Cell Membrane Images Worksheet Answers
If you're struggling to find answers for your cell membrane images worksheet, you've come to the right place. This blog post is here to provide you with helpful information and explanations to effectively tackle this subject.
Table of Images 👆
- Cell Transport Worksheet Answer Key Review
- Cell Membrane Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet Answers
- Cell Membrane Worksheet
- Cell Membrane Transport Worksheet
- Cell Membrane and Transport Worksheet Answers
- Osmosis and Tonicity Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Transport Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Membrane and Transport Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
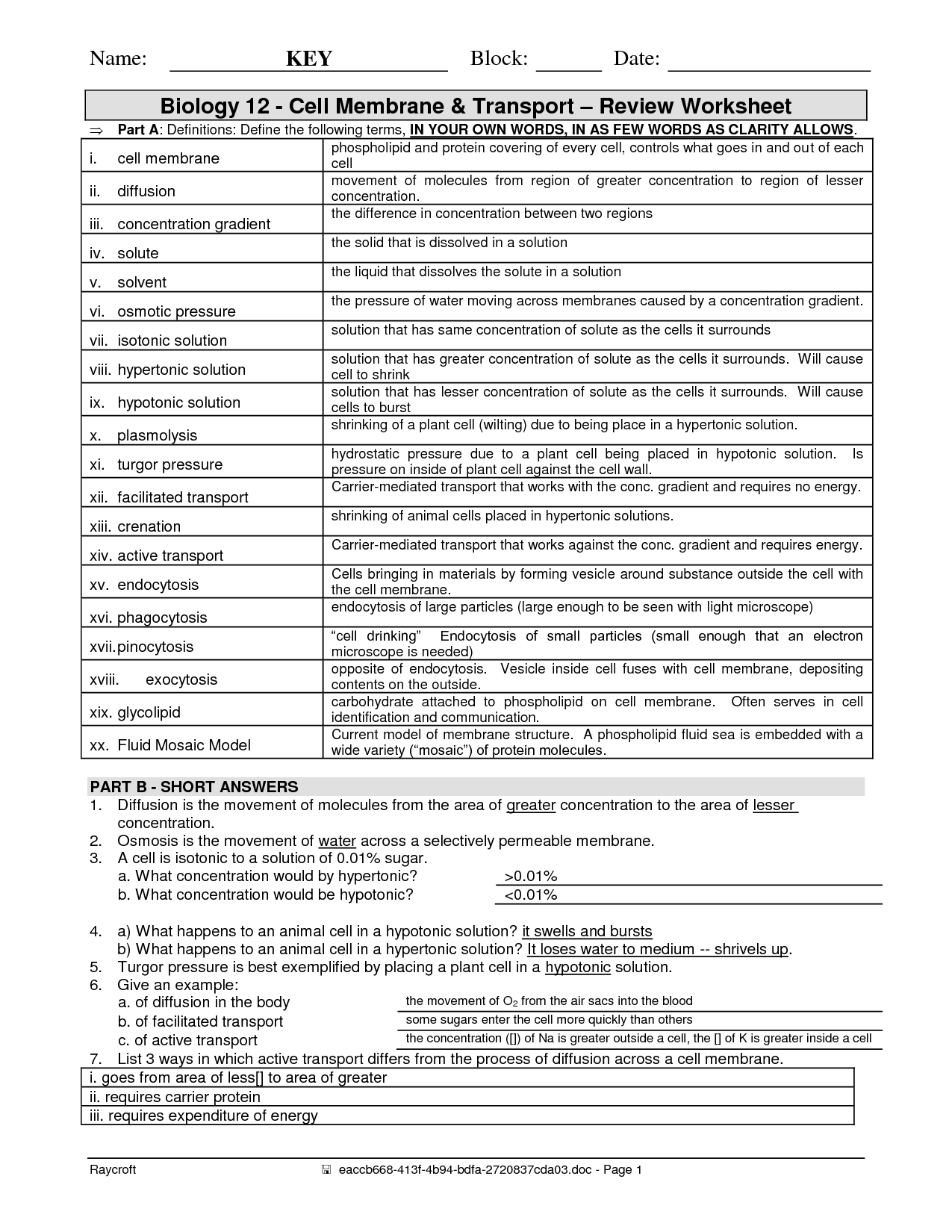
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane acts as a barrier between the cell's internal environment and the external environment, controlling the passage of substances in and out of the cell. It helps maintain the cell's shape, protects the cell's contents, and plays a crucial role in cell communication and recognition.
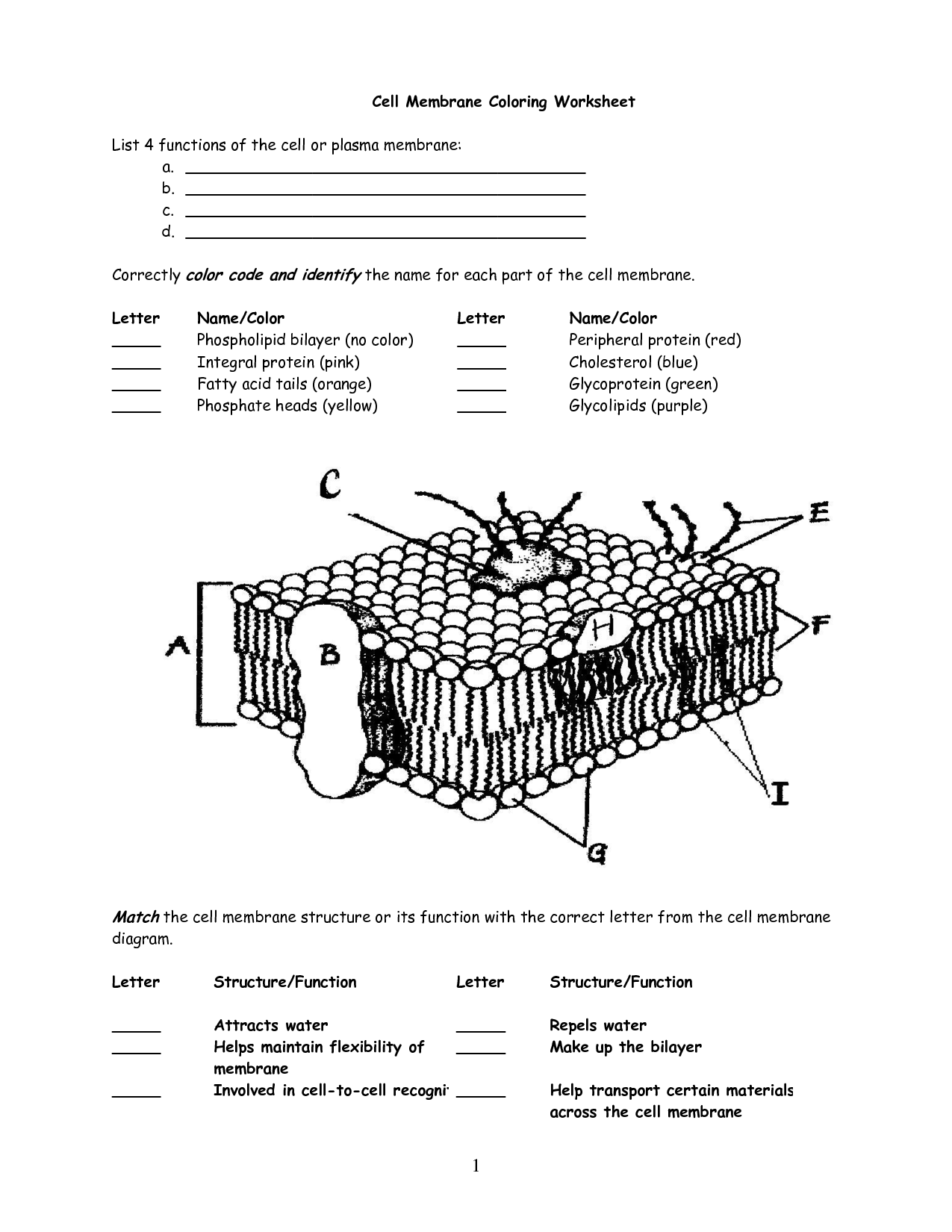
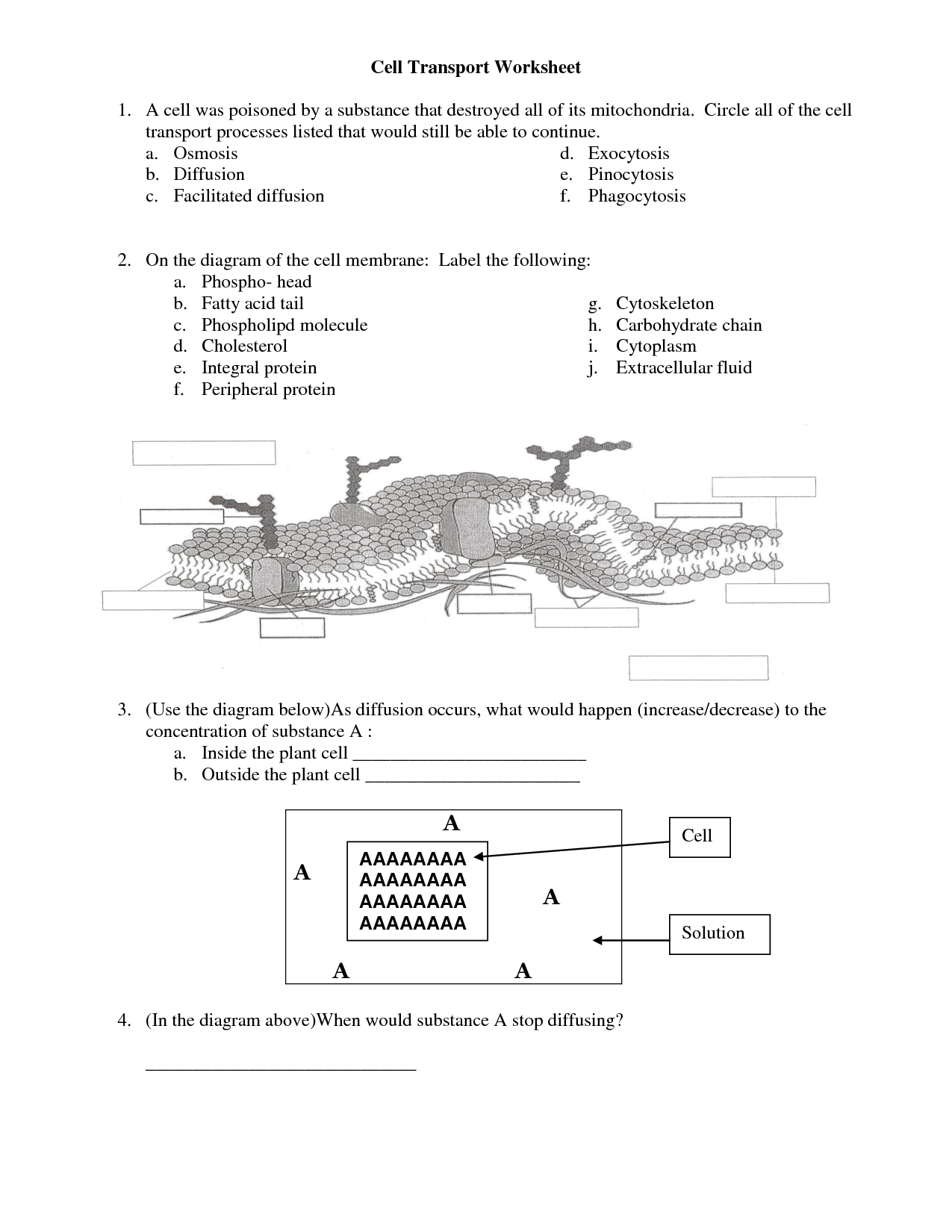
What is the structure of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, which consists of two layers of phospholipid molecules. These molecules have a hydrophilic (water-attracting) head and hydrophobic (water-repelling) tails, creating a barrier that regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell. Embedded within this lipid bilayer are proteins that facilitate transport, cell recognition, and communication. Cholesterol molecules are also interspersed within the membrane to provide stability and regulate fluidity. Together, these components form a dynamic and selectively permeable boundary that separates the cell's internal environment from its external surroundings.
How does the cell membrane regulate the movement of molecules?
The cell membrane regulates the movement of molecules through a process called selective permeability, which allows only certain substances to pass through. This is achieved through the presence of various proteins and channels embedded in the membrane that actively or passively transport specific molecules in and out of the cell. Additionally, the lipid bilayer structure of the cell membrane acts as a barrier to prevent the free movement of hydrophilic molecules, while allowing the passage of hydrophobic molecules. The combination of these mechanisms enables the cell membrane to control the movement of molecules in and out of the cell, maintaining cellular homeostasis.
What is the role of phospholipids in the cell membrane?
Phospholipids play a crucial role in the cell membrane by forming a lipid bilayer that provides structural support and acts as a barrier to regulate the passage of substances in and out of the cell. They also help maintain the fluidity of the membrane, allowing for the movement of membrane proteins and other lipids within the bilayer. Additionally, phospholipids contribute to cell signaling and interactions with other cells and the environment.
What are some examples of integral proteins in the cell membrane?
Some examples of integral proteins in the cell membrane include ion channels that facilitate the movement of ions across the membrane, such as sodium-potassium pumps which help maintain the cell's electrochemical gradient, transport proteins that allow specific molecules to enter and exit the cell, receptors that bind to signaling molecules to initiate cellular responses, and adhesion proteins that help cells stick together and form tissues.
How does cholesterol affect the properties of the cell membrane?
Cholesterol plays a vital role in regulating the fluidity and stability of the cell membrane. It helps to reduce membrane permeability by packing tightly between phospholipid tails, making the membrane less permeable to small water-soluble molecules while maintaining flexibility. Additionally, cholesterol also prevents the saturation and crystallization of lipid tails, ensuring the membrane remains fluid at lower temperatures and more stable at higher temperatures. This dynamic role of cholesterol in the cell membrane is crucial for maintaining membrane structure and function.
What is the significance of glycoproteins and glycolipids in the cell membrane?
Glycoproteins and glycolipids play significant roles in the cell membrane as they are involved in cell-cell recognition, communication, and signaling processes. They help cells adhere to one another, participate in immune responses, and mediate interactions with other cells or molecules. Additionally, they can act as receptors for hormones and other signaling molecules, allowing cells to respond to their environment and regulate various cellular functions. Overall, the presence of glycoproteins and glycolipids on the cell membrane is essential for maintaining cell structure, function, and interaction with the surrounding environment.
How do cells communicate with each other through the cell membrane?
Cells communicate with each other through the cell membrane by utilizing specialized proteins called cell surface receptors. These receptors are embedded in the cell membrane and act as signal detectors for specific molecules or signaling molecules called ligands. When a ligand binds to the receptor, it triggers a cellular response, such as activation of intracellular signaling pathways or regulation of gene expression, allowing cells to coordinate their activities and respond to various external signals in the surrounding environment.
How do cells maintain an electrochemical gradient across the cell membrane?
Cells maintain an electrochemical gradient across the cell membrane through the selective movement of ions using ion pumps and channels. Ion pumps, such as the sodium-potassium pump, actively transport ions against their concentration gradient using ATP as energy source. Ion channels facilitate the passive movement of ions down their concentration gradient. These mechanisms work together to regulate the distribution of ions inside and outside the cell, helping to generate and maintain the membrane potential essential for various cellular functions.
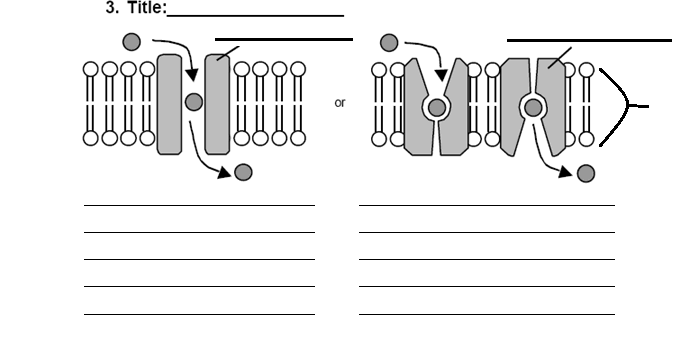
What are the different types of transport mechanisms involved in crossing the cell membrane?
There are three main types of transport mechanisms involved in crossing the cell membrane: passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport. Passive diffusion involves the movement of molecules across the membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration without the need for energy. Facilitated diffusion also moves molecules from high to low concentration but requires the assistance of specialized transport proteins. Active transport, on the other hand, moves molecules against their concentration gradient and requires energy in the form of ATP to drive the process.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments