Astronomy Star Evolution Worksheet
Are you a science teacher or an astronomy enthusiast searching for an engaging and educational resource for your students or personal exploration? Look no further! Introducing the Astronomy Star Evolution Worksheet, a valuable tool designed to deepen your understanding of the fascinating process of star evolution.
Table of Images 👆
- Evolution Activity Worksheet
- Evolution of Stars Worksheet Answers
- Evolution of Stars Worksheet
- Bohr Diagram Practice Worksheets
- Stellar Evolution Worksheet
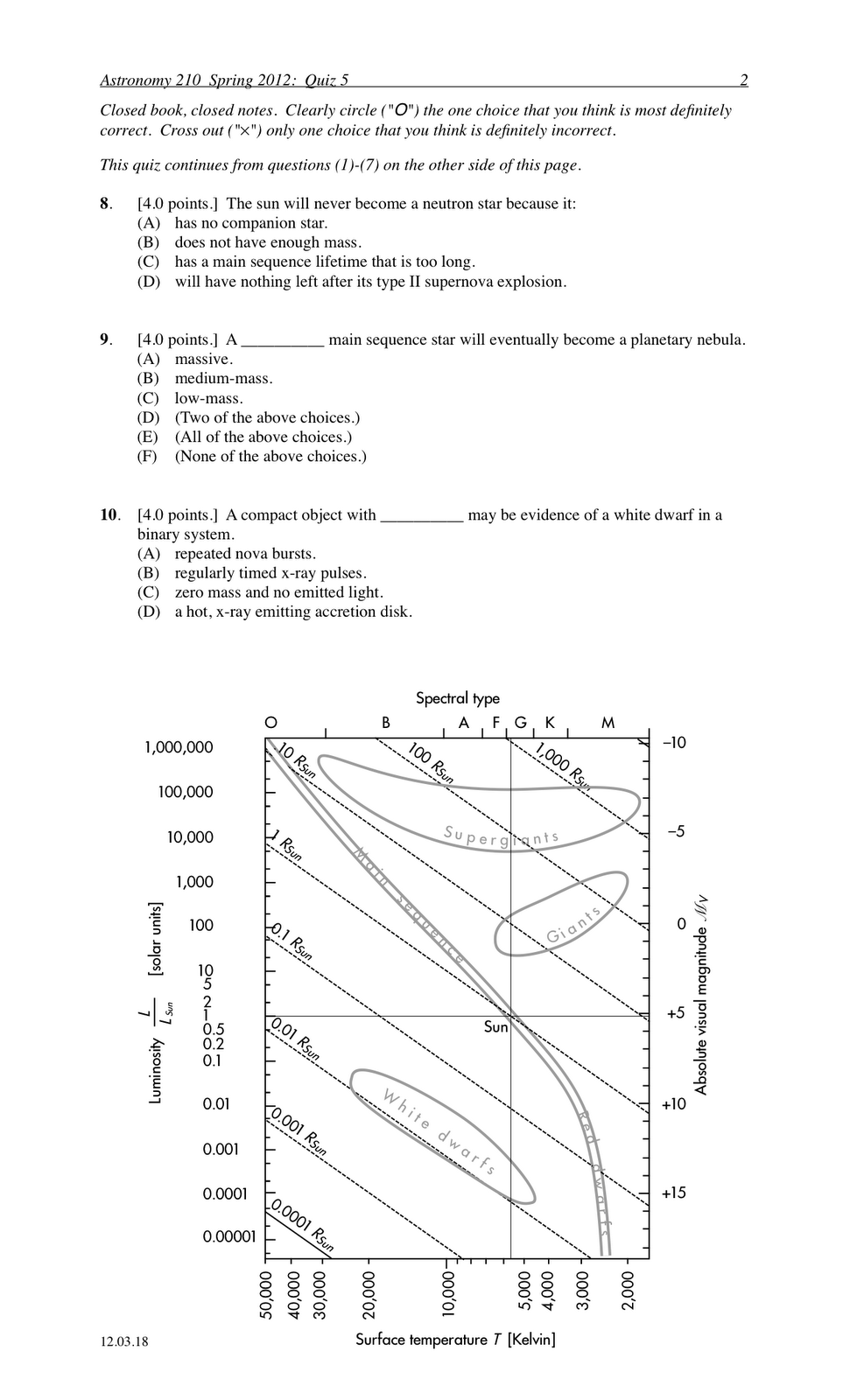
- Blank HR Diagram
- Star Stellar Evolution Stages Chart
- Star Life Cycle Worksheet
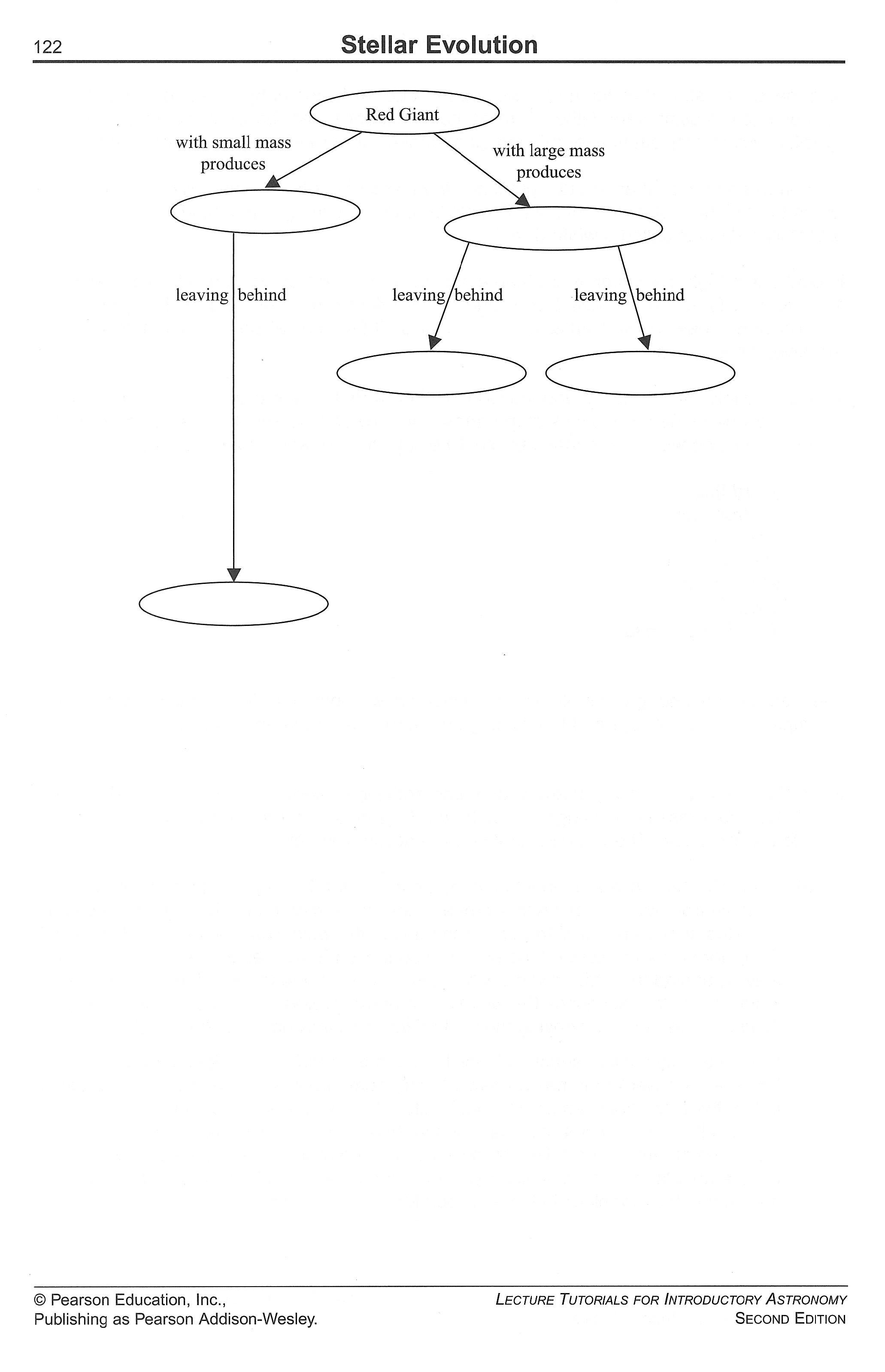
- Stellar Evolution Concept Map
- Sun Moon Stars Worksheets
- Free Printable Word Search Solar System
- MasteringAstronomy Quiz Chapter 9 Visual
- Lecture Tutorials for Astronomy Answer Key
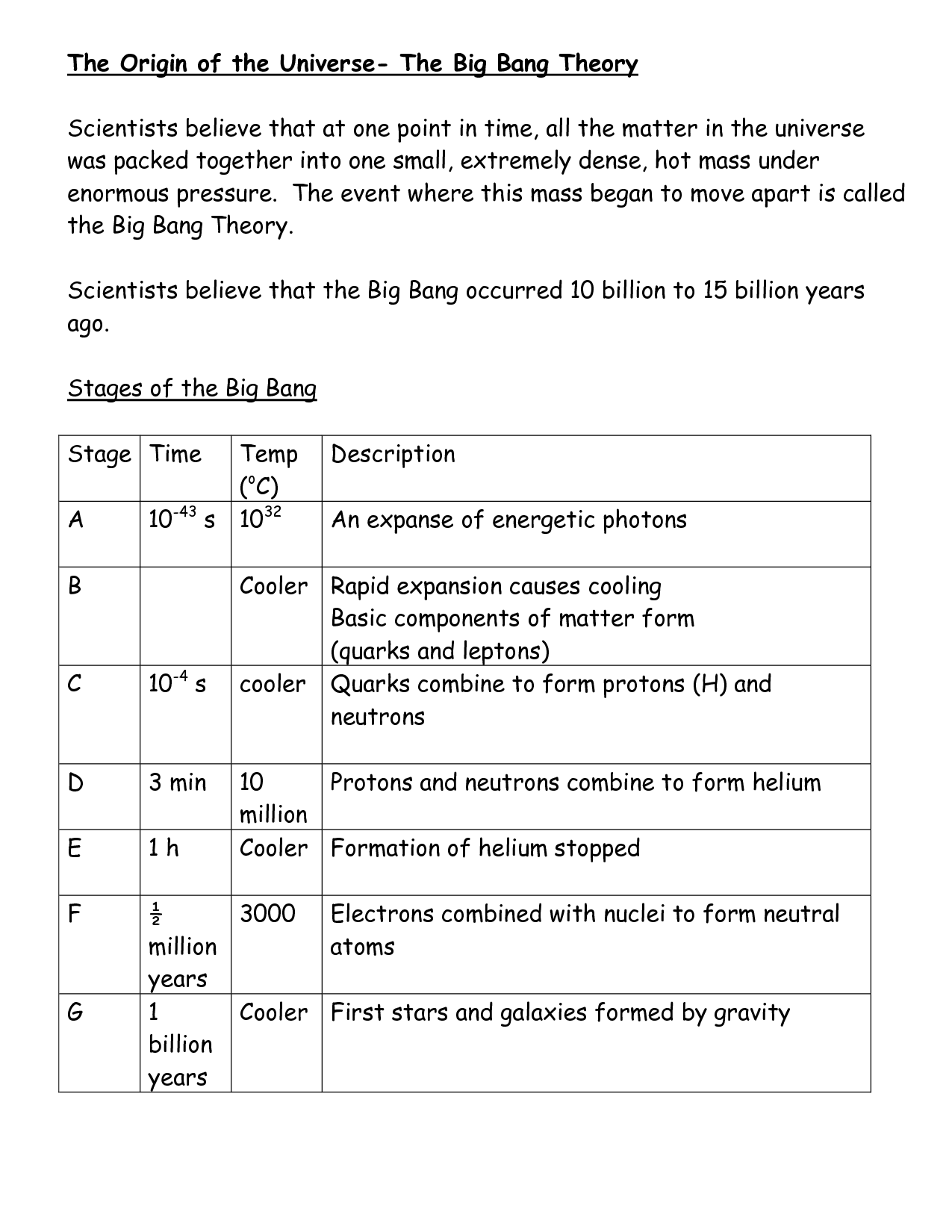
- Big Bang Theory Universe Worksheet
- Evolution Test Questions and Answers
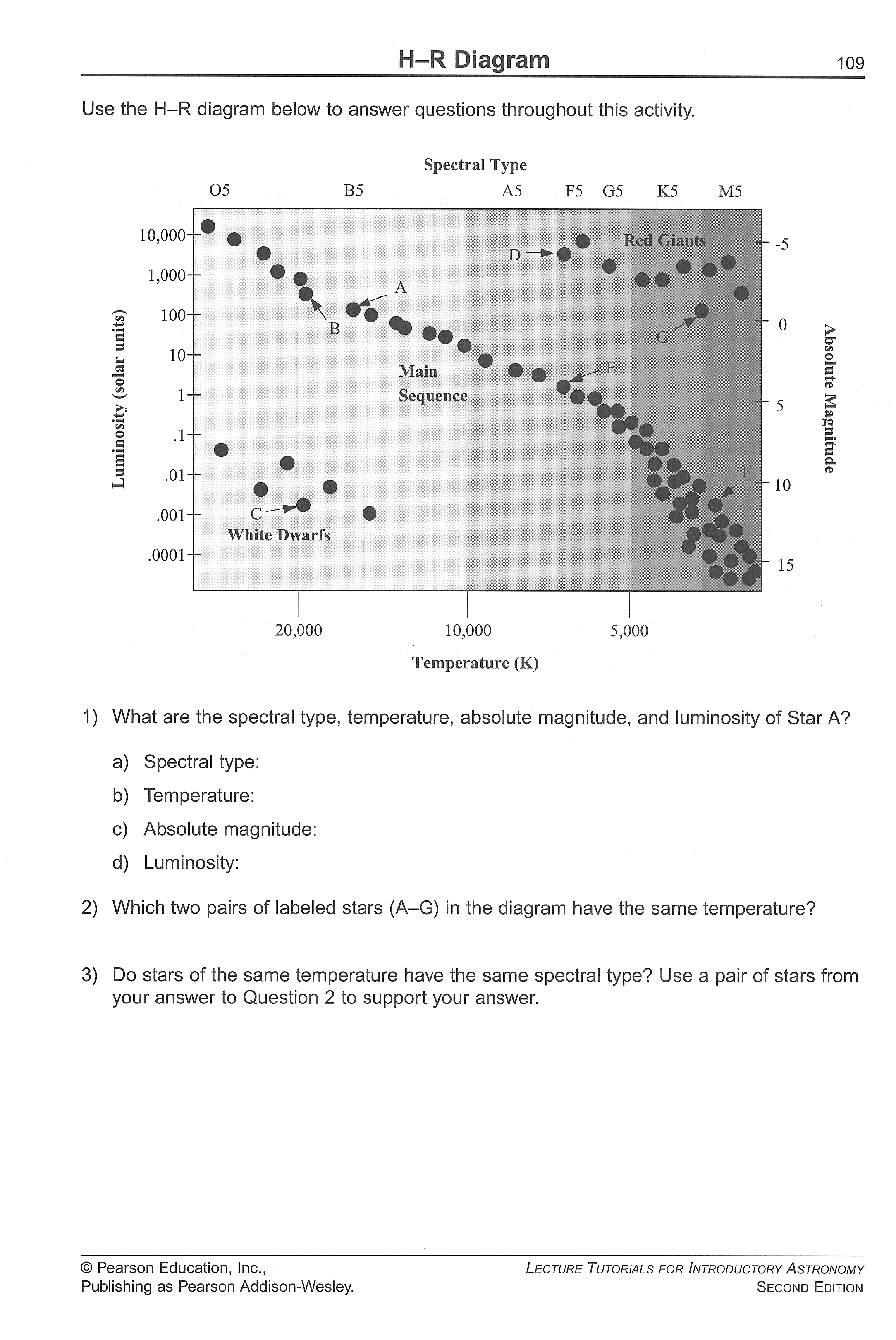
- HR Diagram Stellar Evolution
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
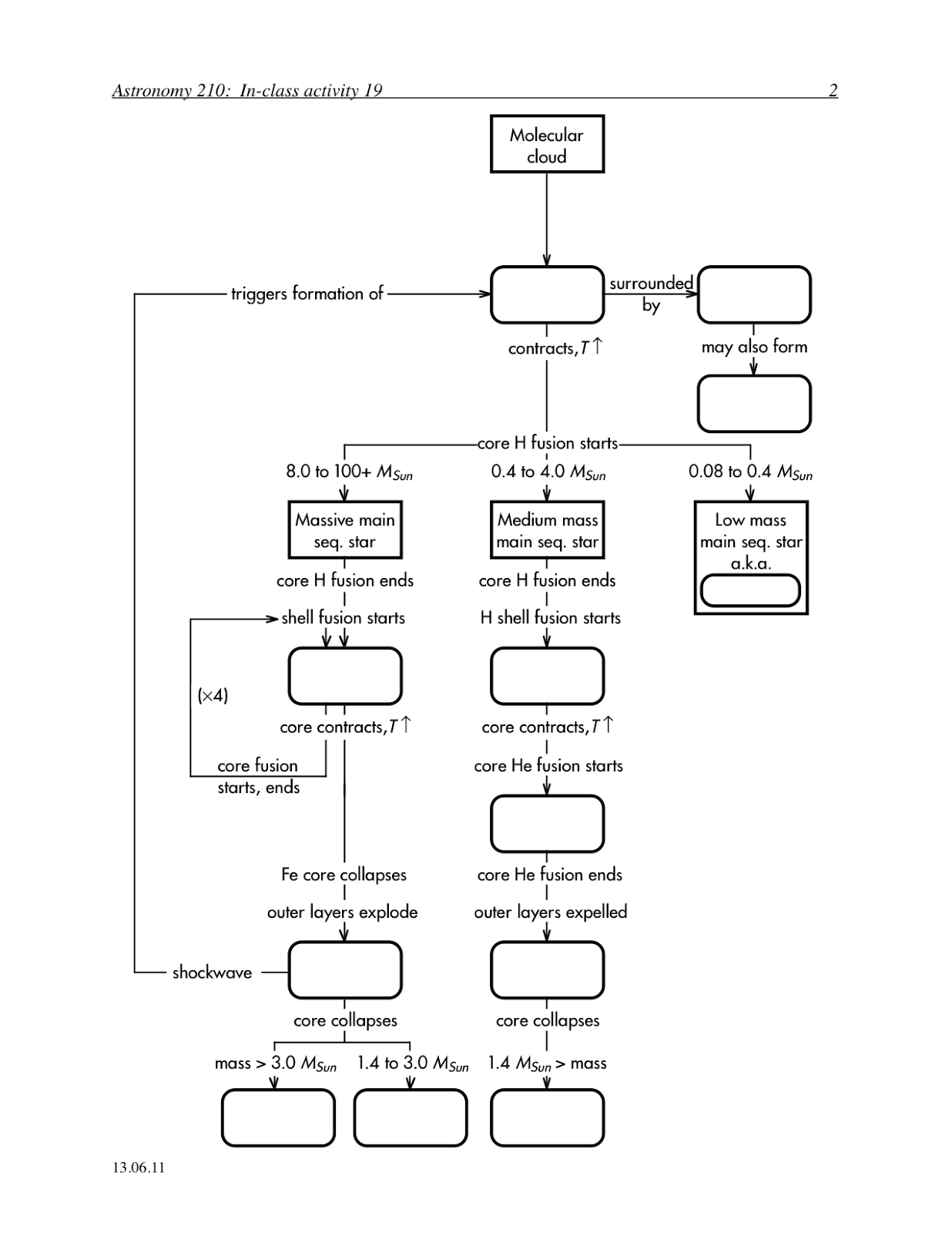
What is the process through which stars are formed?
Stars are formed through a process called stellar nucleosynthesis, where dense regions of gas and dust in space called molecular clouds collapse under their own gravity. As the cloud contracts, it heats up and forms a protostar, a young, hot core with a surrounding disk of material. Over time, the inward pull of gravity and the outward pressure from nuclear fusion in the core reach a balance, and the protostar becomes a stable star, shining brightly as it continues to fuse hydrogen into helium in its core.
How does the mass of a star impact its evolution?
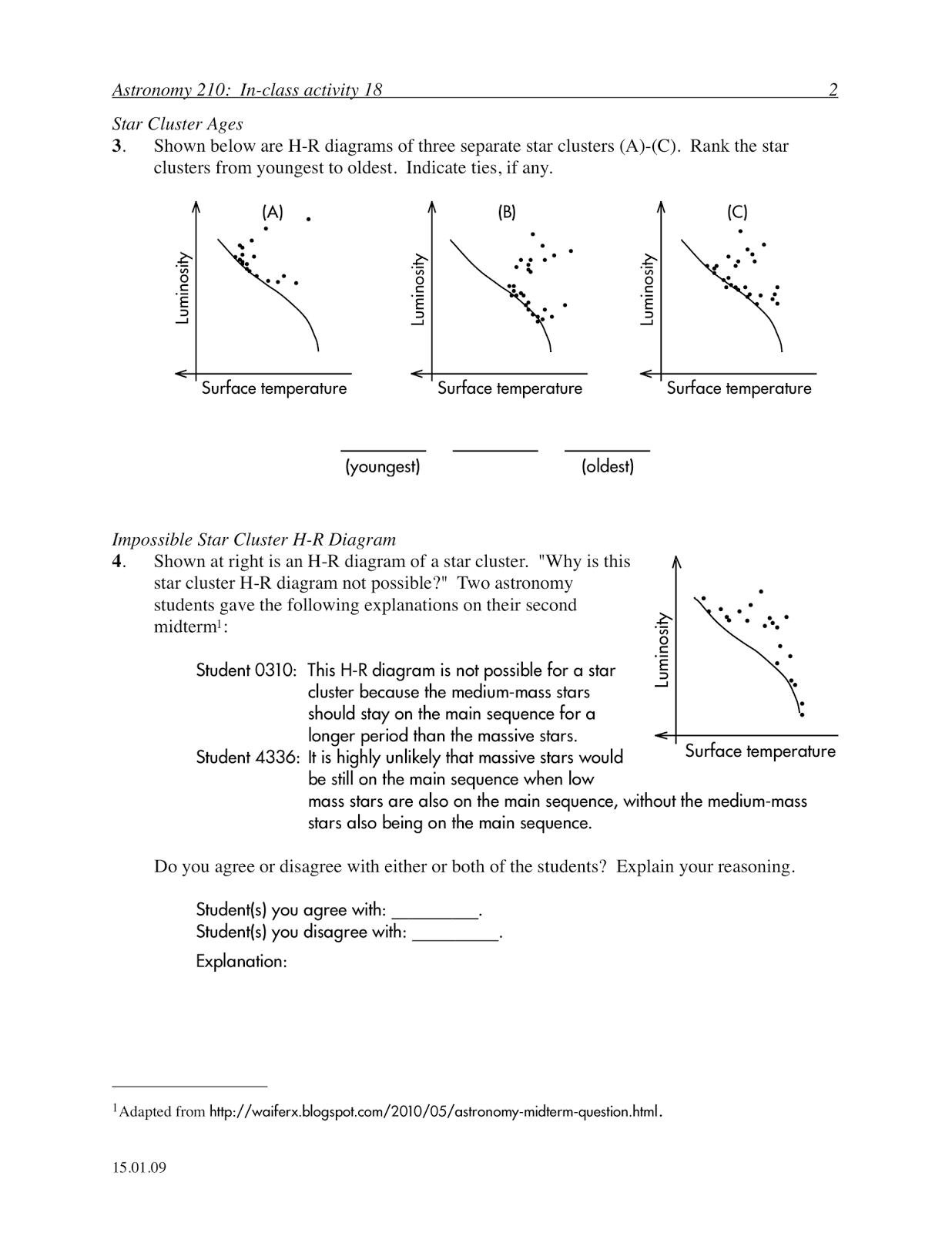
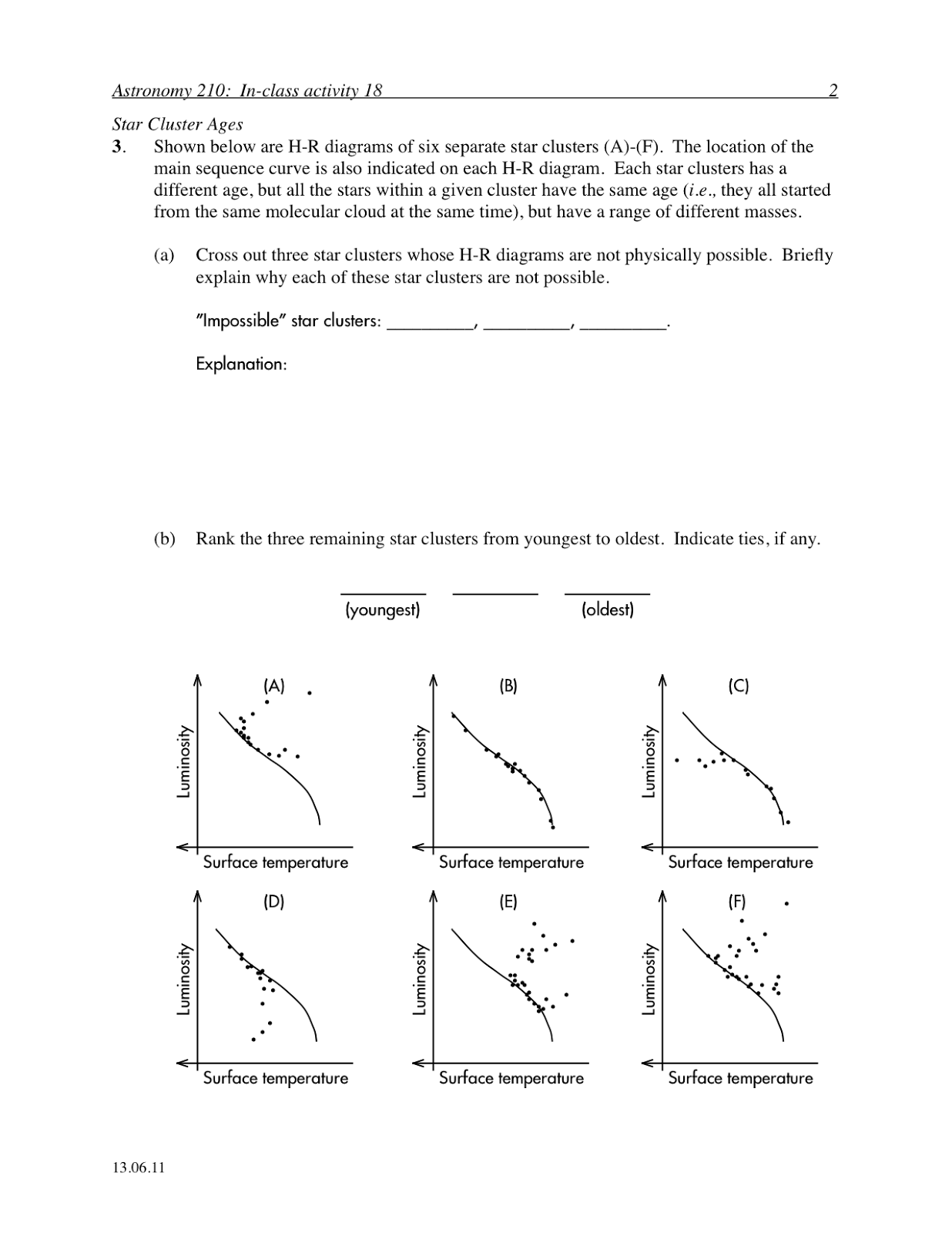
The mass of a star plays a significant role in determining its evolution. Higher mass stars have more gravitational force and pressure in their cores, leading to faster fusion reactions and shorter lifespans. These stars evolve more quickly, burning through their fuel faster and eventually exploding in a supernova. On the other hand, lower mass stars have slower fusion reactions and longer lifespans. They eventually expand into red giants, shed their outer layers, and then collapse into dense white dwarfs. The mass of a star ultimately governs the balance between gravity and radiation pressure, influencing its evolution from birth to death.
What is a main sequence star and what happens during this stage?
A main sequence star is a type of star that is in a stage of stable nuclear fusion, where hydrogen atoms in the core are converted into helium through fusion reactions. This stage is characterized by the balance of inward gravitational forces and outward radiation pressure. During this stage, main sequence stars generate energy through nuclear fusion, maintaining their size, temperature, and luminosity. The Sun is an example of a main sequence star, converting hydrogen into helium in its core through the proton-proton chain reaction.
How do stars generate energy?
Stars generate energy through a process called nuclear fusion, which occurs in their cores. During nuclear fusion, hydrogen atoms combine to form helium atoms, releasing a tremendous amount of energy in the form of light and heat. This fusion process is sustained by the intense pressure and temperature in the core of a star, allowing it to shine bright and provide the energy necessary to support life on planets like Earth.
Describe the process of nuclear fusion within stars.
Nuclear fusion within stars involves the smashing together of light atomic nuclei to form heavier ones, releasing immense amounts of energy in the process. This process occurs in the core of stars where high temperatures and pressures create the conditions necessary for nuclei to overcome their mutual repulsion and fuse together. The most common fusion reaction in stars is the conversion of hydrogen into helium, where four hydrogen nuclei combine to form a helium nucleus, releasing energy in the form of light and heat. This energy sustains the star's internal pressure and prevents it from collapsing under its own gravity, allowing it to shine brightly for billions of years until it exhausts its nuclear fuel.
What happens to a star after it exhausts its nuclear fuel?
When a star exhausts its nuclear fuel, it undergoes a series of transformations based on its mass. For low to medium mass stars, like our Sun, they expand into a red giant phase, shed their outer layers as a planetary nebula, and eventually collapse into a dense core known as a white dwarf. However, high-mass stars undergo more violent processes, such as supernova explosions, which can result in the formation of neutron stars or black holes.
What is a red giant star and how does it form?
A red giant star is a large, luminous star that has expanded and cooled off towards the end of its life cycle. It forms when a star like the Sun runs out of hydrogen fuel in its core, causing the core to contract and the outer layers to expand. As the star expands, it becomes cooler and redder in color, hence the name "red giant." This phase occurs before the star eventually sheds its outer layers and becomes a white dwarf.
How does a massive star end its life compared to a low mass star?
A massive star ends its life in a supernova explosion, where the core collapses and the outer layers are ejected into space. This explosion leaves behind a dense remnant such as a neutron star or a black hole. In contrast, a low mass star like the Sun ends its life by shedding its outer layers to form a planetary nebula, leaving behind a dense core known as a white dwarf.
Explain the concept of a supernova and what causes it.
A supernova is a powerful and catastrophic explosion that occurs at the end of a star's life cycle when it cannot withstand its own gravitational forces. This explosion triggers the sudden and extreme release of energy, leading to a massive burst of light and radiation. There are different types of supernovae - Type I supernovae occur in binary star systems where a white dwarf star accretes matter from a companion star, eventually surpassing its mass limit and exploding, while Type II supernovae occur when a massive star runs out of nuclear fuel and collapses under its own gravity. The resulting explosion disperses newly formed elements into space, enriching the surrounding environment and contributing to the formation of new stars and planetary systems.
What remains after a supernova and what can it potentially form?
After a supernova, what remains is either a neutron star, a dense core composed mostly of neutrons, or a black hole, an infinitely dense singularity in space-time. Neutron stars can potentially form through mechanisms such as electron capture or neutronization, while black holes can form if the remnant core is above a certain critical mass threshold.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments