Enzymes and Chemical Reactions Worksheet
Are you a student studying biology or chemistry? Are you in need of an effective learning tool to help reinforce your understanding of enzymes and chemical reactions? Look no further than the Enzymes and Chemical Reactions Worksheet. This worksheet is designed to provide a clear and concise overview of the important concepts and key terms related to enzymes and chemical reactions.
Table of Images 👆
- Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Worksheet
- Virtual Lab Enzyme-Controlled Reactions Answer Key
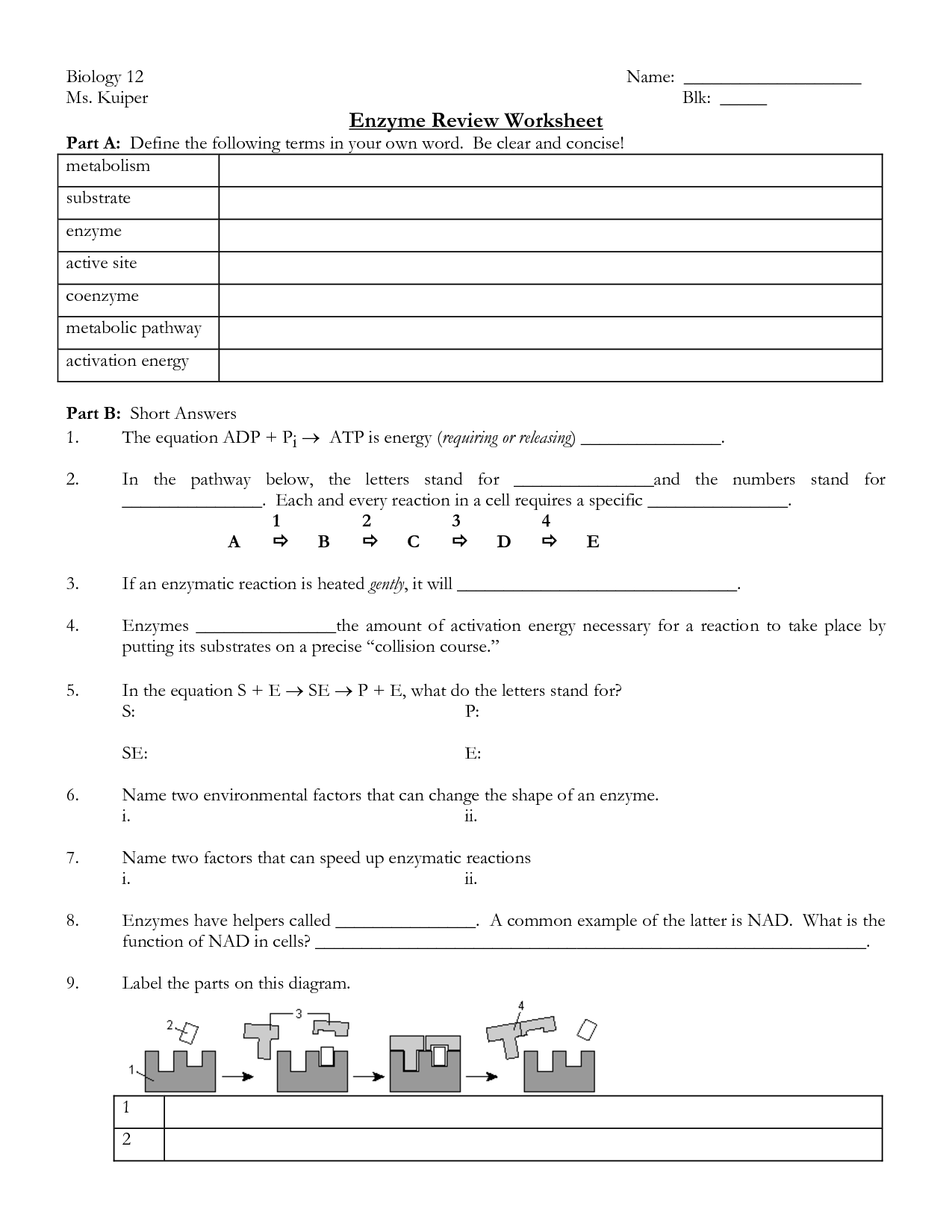
- Enzyme Reactions Worksheet Answer Key
- Enzyme Reactions Worksheet
- Enzymes Worksheet Answers Biology
- Enzymes Worksheet Answer Key
- Energy and Chemical Reactions Worksheet
- Enzyme Practice Worksheet Answers
- Enzymes Worksheet Review Answer Key
- Biology Enzyme Worksheet
- Classification Worksheet and Answer Key
- Biology Enzyme Worksheet High School
- The 12 Cell Review Worksheet Answers Biology
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What are enzymes?
Enzymes are biological molecules that act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions in living organisms. They are protein-based compounds that help facilitate and regulate various biochemical processes in the body by lowering the activation energy needed for reactions to occur. Enzymes are highly specific in their function and can only catalyze specific reactions, playing a crucial role in maintaining the overall functioning of cells and metabolic pathways.
What is the role of enzymes in chemical reactions?
Enzymes act as biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. They achieve this by binding to specific substrates and facilitating the conversion of reactants into products at a faster rate. Enzymes are highly specific, each one designed to catalyze a particular reaction or set of reactions, making them essential for various metabolic processes in living organisms.
How do enzymes speed up chemical reactions?
Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. They achieve this by binding to the substrates involved in the reaction and bringing them into close proximity, facilitating the formation of the transition state. This alignment of the substrates in the enzyme's active site lowers the energy barrier for the reaction, allowing it to proceed more quickly. Additionally, enzymes may also stabilize the transition state or provide an alternative pathway for the reaction to occur, further enhancing the reaction rate.
What is an active site of an enzyme?
The active site of an enzyme refers to a specific region on the enzyme where the substrate binds and where the chemical reaction catalyzed by the enzyme takes place. It is a highly specific area that complements the shape and chemical properties of the substrate, allowing the enzyme to catalyze the conversion of the substrate into the product efficiently. The interactions at the active site determine the enzyme's specificity, efficiency, and overall function.
What are substrates and how do they interact with enzymes?
Substrates are the molecules that enzymes act upon to catalyze chemical reactions. They interact with enzymes through a process known as the lock and key model, where the substrate's shape fits into the active site of the enzyme like a key into a lock. This binding allows the enzyme to lower the activation energy required for the reaction to occur, leading to a more efficient and faster chemical transformation. The enzyme-substrate complex then undergoes specific changes to form the products of the reaction before releasing them.
Can enzymes be reused in multiple reactions? Why or why not?
Yes, enzymes can be reused in multiple reactions because they are not consumed or altered during the reaction they catalyze. Enzymes function by lowering the activation energy required for a reaction to occur, which allows them to speed up chemical reactions without being used up in the process. This, coupled with their ability to bind and release substrates, enables enzymes to be used repeatedly in multiple reactions until they are denatured or degraded.
What factors can affect enzyme activity?
Factors that can affect enzyme activity include pH levels, temperature, substrate concentration, enzyme concentration, presence of inhibitors or activators, and the presence of cofactors or coenzymes. Changes in these factors can significantly impact the rate at which enzymes catalyze biochemical reactions.
What is an inhibitor and how does it affect enzyme function?
An inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and disrupts its activity, usually by blocking the enzyme's active site or altering its structure. This interference can prevent the enzyme-substrate complex from forming, slowing down or halting the catalytic reaction. Inhibitors can be reversible or irreversible, competitive or non-competitive, and can be naturally occurring or synthetic. Overall, inhibitors play a crucial role in regulating enzyme function and can be used for therapeutic purposes in treating diseases.
How does temperature affect enzyme activity?
Temperature can have a significant impact on enzyme activity as it affects the overall rate of enzymatic reactions. Initially, an increase in temperature can enhance enzyme activity by speeding up the movement of molecules and the collision frequency between enzymes and substrates. However, if the temperature increases beyond a certain point, enzymes can denature and lose their shape, therefore losing their functionality. This optimal temperature range varies depending on the enzyme, but in general, a slight increase in temperature can boost enzyme activity until a certain threshold, after which the enzyme activity rapidly declines. Conversely, low temperatures can slow down enzymatic reactions due to decreased kinetic energy and molecular movement.
How do pH levels influence enzyme activity?
pH levels influence enzyme activity by affecting the enzyme's structure and function. Enzymes have an optimal pH at which they function most effectively, with deviations from this pH resulting in decreased activity. Changes in pH can disrupt the interactions between the enzyme and its substrate, leading to denaturation or alteration of the enzyme's shape, which may prevent the substrate from binding properly. This can ultimately affect the enzyme's catalytic activity and efficiency.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

































Comments