row operations. By applying a sequence of elementary row operations to the original matrix, we can reduce it to an identity matrix on the left side, while the right side will be the inverse of the original matrix. This process allows us to systematically determine the inverse of a matrix by simplifying the calculations and making it easier to solve for the unknown entries.
Can non-square matrices have inverses?
Not all non-square matrices have inverses. Only square matrices, which have the same number of rows and columns, can have inverses. The inverse of a square matrix exists if and only if the matrix is invertible, meaning its determinant is non-zero.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments