Atomic Structure Worksheet
The Atomic Structure Worksheet is designed to help students deepen their understanding of this fundamental topic in chemistry. This comprehensive resource covers various aspects of atomic structure, including the arrangement of particles, the role of protons, neutrons, and electrons, and the organization of elements on the periodic table. Whether you're a high school student starting to explore the world of chemistry or a college student looking to review key concepts, this worksheet is an excellent tool to enhance your knowledge and comprehension of atomic structure.
Table of Images 👆
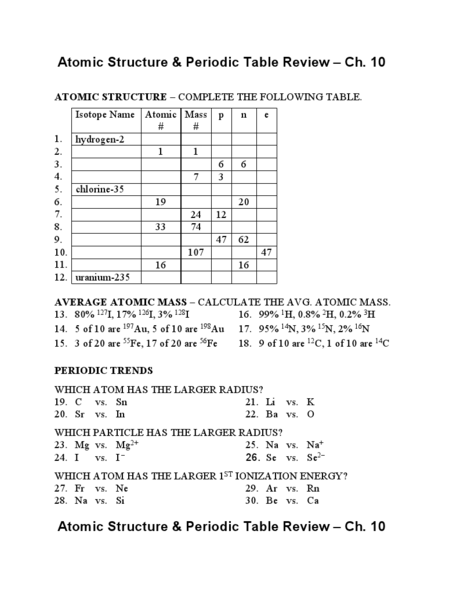
- Review Atomic Structure and Periodic Table
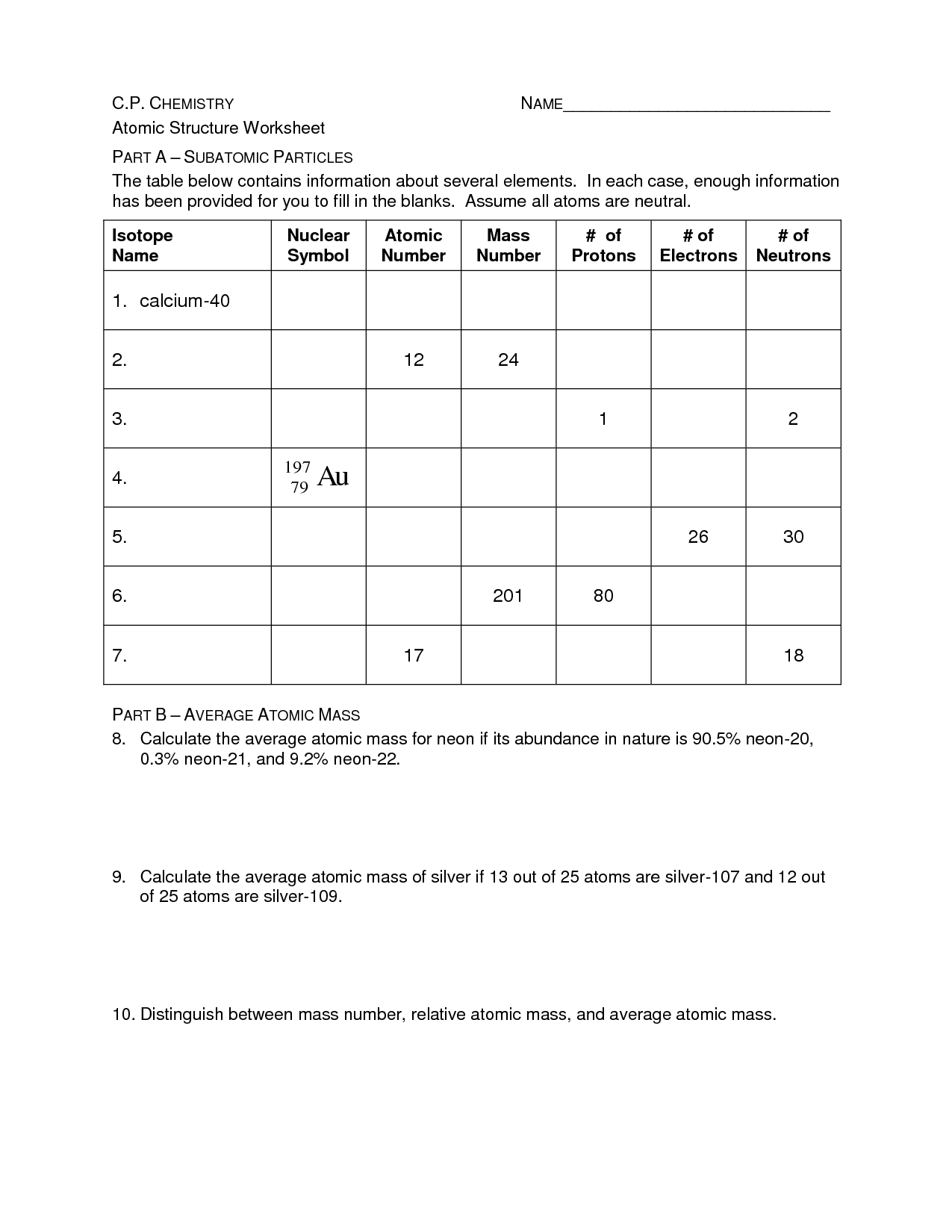
- Basic Atomic Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
- Inside the Atom Worksheet
- Periodic Table Elements and Atoms Worksheets
- Atomic Structure of an Atom Worksheet
- Chemistry If8766 Worksheet Answer Key
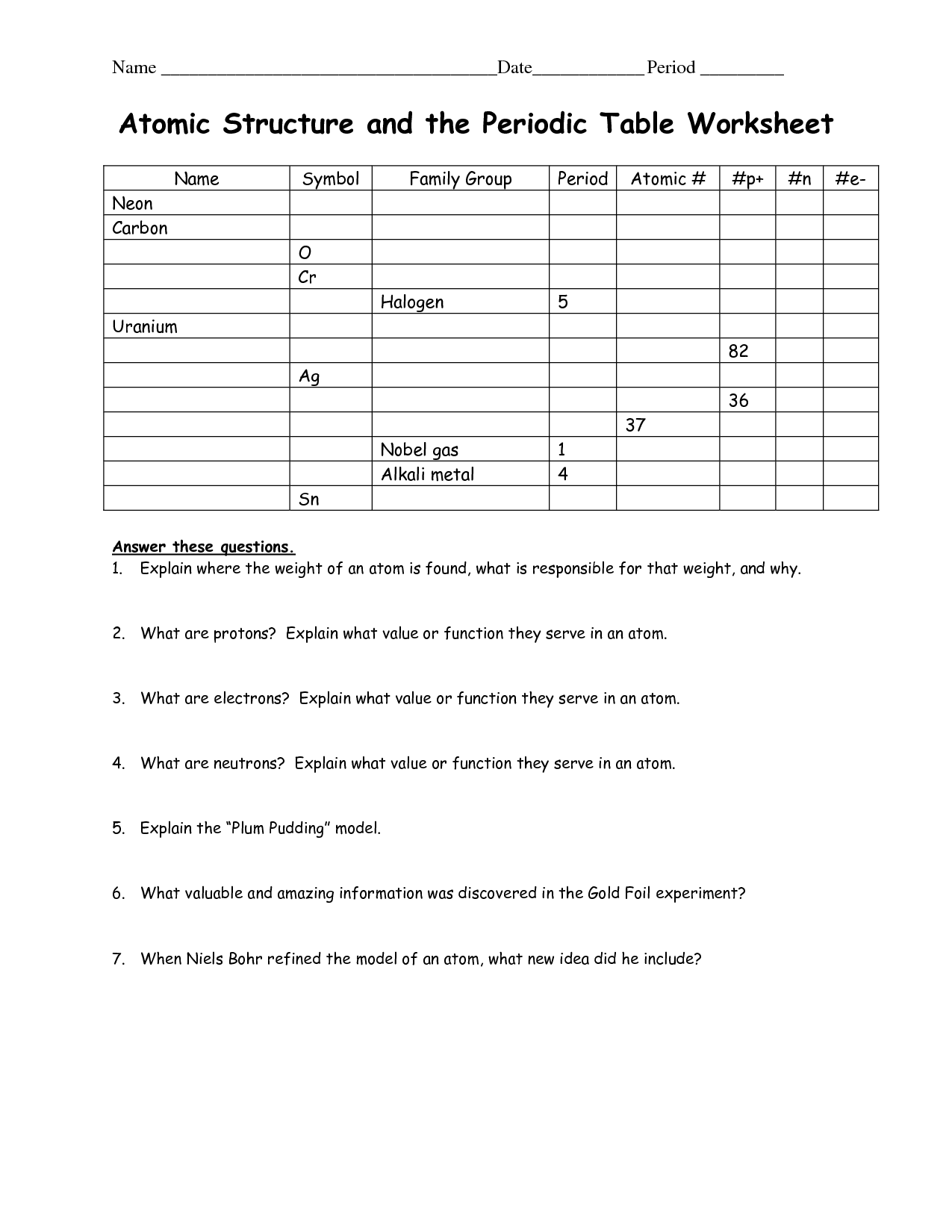
- Atomic Structure Worksheet and Periodic Table
- Percent Composition Worksheet with Solutions
- Electron Shell Atom Diagram Worksheet
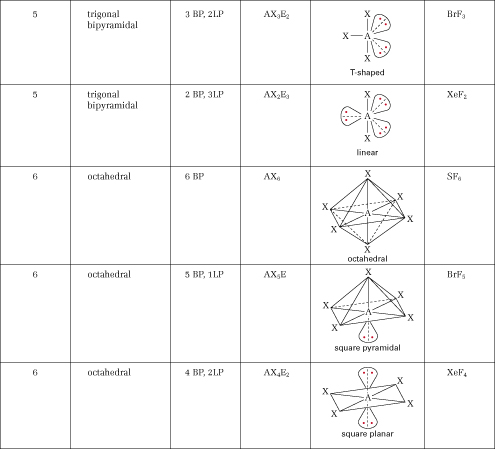
- VSEPR Theory Chart
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is an atom?
An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element. It consists of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells or energy levels. Atoms combine to form molecules and are the building blocks of all substances in the universe.
What are the three main subatomic particles found in an atom and what are their charges?
The three main subatomic particles found in an atom are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons have a positive charge, neutrons have no charge (neutral), and electrons have a negative charge.
How are electrons arranged in an atom?
Electrons are arranged in an atom in energy levels or shells, with each shell corresponding to a specific distance from the nucleus and having a maximum number of electrons it can hold. The first energy level can hold up to 2 electrons, the second energy level can hold up to 8 electrons, and so on. Electrons fill the lowest energy levels first before moving to higher energy levels, following a specific pattern known as the electron configuration, which is based on the principles of quantum mechanics.
What is the atomic number of an element and how is it related to the number of protons in an atom?
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. It uniquely identifies an element and determines its chemical properties. The number of protons also dictates the element's place on the periodic table. In a neutral atom, the number of protons equals the number of electrons, giving the atom an overall neutral charge.
What is the mass number of an element and how is it calculated?
The mass number of an element is the total number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. It is calculated by adding the number of protons (which is equal to the element's atomic number) to the number of neutrons in the nucleus of the atom. So, mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons.
What is an isotope and how does it differ from a regular atom?
An isotope is a variant of a chemical element that has the same number of protons in its nucleus but a different number of neutrons, resulting in a different atomic mass. This means that isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties but different physical properties due to their varying atomic masses. In contrast, a regular atom refers to the most common form of an element with a specific number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus.
What is the significance of the valence electrons in an atom?
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons in an atom and are crucial for determining the atom's chemical properties, including how it bonds with other atoms. The number of valence electrons largely influences an atom's reactivity and bonding behavior, as atoms generally seek to attain a full outer electron shell through gaining, losing, or sharing electrons to achieve greater stability. This process of forming bonds with other atoms is the basis of chemical reactions and the formation of molecules.
What determines the chemical properties of an element?
The chemical properties of an element are determined by its atomic structure, specifically the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons it has. These factors influence an element's reactivity, ability to bond with other elements, and physical characteristics such as melting and boiling points. The arrangement of electrons in an element's outer shell is particularly important in determining its chemical behavior and interactions with other elements.
What is the Bohr model and how does it describe the structure of an atom?
The Bohr model is a representation of the structure of an atom proposed by Niels Bohr in 1913. In this model, electrons orbit around the nucleus in circular paths at specific energy levels or shells. Each shell can hold a specific number of electrons, with the electrons associated with the outermost shell determining the chemical properties of the element. The Bohr model was one of the first successful attempts to describe the behavior of electrons in an atom and laid the foundation for modern quantum mechanics.
How does the concept of electron energy levels contribute to our understanding of atomic structure?
The concept of electron energy levels contributes significantly to our understanding of atomic structure by explaining the organization of electrons around the atomic nucleus. Electrons occupy specific energy levels or shells around the nucleus, with each level capable of holding a specific number of electrons. This arrangement helps to explain the stability and reactivity of different elements, as well as the formation of chemical bonds between atoms. Understanding electron energy levels provides insights into the behavior of atoms and the properties of elements, leading to further advancements in fields such as chemistry and physics.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments