Elementary Science Plant Worksheets
Are you searching for engaging and educational worksheets to supplement your elementary science lessons on plants? Look no further! Our collection of plant worksheets is designed to thoroughly cover the essential concepts and principles of plant biology. These worksheets will keep your young learners fully engaged while helping them grasp the fundamental aspects of plant structure, growth, and reproduction.
Table of Images 👆
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
What is photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy by using carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose and oxygen. This process is essential for life on Earth as it is the primary way in which producers in ecosystems create food and release oxygen into the atmosphere.
How do plants obtain water from the soil?
Plants absorb water from the soil through their roots, which have tiny hairs called root hairs that increase the surface area for water absorption. This process is facilitated by osmosis, where water moves from areas of high water concentration in the soil to lower water concentration within the roots, eventually being transported throughout the plant for various metabolic processes and growth.
What is the function of stems in plants?
The main function of stems in plants is to provide support for the plant, holding up the leaves, flowers, and fruits. Stems also transport water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant, and they also store food and water for times of need. Additionally, stems can have specialized structures such as thorns, tendrils, and stolons, which aid in defense, climbing, and reproduction, respectively.
Explain the process of pollination.
Pollination is the process where pollen grains are transferred from the male reproductive organ of a flower (anther) to the female reproductive organ (stigma) of the same or another flower. This transfer can be done by wind, insects, birds, or other animals. Once the pollen reaches the stigma, it germinates and grows a tube that travels down to the ovary where fertilization takes place, leading to the formation of seeds. Pollination is crucial for the reproduction of flowering plants and plays a key role in maintaining biodiversity and food production.
What is the purpose of flowers in a plant's life cycle?
The purpose of flowers in a plant's life cycle is primarily for sexual reproduction. Flowers contain the reproductive structures of plants, including the male pollen-bearing anthers and the female ovule-containing pistil. Through the process of pollination, flowers facilitate the transfer of pollen from the male parts of one plant to the female parts of another, leading to the formation of seeds and ultimately the production of new plants. Additionally, flowers also play a crucial role in attracting pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and birds, which aid in the pollination process.
How do plants reproduce?
Plants reproduce through a process called pollination, where pollen from the male reproductive organs of a plant is transferred to the female reproductive organs. This can happen through self-pollination within the same plant or through cross-pollination between different plants. Once fertilization occurs, a seed is produced which can then grow into a new plant. Additionally, some plants can reproduce asexually through methods such as cloning or producing offspring from structures like runners or bulbs.
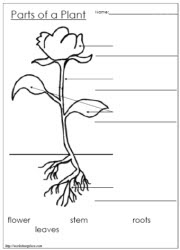
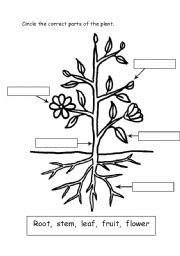
What are the different parts of a plant and their functions?
Plants consist of various parts that serve different functions. Roots anchor the plant, absorb water and nutrients from the soil. The stem provides support for the plant and transports water and nutrients throughout. Leaves are where photosynthesis occurs, converting sunlight into energy. Flowers attract pollinators and produce seeds for reproduction. Fruits protect and disperse seeds. Lastly, the plant's reproductive structures, such as stamens and pistils, facilitate pollination and seed production.
Describe the process of seed germination.
Seed germination starts with the absorption of water by the seed, which triggers metabolic processes and activates enzymes that break down stored nutrients. This leads to the swelling and softening of the seed coat, allowing the radicle (embryonic root) to emerge and penetrate the soil. As the radicle grows, it anchors the seedling and starts absorbing water and nutrients from the soil. Next, the hypocotyl (embryonic stem) elongates and pushes the cotyledons (seed leaves) above the ground. The cotyledons then provide energy for further growth until the seedling can photosynthesize. This marks the completion of seed germination and the beginning of the plant's independent growth.
How do plants adapt to different environments?
Plants adapt to different environments through various mechanisms such as changing leaf structures, developing deep root systems, altering water storage capabilities, and adjusting their growth patterns. They can also modify their reproductive strategies, seed dispersal methods, and flowering times based on the specific conditions of their environment. Over time, natural selection has played a crucial role in shaping plant characteristics that increase their chances of survival and reproduction in diverse habitats, allowing them to thrive in a wide range of environmental conditions.
What are some examples of carnivorous plants and how do they obtain nutrients?
Some examples of carnivorous plants include Venus flytrap, pitcher plants, sundews, and bladderworts. These plants obtain nutrients by capturing and digesting insects or other small organisms. They have specialized structures such as trapping mechanisms, sticky hairs, or pitcher-shaped organs filled with digestive enzymes to attract, trap, and digest their prey. This allows carnivorous plants to supplement their nutrient intake, typically in environments with nutrient-poor soils.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments