9th Grade Geometry Worksheets
Geometry is a fundamental subject in 9th grade that focuses on the study of shapes, sizes, and properties of various entities. To ensure a comprehensive understanding of this subject and to strengthen your skills, utilizing worksheets can be incredibly helpful. These worksheets serve as valuable tools, providing practice problems and exercises that cover a wide range of geometry topics. Whether you are a student aiming to sharpen your knowledge or a teacher searching for additional resources, 9th grade geometry worksheets can offer a practical and efficient way to reinforce your learning.
Table of Images 👆
- 9th Grade Math Worksheets Printable
- 8th Grade Math Worksheets Geometry
- Printable 9th Grade Reading Comprehension Worksheets
- 7th Grade Math Worksheets and Answer Key
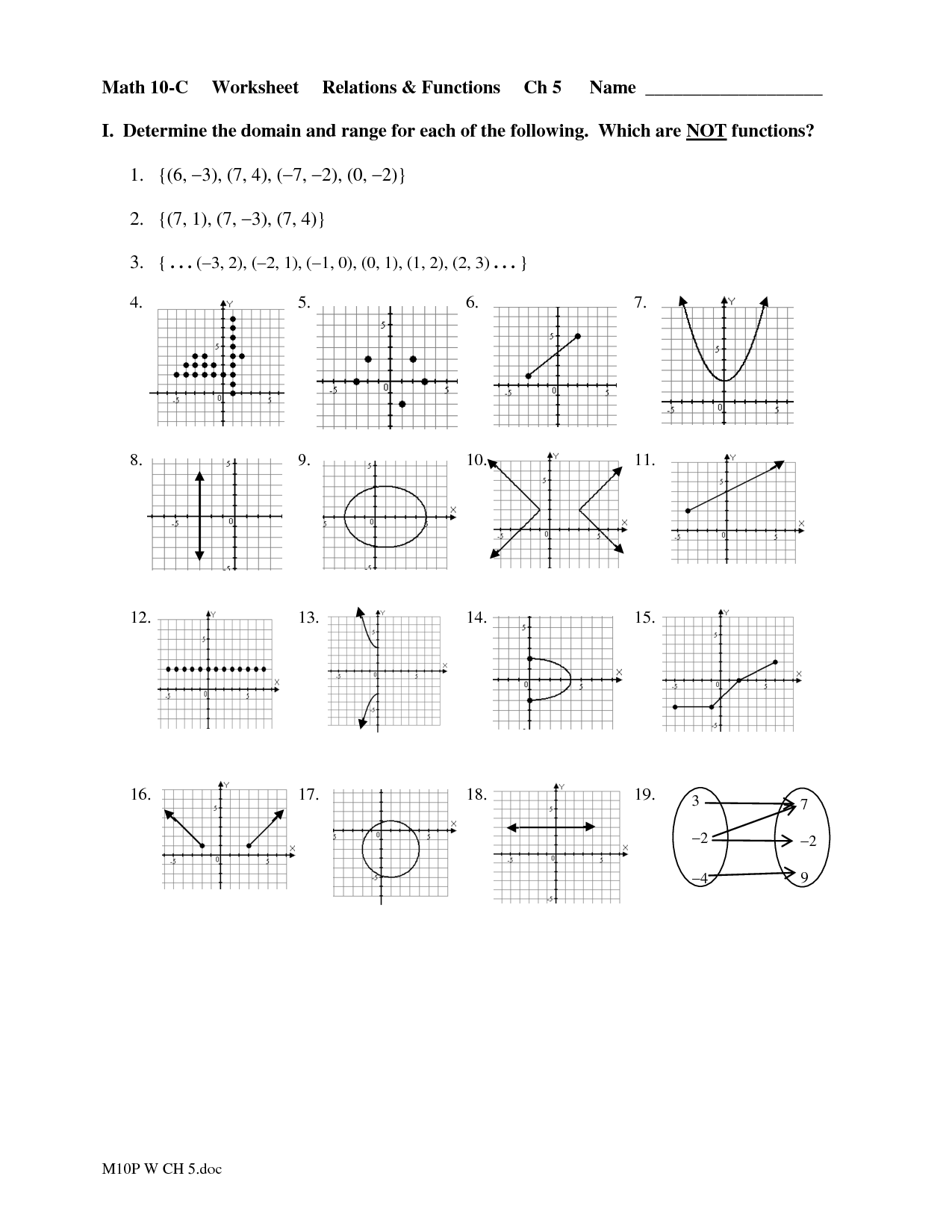
- Math Relations and Functions Worksheet
- 10th Grade Geometry Study Guide
- 8th Grade Math Worksheets Algebra
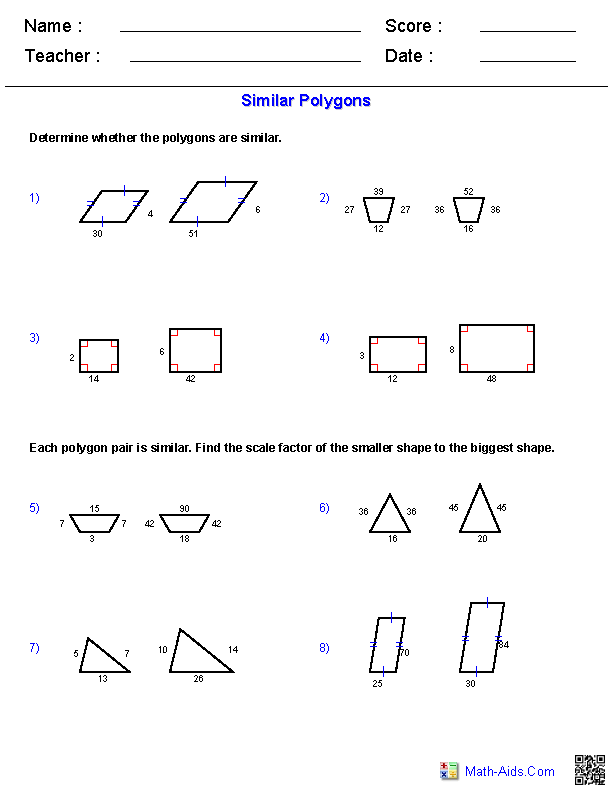
- Geometry Similar Polygons Worksheet
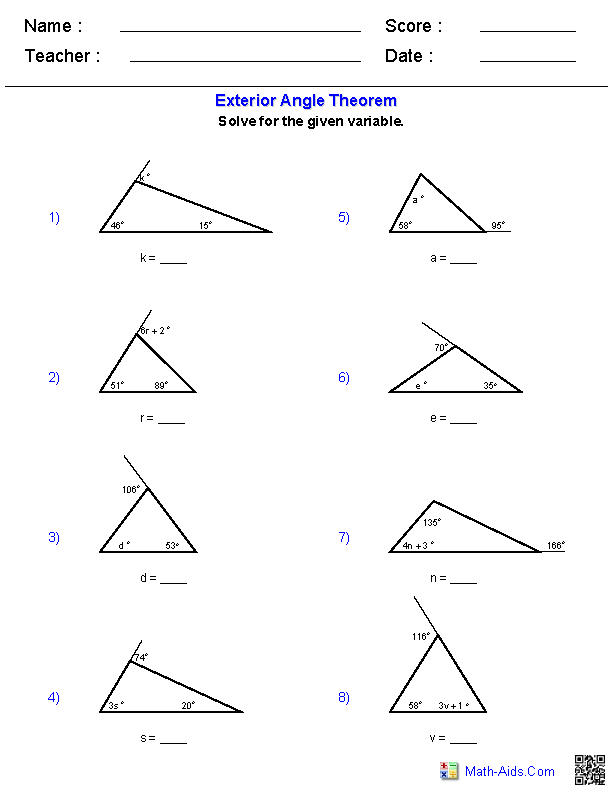
- Triangle Angle Sum Theorem Worksheet
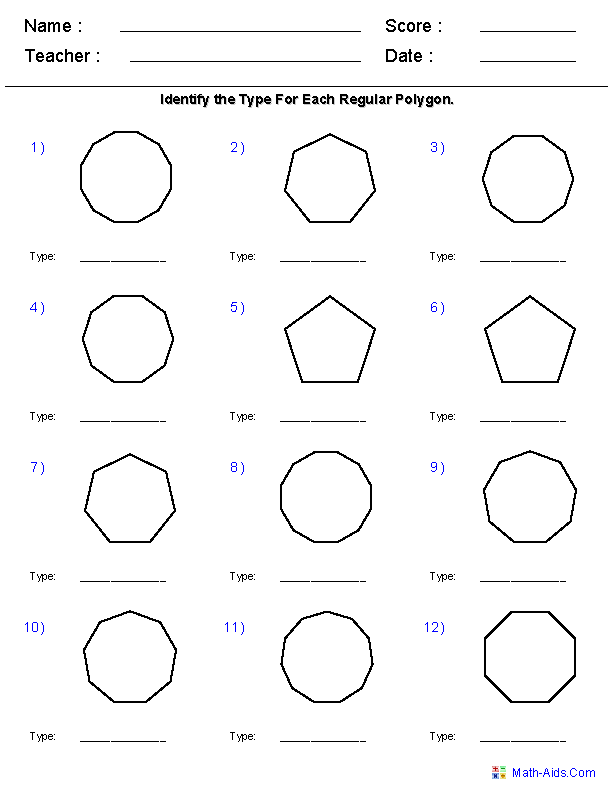
- Regular Polygons Worksheet
- Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Worksheet with Answers
What are the basic principles of geometry?
The basic principles of geometry include points, lines, planes, shapes, angles, and dimensions. Geometry examines the properties and relationships of these fundamental elements and explores concepts such as symmetry, congruence, similarity, and transformations. It also involves the study of spatial figures such as circles, triangles, and polygons in both two-dimensional and three-dimensional space. Overall, geometry provides a framework for understanding spatial relationships and is essential in fields such as mathematics, engineering, architecture, and art.
Explain the properties of points, lines, and planes.
Points are basic elements with no size or shape, lines are formed by an infinite number of points and extend indefinitely in two directions, while planes are flat surfaces made up of an infinite number of lines that extend in two dimensions. Points have location but no size, lines have length but no width or depth, and planes have length and width but no depth. Points are denoted by a single capital letter, lines by two points with a line symbol over them, and planes by a script letter or by naming three non-collinear points that lie in the plane.
What are the different types of angles and their characteristics?
There are four main types of angles: acute angles (less than 90 degrees), right angles (exactly 90 degrees), obtuse angles (greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees), and straight angles (exactly 180 degrees). Additionally, there are reflex angles (greater than 180 degrees) and full angles (exactly 360 degrees). Each type of angle has unique characteristics and properties that determine its measurement and relationship to other angles in geometric shapes and calculations.
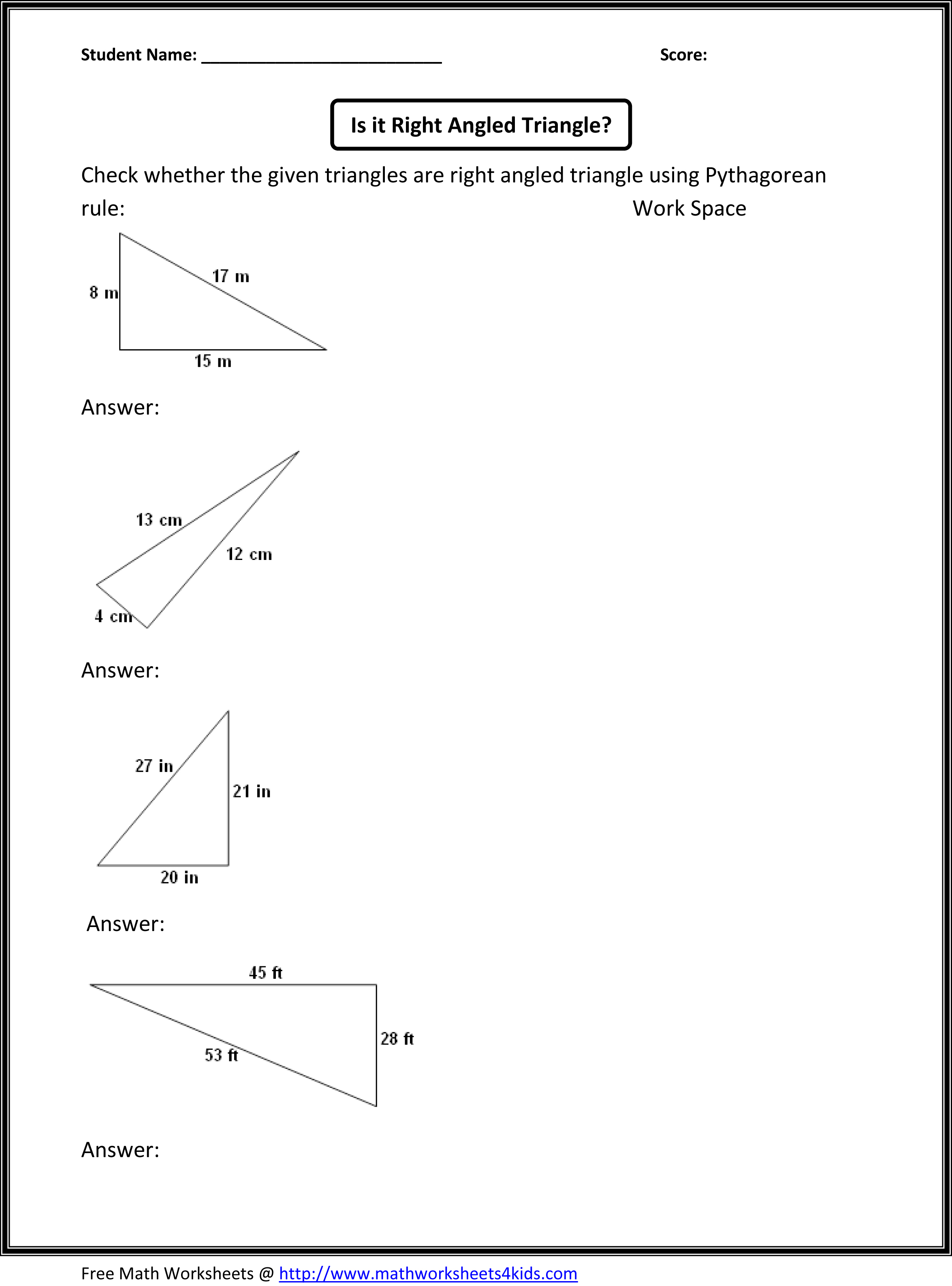
Describe the different types of triangles and their properties.
There are three main types of triangles based on their sides: equilateral (with all sides and angles equal), isosceles (with at least two sides and corresponding angles equal), and scalene (with all sides and angles different). Triangles are also classified by their angles as acute (all angles less than 90 degrees), obtuse (one angle more than 90 degrees), and right triangles (one angle exactly 90 degrees). Additionally, the sum of angles in any triangle is always 180 degrees, and the longest side is opposite the largest angle. These properties help in identifying and working with different types of triangles in geometry.
Explain the concept of congruence and how it is used in geometry.
Congruence in geometry refers to the idea that two geometric figures are identical in shape and size. In other words, if two shapes are congruent, all their corresponding sides are equal in length, and all their corresponding angles are equal in measure. Congruence is used in geometry to demonstrate that two shapes are equal without having to measure every single side and angle. When two shapes are proven to be congruent, it allows for the transfer of properties and measurements between the shapes, making it a powerful tool in geometric proofs and constructions.
What are the formulas used to calculate the perimeter and area of various polygons?
The formulas used to calculate the perimeter of various polygons are: For a rectangle - P = 2(l + w); For a square - P = 4s; For a triangle - P = a + b + c (where a, b, and c are the side lengths); For a regular polygon - P = n * s (where n is the number of sides and s is the side length). The formula used to calculate the area of various polygons are: For a rectangle - A = l * w; For a square - A = s^2; For a triangle - A = 1/2 * b * h (where b is the base and h is the height); For a regular polygon - A = (1/2) * P * apothem.
Describe the different types of quadrilaterals and their properties.
Quadrilaterals are four-sided polygons. They can be classified into various types based on their properties. A square has four equal sides and four right angles. A rectangle has four right angles, with opposite sides being parallel and equal in length. A parallelogram has opposite sides that are parallel. A rhombus has four equal sides, with opposite angles being equal. A trapezoid has one pair of opposite sides that are parallel. These properties distinguish the different types of quadrilaterals and help us identify and classify them.
Explain the concept of similarity and how it relates to geometric figures.
Similarity in geometry refers to the property of two or more geometric figures having the same shape, but not necessarily the same size. Figures are considered similar if their corresponding angles are equal and their corresponding sides are proportional in length. This means that one figure can be an enlarged or reduced version of the other, with the same overall shape but different sizes. Similarity allows us to compare and analyze geometric figures by focusing on their shapes and relative proportions, rather than just their absolute measurements.
What are the different types of transformations (translations, rotations, reflections, dilations) and how are they applied in geometry?
The different types of transformations in geometry are translations, rotations, reflections, and dilations. Translations move an object without changing its size or shape. Rotations turn an object around a fixed point. Reflections flip an object over a line or point. Dilations resize an object while preserving its shape. These transformations are used in geometry to manipulate shapes, figures, or objects to explore relationships, symmetries, and properties in geometric space.
Describe the relationships between angles in a circle and the properties of arcs and chords.
The relationships between angles in a circle and the properties of arcs and chords are interconnected. An inscribed angle in a circle is half the measure of its intercepted arc, while a central angle is equal to the measure of its intercepted arc. Additionally, the measure of an arc is equal to the sum of the measures of the central and inscribed angles that intercept it. Chords that subtend equal arcs are congruent, and a chord is perpendicular to a radius if and only if it bisects the arc it intersects. These relationships demonstrate the intricate connections between angles, arcs, and chords in a circle.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

















Comments