Genetics Problems Worksheet with Answer Keys
Are you a biology student looking for a helpful tool to practice genetics problems? Look no further! In this blog post, we will introduce you to genetics problems worksheets with answer keys. These worksheets are designed to help you improve your understanding of the intricate world of genetics by providing a wide range of problems to solve and check your answers against.
Table of Images 👆
- Genetics Practice Problems Worksheet Answers
- Genetics Problems Worksheet Answer Key
- Genetics Monohybrid Crosses Worksheet Answer Key
- Monohybrid Cross Worksheet Answer Key
- Zork Genetics Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA the Molecule of Heredity Worksheet Answer Key
- Incomplete and Codominance Worksheet Answer Key
- Genetics Worksheet Answer Key
- Section 9.1 Review Mendels Legacy Answers
- Genetics Pedigree Worksheet Answer Key
- Genetics Problems Worksheet
- Genetics Practice Problems Answer Key 5
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the relationship between genes and DNA?
Genes are segments of DNA that contain instructions for making proteins, which are essential molecules for the structure and function of cells. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the molecule that carries the genetic information in all living organisms. In essence, genes are specific sequences of DNA that encode information for specific traits, functions, and characteristics of an organism.
How does a gene mutation occur?
A gene mutation occurs when there is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene. This can happen due to errors during DNA replication, exposure to mutagens such as chemicals or radiation, or through genetic recombination. Gene mutations can be passed down from parent to offspring or can occur spontaneously in an individual's lifetime.
What is meant by the term "allele" in genetics?
An allele in genetics refers to one of two or more versions of a gene that can exist at a particular locus on a chromosome. These alternate versions of a gene may differ in their DNA sequence and can lead to different traits or characteristics being expressed in an organism.
Explain the difference between dominant and recessive alleles.
Dominant alleles are expressed phenotypically when present in an individual, overriding the expression of recessive alleles. On the other hand, recessive alleles are only expressed phenotypically when an individual has two copies of the recessive allele. In the presence of a dominant allele, the recessive allele is masked and its trait is not observed unless an individual is homozygous for the recessive allele.
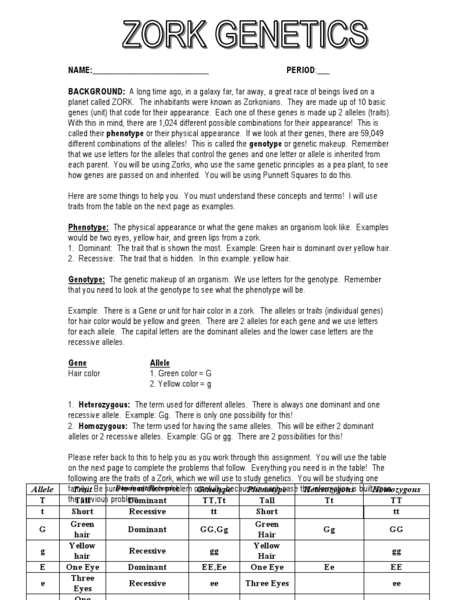
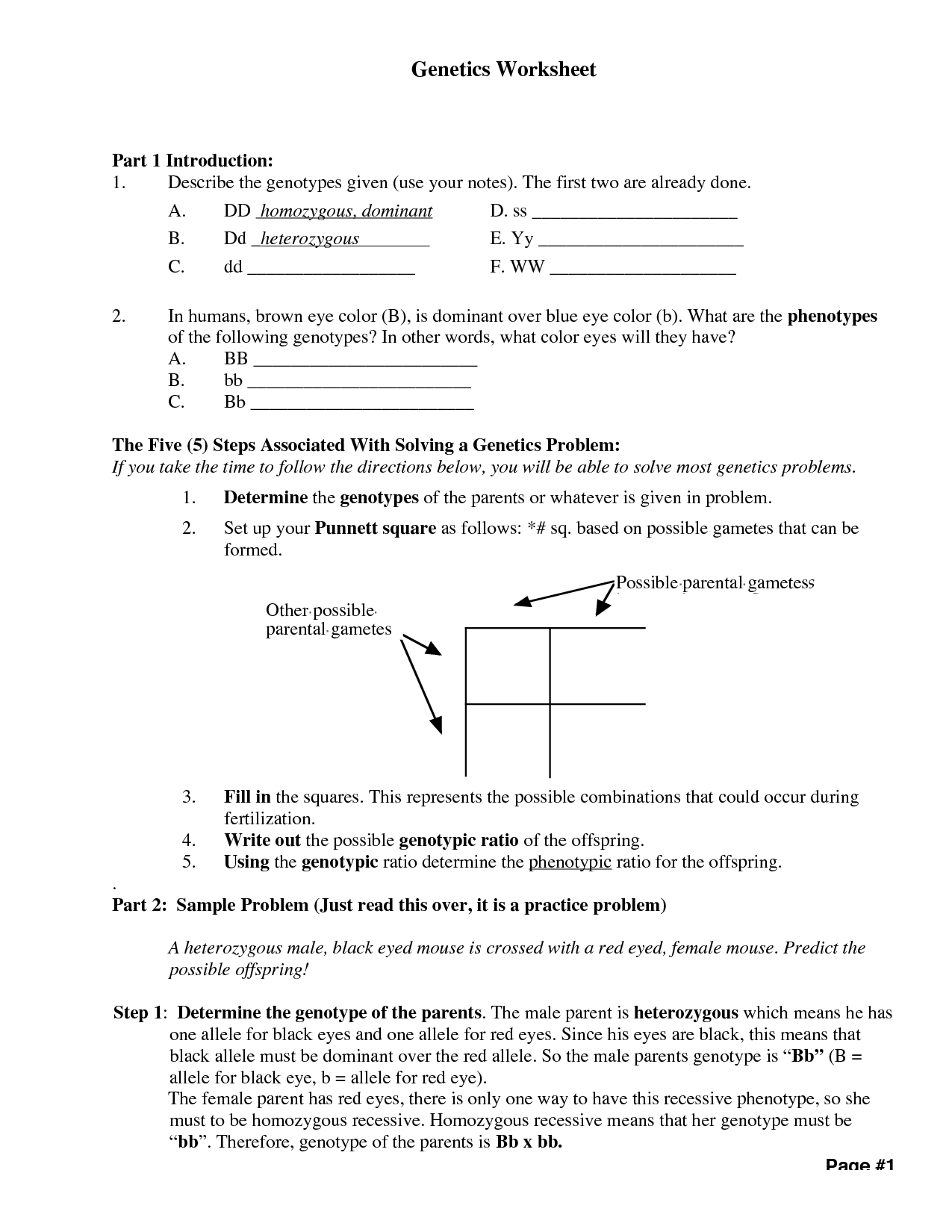
What is a Punnett square and how is it used in genetics?
A Punnett square is a visual representation of the possible genetic outcomes of a cross between two individuals. It is used in genetics to predict the probability of offspring inheriting certain traits or genetic characteristics from their parents. By organizing the possible combinations of alleles from each parent, a Punnett square can help determine the expected genotype and phenotype frequencies of offspring in a genetic cross.
Define the terms homozygous and heterozygous, and give an example of each.
Homozygous refers to having two identical alleles for a particular gene, either dominant or recessive. Heterozygous, on the other hand, means having two different alleles for the same gene. An example of homozygous would be a plant with two dominant alleles for flower color (RR), resulting in red flowers. An example of heterozygous would be a person with one dominant allele and one recessive allele for widows peak (Ww), showing the dominant trait of a widows peak.
How does meiosis contribute to genetic variation?
Meiosis contributes to genetic variation by allowing for the shuffling and exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during the crossing over process in prophase I and by the random assortment of chromosomes during metaphase I. This results in the production of unique combinations of alleles in gametes, ultimately leading to increased genetic diversity among offspring.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism, including all the genes and alleles present in its DNA, while phenotype refers to the observable physical, biochemical, and physiological traits of an organism that result from the interaction of its genotype with the environment. Genotype determines the potential traits that an organism can have, while phenotype is the actual expression of those traits in the organism's appearance and behavior.
Explain the concept of incomplete dominance and provide an example.
Incomplete dominance is a genetic phenomenon where neither allele is completely dominant over the other, resulting in a blending of traits in the heterozygous individual. This means that the heterozygous genotype displays an intermediate phenotype that is a blend of the two homozygous phenotypes. An example of incomplete dominance is in snapdragons, where a cross between a red-flowered plant (RR) and a white-flowered plant (WW) produces pink-flowered offspring (RW).
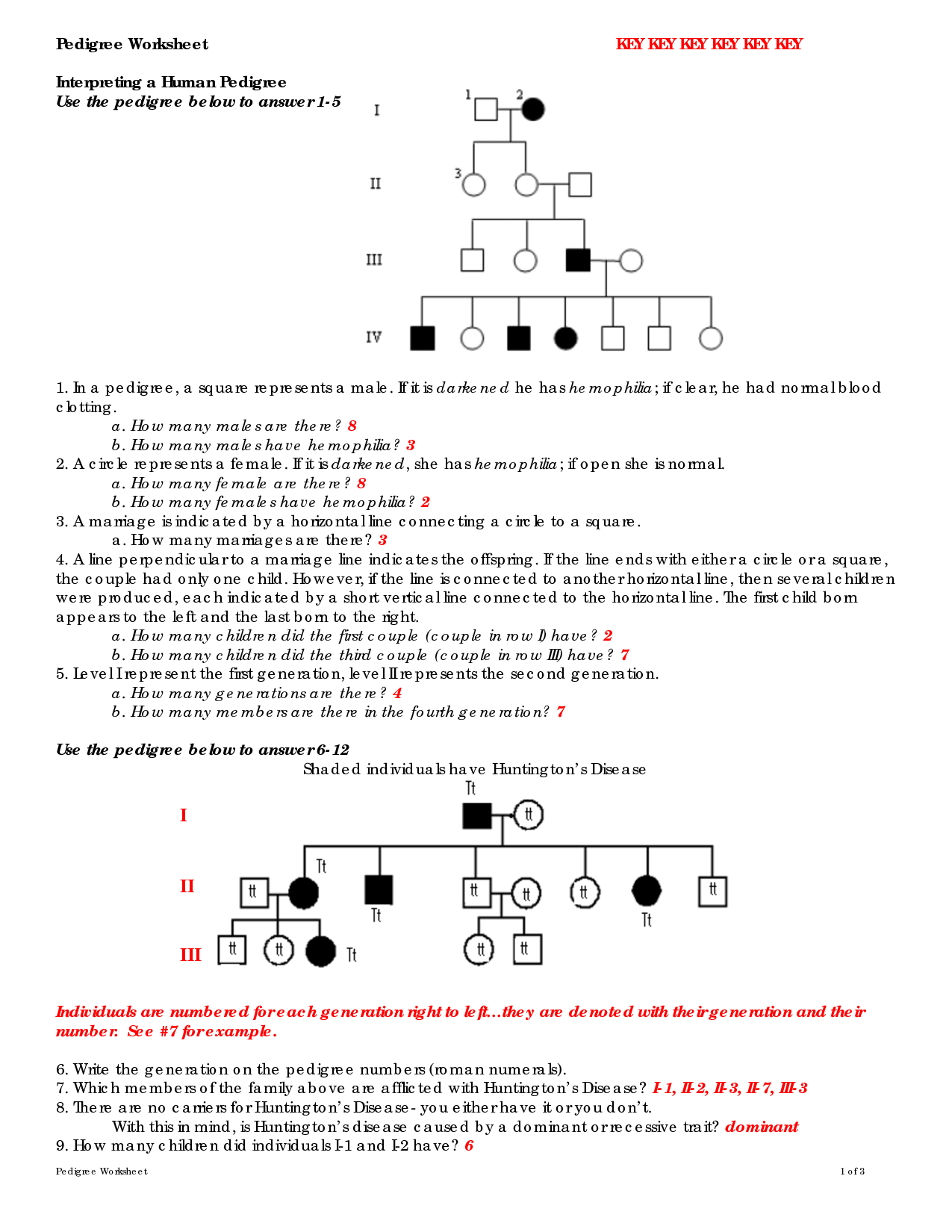
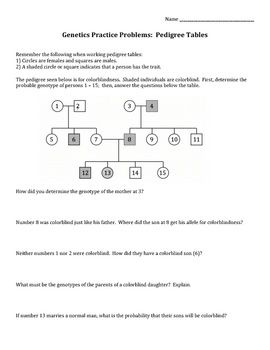
Describe how genetic disorders can be inherited and give an example of a commonly inherited disorder.
Genetic disorders can be inherited through the passing down of abnormal genes from parents to their offspring. There are various inheritance patterns, including autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, and X-linked. For example, cystic fibrosis is a commonly inherited disorder caused by a genetic mutation in the CFTR gene. It is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning that a child needs to inherit two copies of the defective gene - one from each parent - to develop the disorder.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





























Comments