DNA Double Helix Worksheet
The DNA double helix worksheet is designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the structure and function of DNA for biology students. With clear and concise content, this worksheet offers an engaging way to explore the intricate details of the DNA molecule.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
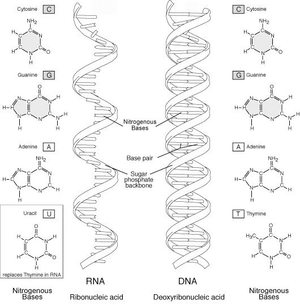
What is the structure of the DNA double helix?
The DNA double helix structure consists of two strands that coil around each other in a twisted ladder-like manner, with the nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine) forming the rungs of the ladder and the sugar-phosphate backbones forming the sides. The strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases (A with T, and G with C), providing stability to the structure.
Which type of bond holds the two strands of DNA together?
The two strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds.
What are the four nitrogenous bases found in DNA?
The four nitrogenous bases found in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T).
How do these bases pair up within the DNA double helix?
In the DNA double helix, adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine through hydrogen bonding. Adenine and thymine form two hydrogen bonds, while cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds, which contributes to the stability of the DNA molecule.
What role do hydrogen bonds play in the stability of the DNA double helix?
Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the stability of the DNA double helix by providing the structural integrity necessary for maintaining the shape of the molecule. These bonds form between the complementary nitrogenous base pairs (adenine-thymine, guanine-cytosine) on the two strands of DNA, helping to hold the helix structure together. This bonding contributes to the overall stability of the DNA molecule and allows for the necessary flexibility for processes such as DNA replication and transcription.
What is the function of DNA in living organisms?
The function of DNA in living organisms is to store and transmit genetic information. DNA contains the instructions needed for an organism to develop, grow, and function properly. It carries the genetic code that determines an organism's traits and characteristics through the process of protein synthesis. In essence, DNA serves as the blueprint for the development and functioning of all living organisms.
How does DNA store and transmit genetic information?
DNA stores and transmits genetic information through its double-helix structure made up of nucleotide base pairs. These base pairs form the genetic code that contains instructions for building and regulating every aspect of an organism. During cell division, the DNA replicates, ensuring that the genetic information is passed on to daughter cells. This process allows for the transmission of traits from one generation to the next, playing a crucial role in inheritance and the diversity of life on Earth.
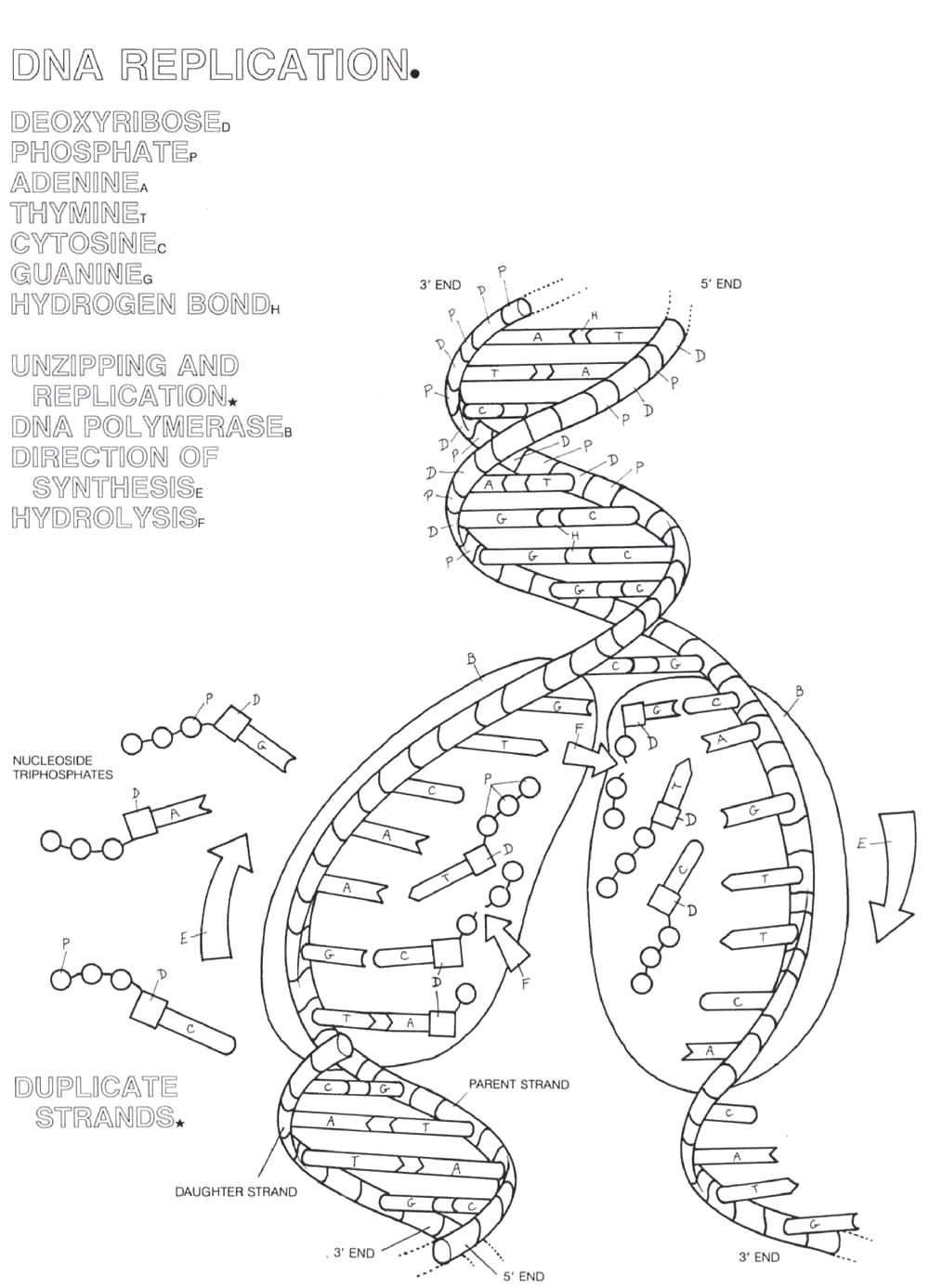
What is the significance of the complementary base pairing in DNA replication?
Complementary base pairing in DNA replication is significant because it ensures the accuracy and fidelity of the process. During replication, the enzyme DNA polymerase uses the complementary base pairing rules (A with T, C with G) to accurately synthesize a new strand of DNA that is identical to the original template. This pairing mechanism helps to minimize errors and mutations, ultimately preserving the genetic information passed on to the daughter cells.
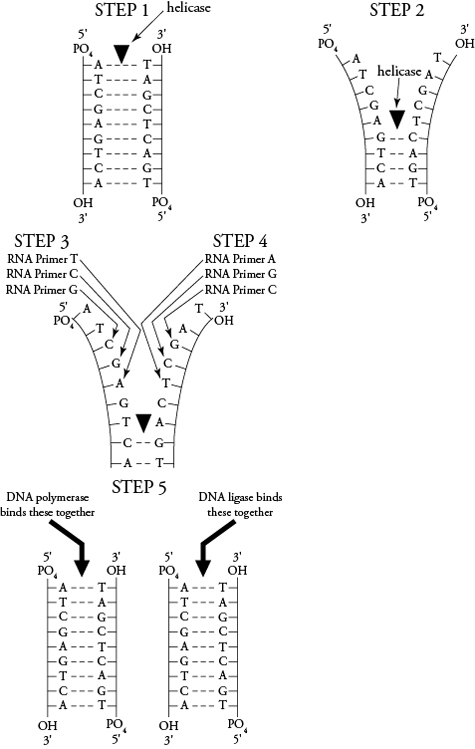
How does the structure of the DNA double helix allow for easy replication?
The structure of the DNA double helix allows for easy replication because the two strands are complementary and run in opposite directions. This means that during replication, each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new strand, with the pairing of complementary nucleotides facilitating accurate replication. The double helix structure also allows for the DNA molecule to unzip easily, exposing the individual nucleotide bases for pairing with their complementary bases, thus ensuring fidelity in the replication process.
Why is the DNA double helix considered a stable molecule?
The DNA double helix is considered a stable molecule because of its structure. The two strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs (adenine and thymine, guanine and cytosine), which run antiparallel to each other. Additionally, the sugar-phosphate backbones on the outside provide structural support and protection for the genetic information within. This intricate arrangement of bonds and structure makes the DNA double helix resistant to damage and allows it to maintain its shape under various environmental conditions, ultimately contributing to its stability as a molecule.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments