DNA Replication Diagram Worksheet
The DNA replication diagram worksheet provides an interactive and informative tool for students and individuals interested in understanding the intricacies of DNA replication. This worksheet aims to simplify complex concepts by breaking them down into manageable, easily digestible parts. Whether you are a student studying biology or a science enthusiast wanting to deepen your understanding of how DNA replicates, this worksheet is designed to make the subject accessible and engaging.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Replication Coloring Worksheet
- DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet
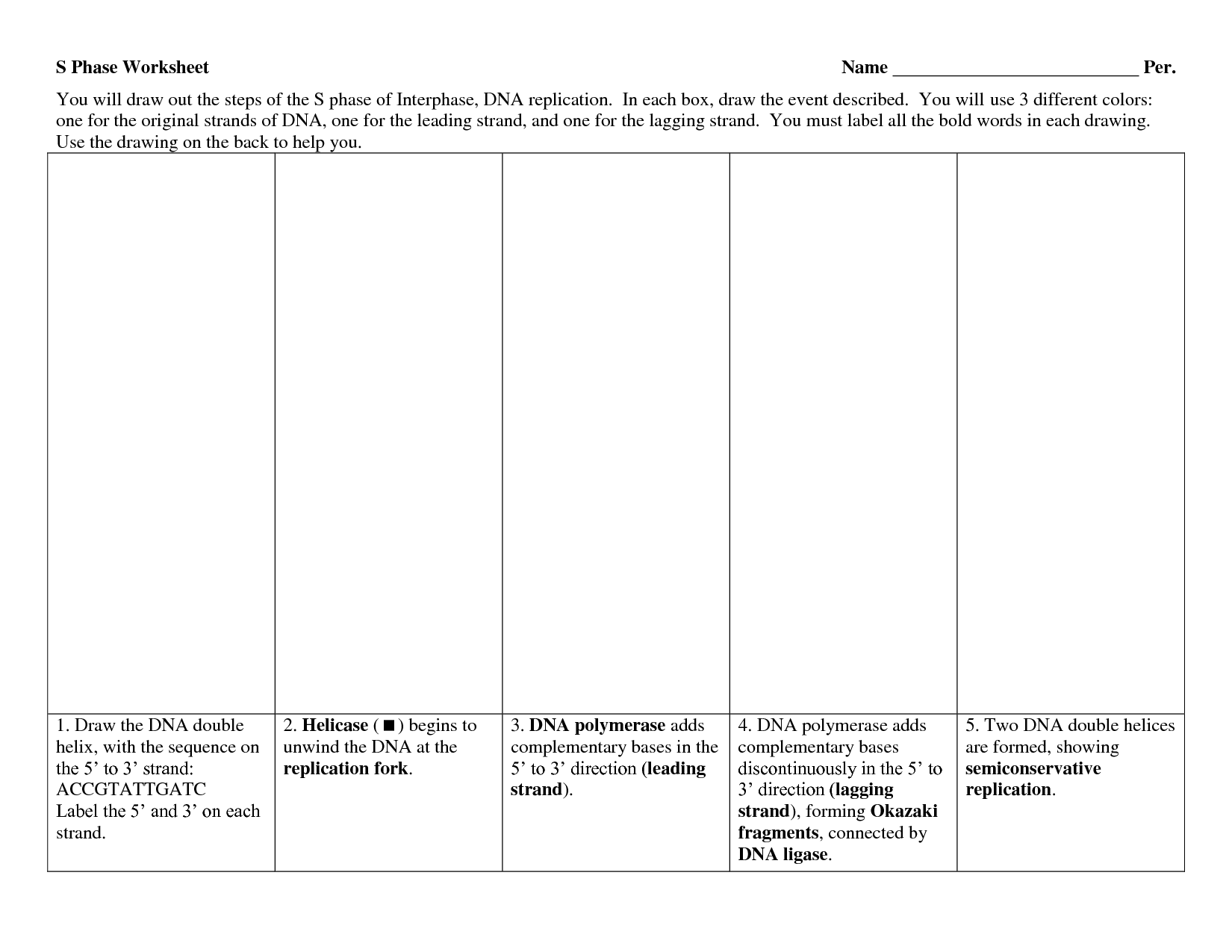
- DNA Replication Worksheet
- DNA Replication Structure Worksheet
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Replication Transcription Translation Worksheet
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answers
- DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
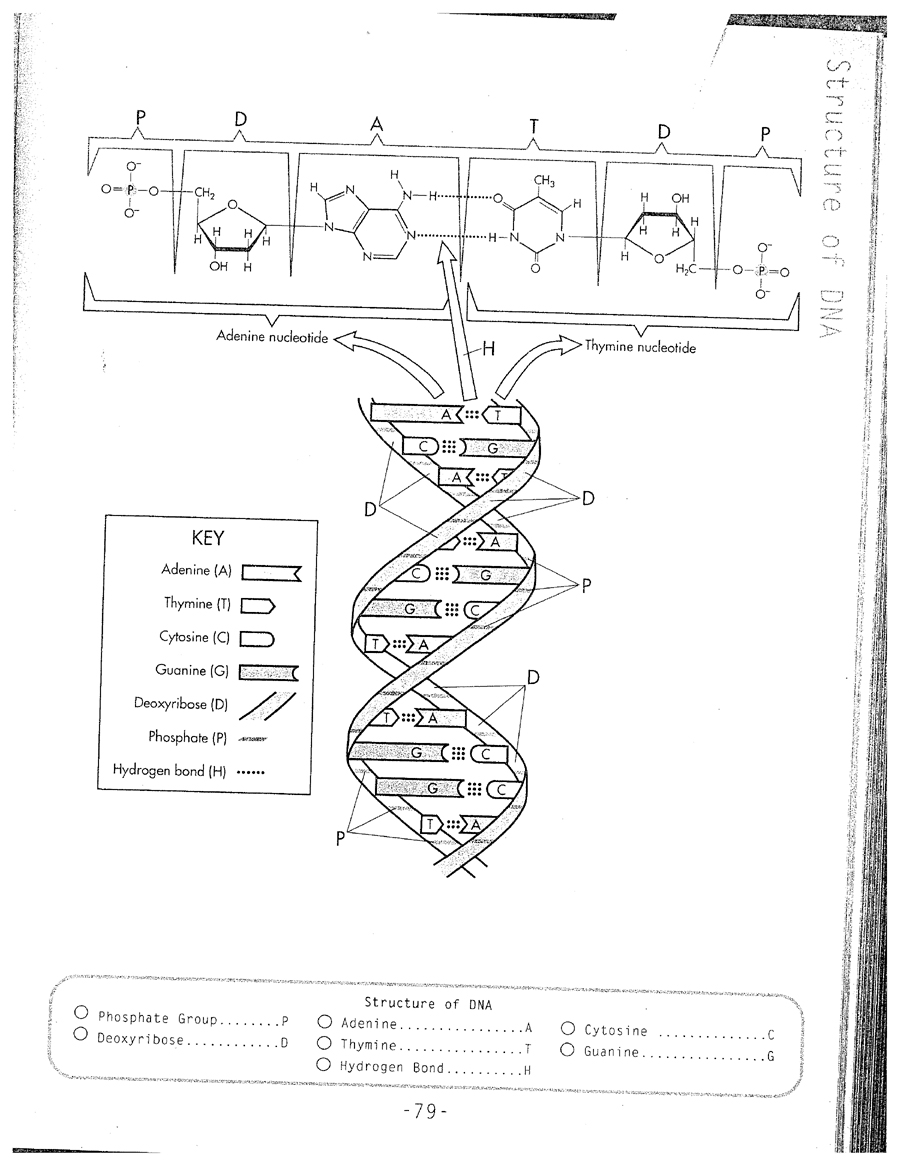
Describe the overall shape of the DNA molecule.
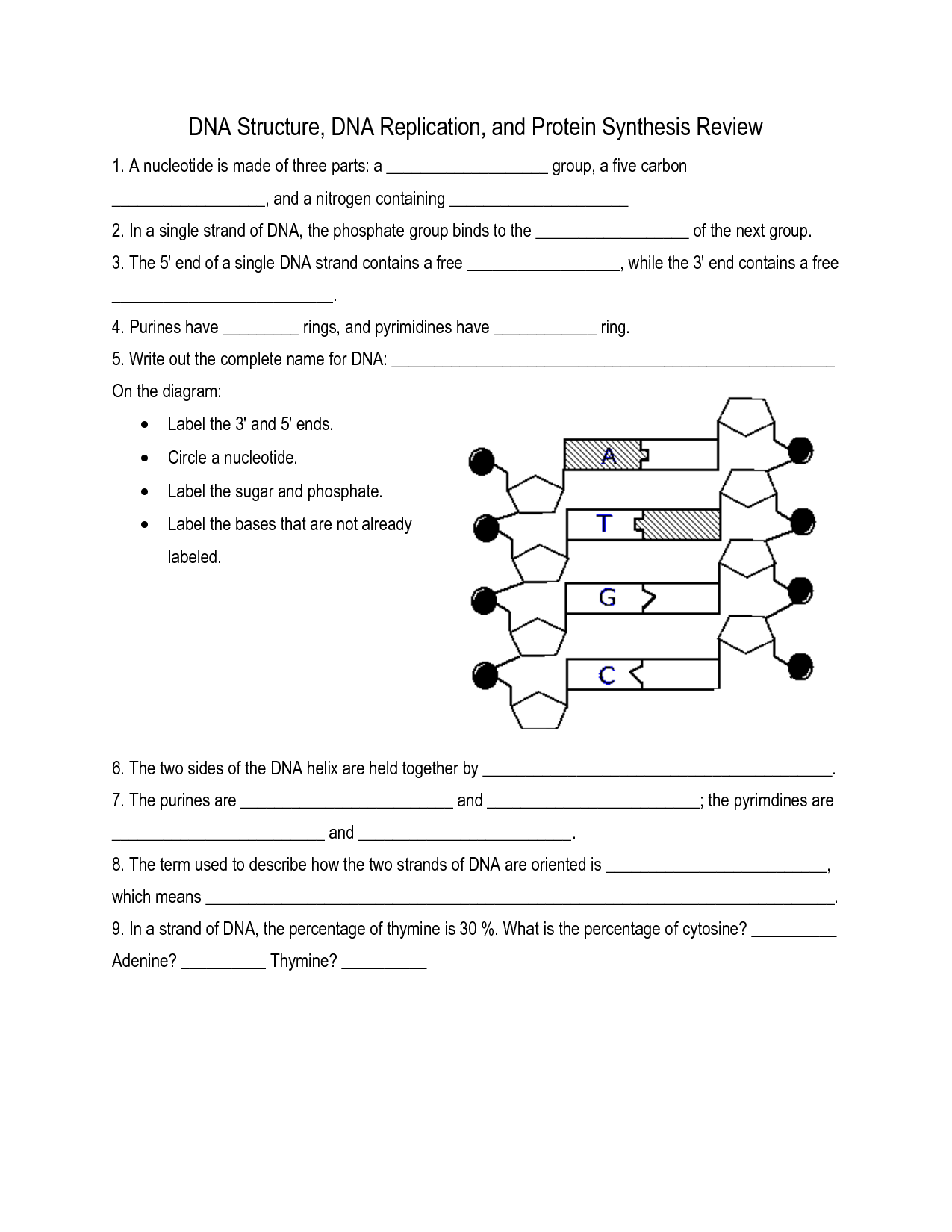
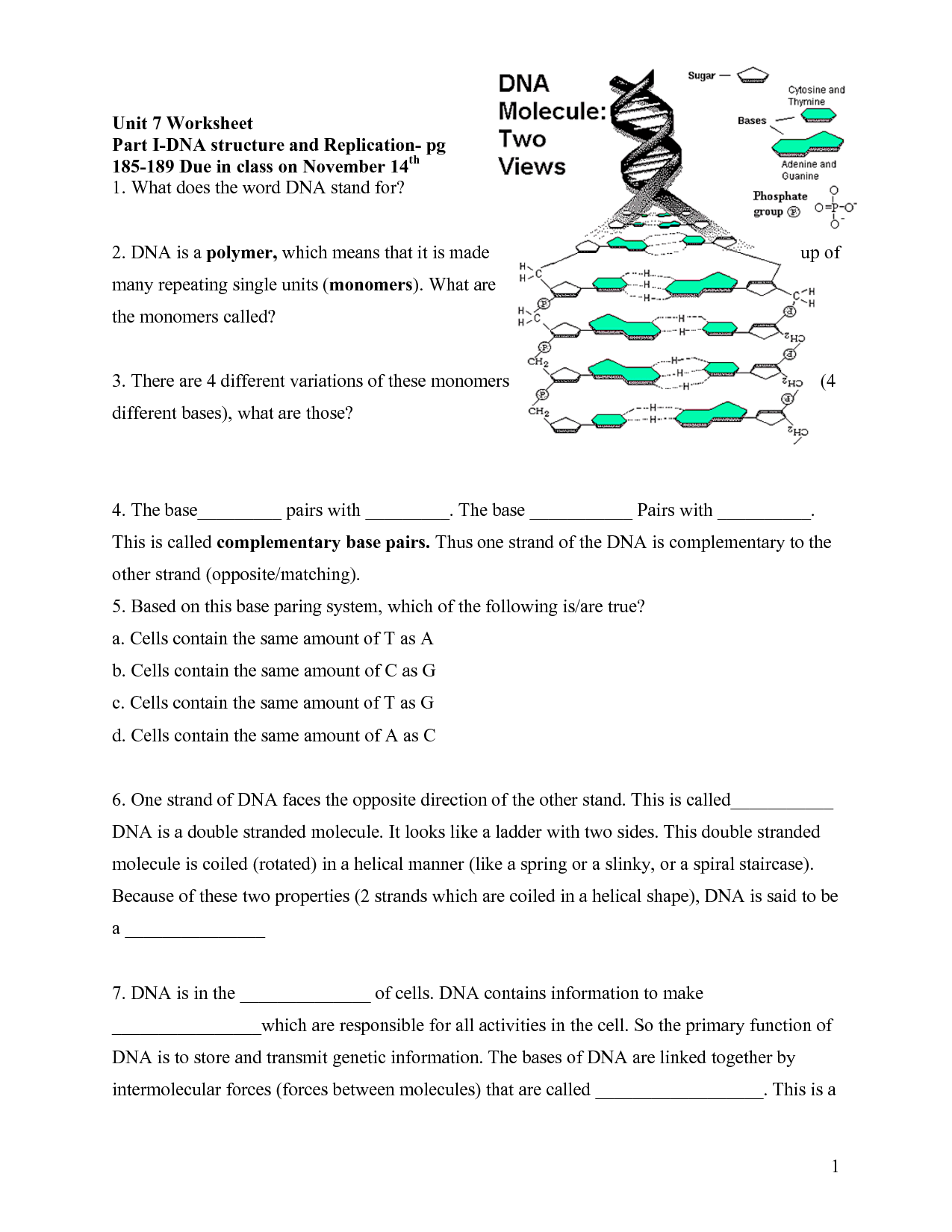
The overall shape of the DNA molecule is a double helix, resembling a twisted ladder. The two strands of the helix run in opposite directions and are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs. This structure allows for the genetic information to be stored and replicated accurately during cell division.
Identify the specific nitrogenous bases found in DNA.
The specific nitrogenous bases found in DNA are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C).
Explain the purpose of DNA replication.
The purpose of DNA replication is to ensure the faithful transmission of genetic information from one cell generation to the next. By creating an identical copy of the DNA molecule, cells can accurately pass on their genetic material during cell division. This process is essential for growth, development, and reproduction in all living organisms, as it allows for the preservation and inheritance of genetic traits and information.
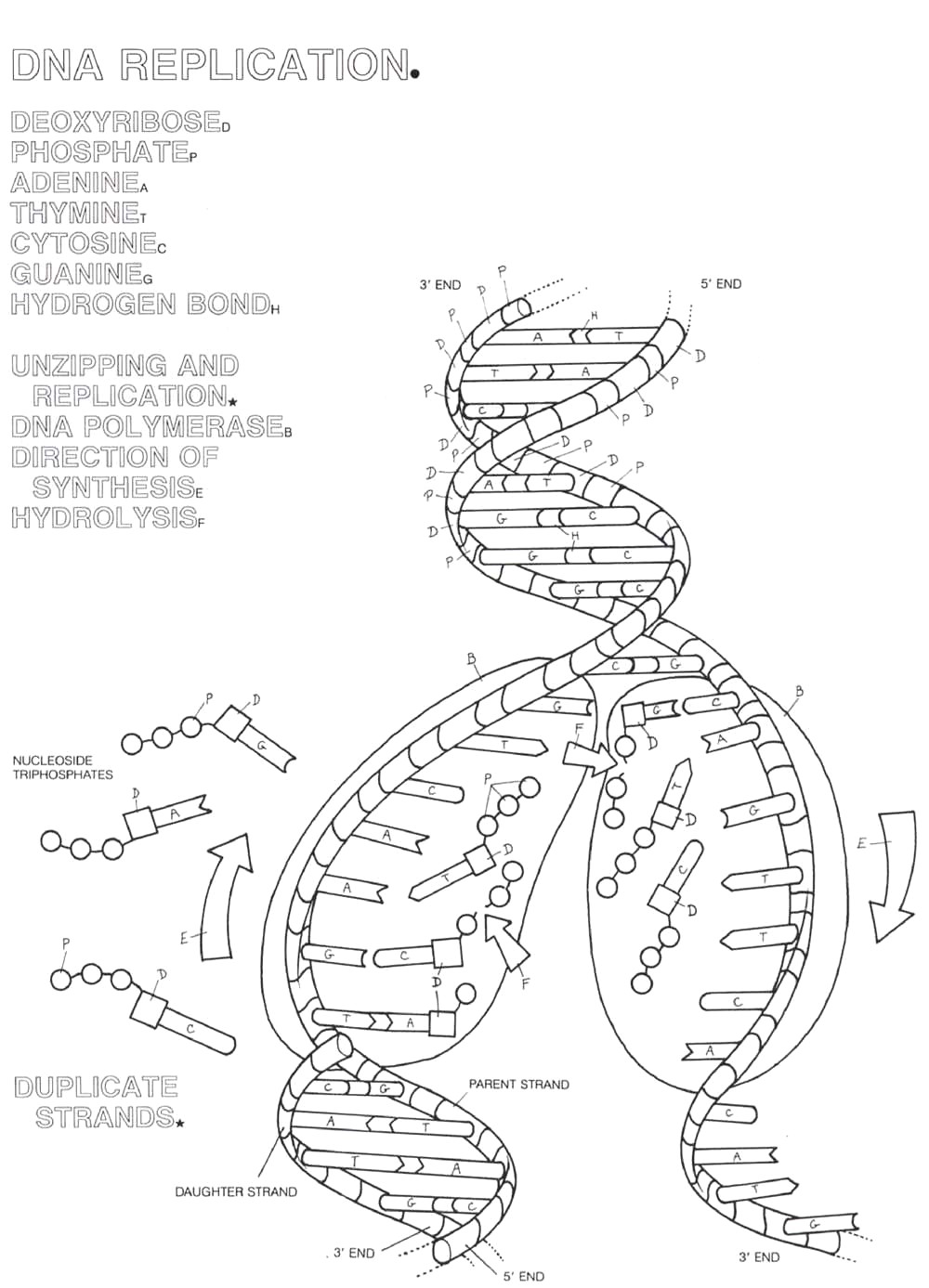
Define the term "replication fork" and its role in DNA replication.
A replication fork is a structure that forms during DNA replication where the DNA double helix unwinds and separates into two strands. It is the site where the DNA polymerase enzyme synthesizes new DNA strands by adding complementary nucleotides to each separated parental strand. This process allows for the accurate replication and duplication of the genetic material in a cell during cell division.
Identify the enzyme responsible for unwinding the DNA double helix.
The enzyme responsible for unwinding the DNA double helix is helicase.
Describe the function of DNA polymerase in DNA replication.
DNA polymerase is an enzyme responsible for the synthesis of new DNA strands during DNA replication. It catalyzes the addition of nucleotides to the growing DNA chain by creating phosphodiester bonds between them. DNA polymerase is essential for accurately copying the genetic information in a cell's DNA during cell division, ensuring that the daughter cells receive an exact replica of the parent cell's genetic material. Additionally, DNA polymerase also possesses proofreading abilities to correct any mistakes that may occur during DNA replication, thereby maintaining the integrity of the genetic information.
What is the purpose of primase in DNA replication?
Primase is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in DNA replication by synthesizing short RNA primers. These primers provide the starting point for DNA polymerase to begin synthesis of the new DNA strand during replication. Without primase, DNA polymerase would not be able to initiate the construction of a new DNA strand, making primase essential for ensuring accurate and efficient DNA replication.
Explain the role of DNA ligase in DNA replication.
DNA ligase is an enzyme crucial for DNA replication as it seals breaks in the phosphodiester backbone of DNA strands by catalyzing the formation of phosphodiester bonds between adjacent nucleotides. This process helps to join Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand and connect the continuous leading strand, ensuring the accurate and complete duplication of the genetic material. DNA ligase plays a fundamental role in the overall fidelity and efficiency of DNA replication by preserving the integrity of the genome and allowing for the faithful transmission of genetic information during cell division.
Describe the direction in which DNA is synthesized during replication.
DNA is synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction during replication. This means that new nucleotides are added to the growing DNA strand at the 3' end of the primer, which provides the template for the synthesis of the new strand. As a result, DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to the 3' end of the existing chain, leading to the continuous synthesis of one DNA strand and the discontinuous synthesis of the other.
How is DNA replication different in eukaryotes compared to prokaryotes?
DNA replication in eukaryotes is more complex and takes place in the nucleus, involving multiple origins of replication and a larger number of proteins. Eukaryotic DNA replication is also bidirectional and discontinuous on the lagging strand due to the presence of Okazaki fragments. In contrast, prokaryotic DNA replication occurs in the cytoplasm, is unidirectional, and is continuous in nature. Additionally, prokaryotes have a circular chromosome, whereas eukaryotes have linear chromosomes, requiring the use of telomeres to prevent loss of genetic material during replication.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments