Atomic Structure Practice Worksheet Answers
Are you a high school or college student looking for a reliable source of atomic structure practice worksheet answers? If so, you've come to the right place. This blog post aims to provide you with a comprehensive overview of the topic while offering accurate answers to help you enhance your understanding of atomic structure. Whether you need assistance with electron configuration or isotopes, we've got you covered. So, let's delve into the fascinating world of atomic structure together.
Table of Images 👆
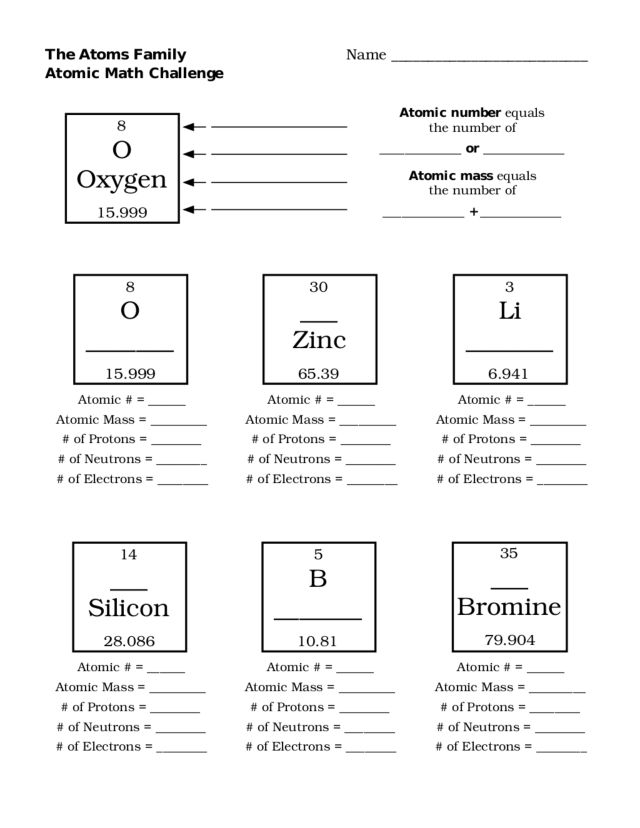
- Atoms Family Atomic Math Challenge Worksheet
- Basic Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
- Stoichiometry Practice Worksheet Answer Key
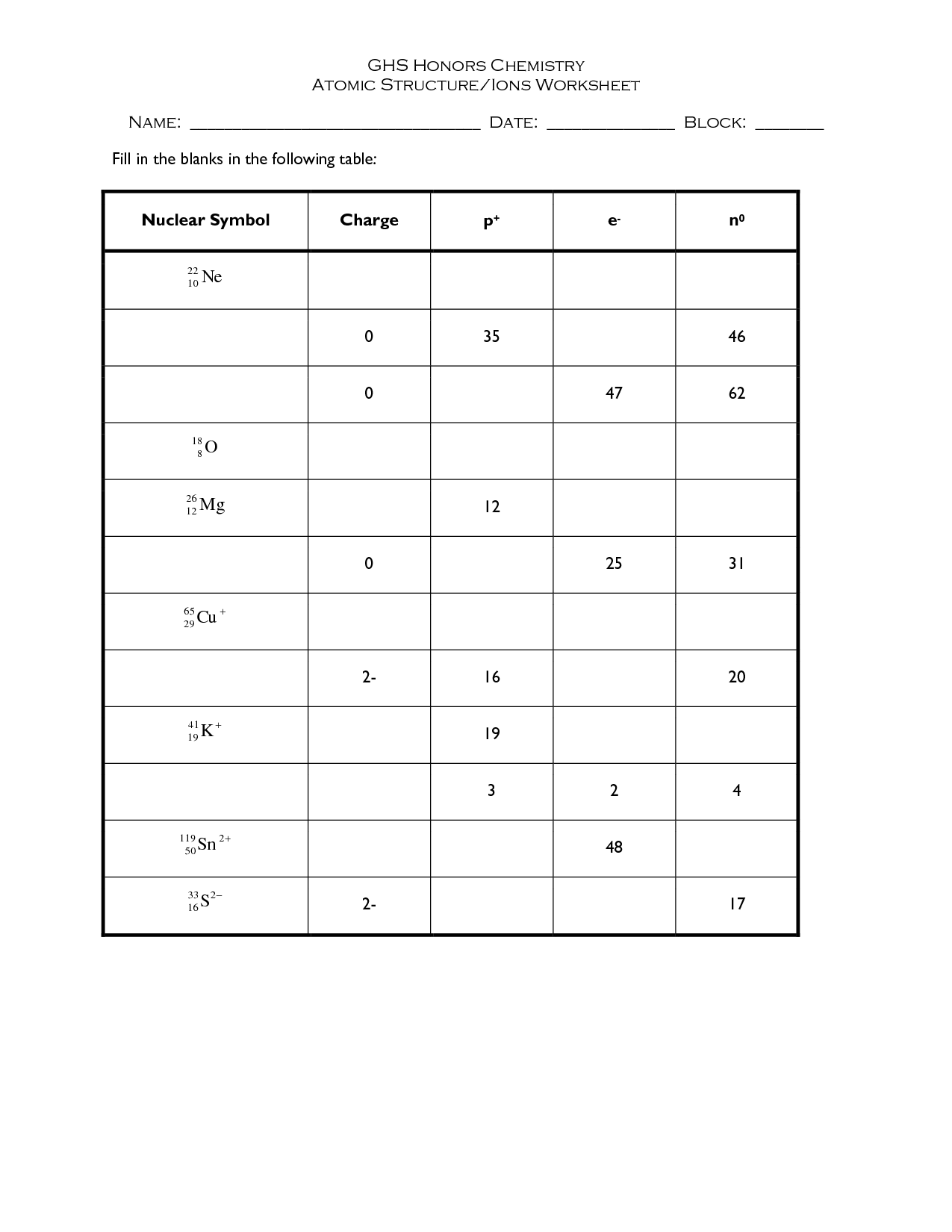
- Chemistry Atomic Structure Worksheet
- Electron Configuration Practice Worksheet Answer Key
- Electron Configuration Worksheet Answers
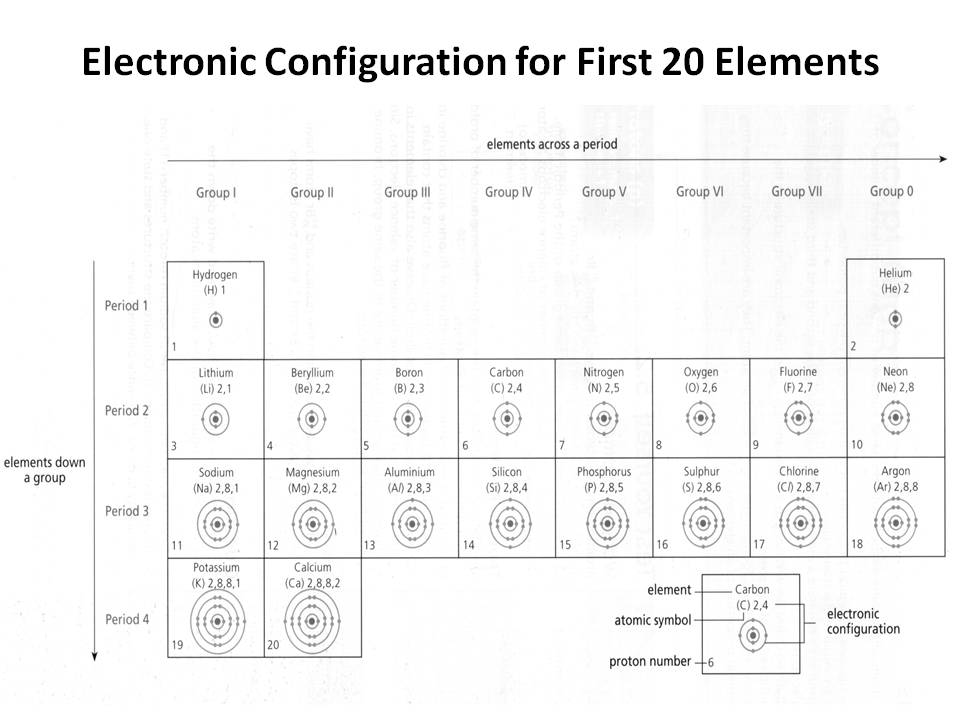
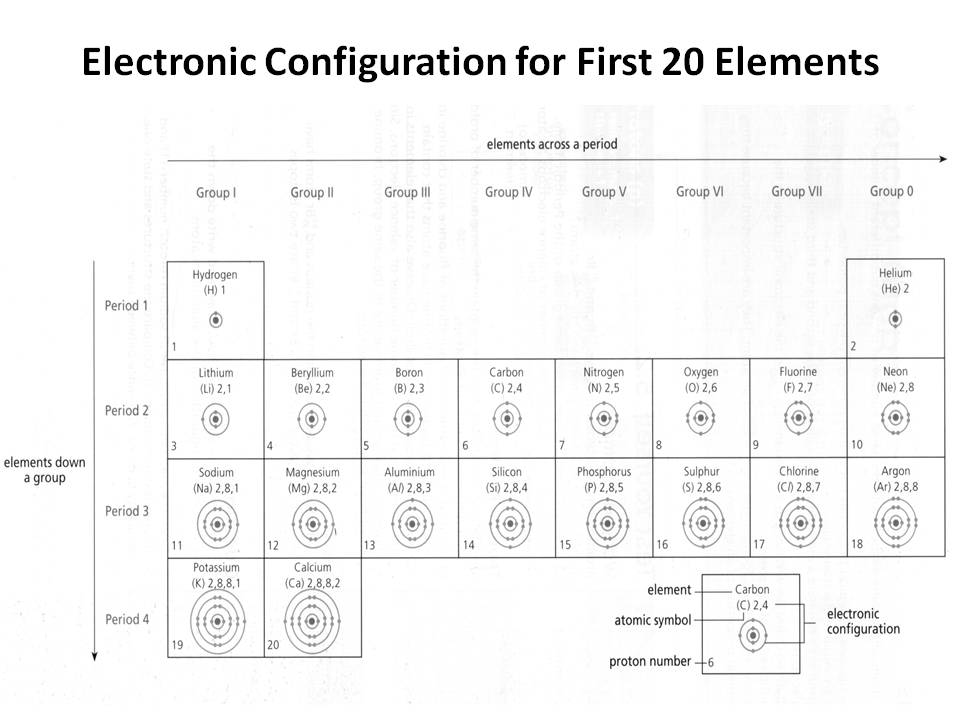
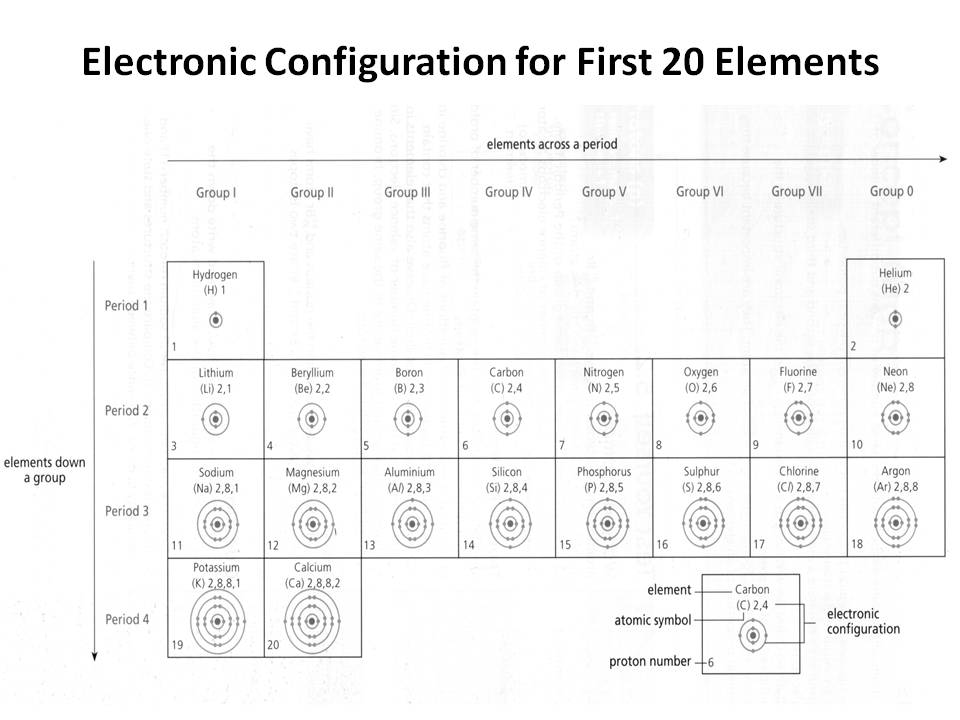
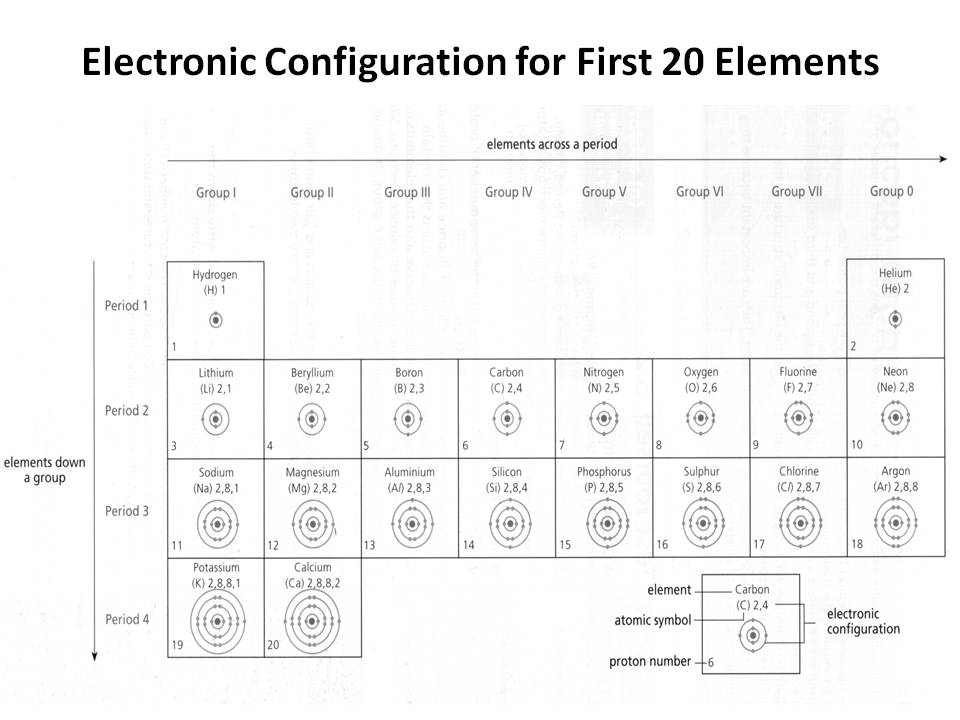
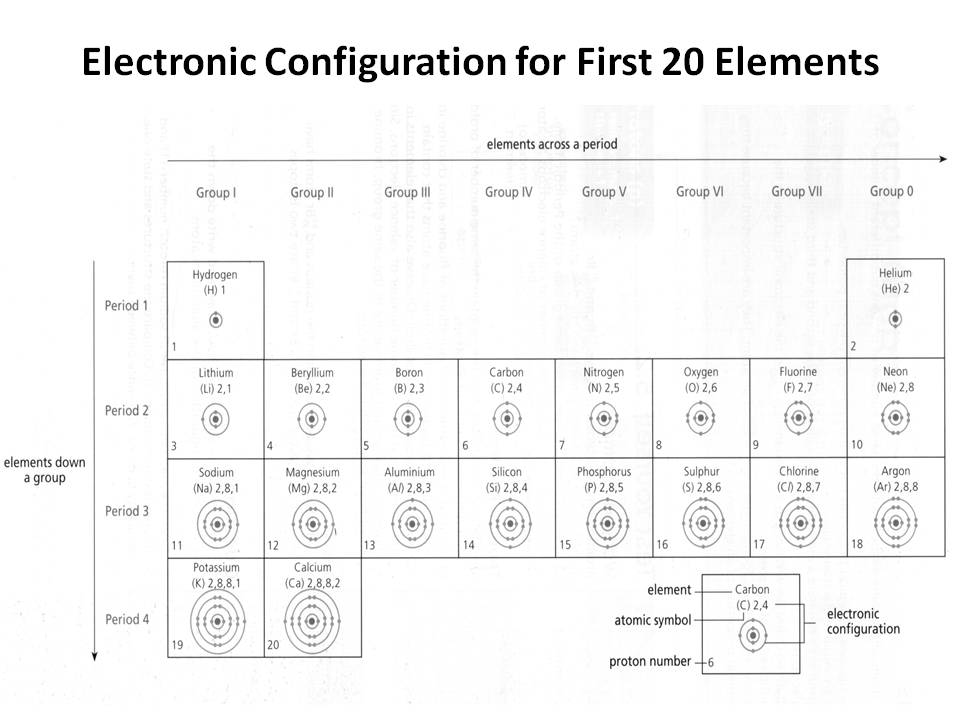
- Electronic Configuration of First 20 Elements
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is an atom?
An atom is the basic unit of matter that consists of a dense nucleus containing positively charged protons and neutrally charged neutrons, surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. These subatomic particles are held together by strong electromagnetic forces, determining the chemical and physical properties of the element it represents.
What are the subatomic particles found in an atom?
An atom is composed of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons carry a positive charge, neutrons carry no charge (neutral), and electrons carry a negative charge. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of the atom, while electrons orbit around the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells.
How are protons and electrons different?
Protons are positively charged particles found in the nucleus of an atom, while electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus. Protons have a much larger mass than electrons, and their number determines the atomic number of an element. Electrons play a vital role in chemical reactions, bonding, and determining the reactivity of atoms.
What is the role of neutrons in an atom?
Neutrons play a crucial role in an atom as they help stabilize the nucleus along with protons by providing the strong nuclear force that holds the nucleus together. They also contribute to the mass of the atom without affecting its chemical properties, allowing different isotopes of an element to exist based on the number of neutrons in the nucleus. In nuclear reactions and processes like nuclear fission and fusion, neutrons are instrumental in initiating and sustaining the reaction by colliding with other nuclei.
What is the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom of that element. It is a unique and defining characteristic of each element in the periodic table and determines its placement within the table.
What is the mass number of an element?
The mass number of an element is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. It is denoted by the symbol A and is used to differentiate between different isotopes of an element, which have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
What is an isotope?
An isotope is a variant of a chemical element that has the same number of protons in its nucleus but a different number of neutrons, resulting in variations in atomic mass. Isotopes of an element share similar chemical properties but may exhibit different physical properties, such as stability and radioactive decay rates.
How is the atomic mass of an element calculated?
The atomic mass of an element is calculated by taking into account the mass of each isotope of the element and its abundance in nature. This involves multiplying the mass of each isotope by its relative abundance, then summing these values to calculate the weighted average atomic mass. This value is expressed in atomic mass units (amu) and is listed on the periodic table for each element.
What is the Bohr model of the atom?
The Bohr model of the atom, proposed by Niels Bohr in 1913, suggests that electrons orbit the atomic nucleus in fixed, quantized orbits at specific energy levels. These orbits are characterized by specific distances from the nucleus and energy values. The model also explains the emission of light when electrons jump between these quantized energy levels. Despite its limitations and later advancements in atomic theory, the Bohr model remains a fundamental concept in understanding the structure of atoms.
How does the electron configuration determine the chemical properties of an element?
The electron configuration of an element determines its chemical properties by indicating the number and arrangement of electrons in its outermost energy level. This determines how easily an element can gain, lose, or share electrons to form chemical bonds with other elements. Elements with similar electron configurations tend to exhibit similar chemical behavior, as they have similar tendencies to form specific types of chemical bonds and participate in reactions. Additionally, the number of electrons in the outer energy level influences an element's reactivity and ability to form compounds with other elements.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments