Biology Biochemistry Enzymes Worksheet
Biochemistry is a fascinating subject that involves the study of biological molecules and their interactions within living organisms. As a student or enthusiast in the field of biology, having a well-structured and comprehensive worksheet on enzymes can greatly enhance your understanding of this crucial aspect of biochemical processes.
Table of Images 👆
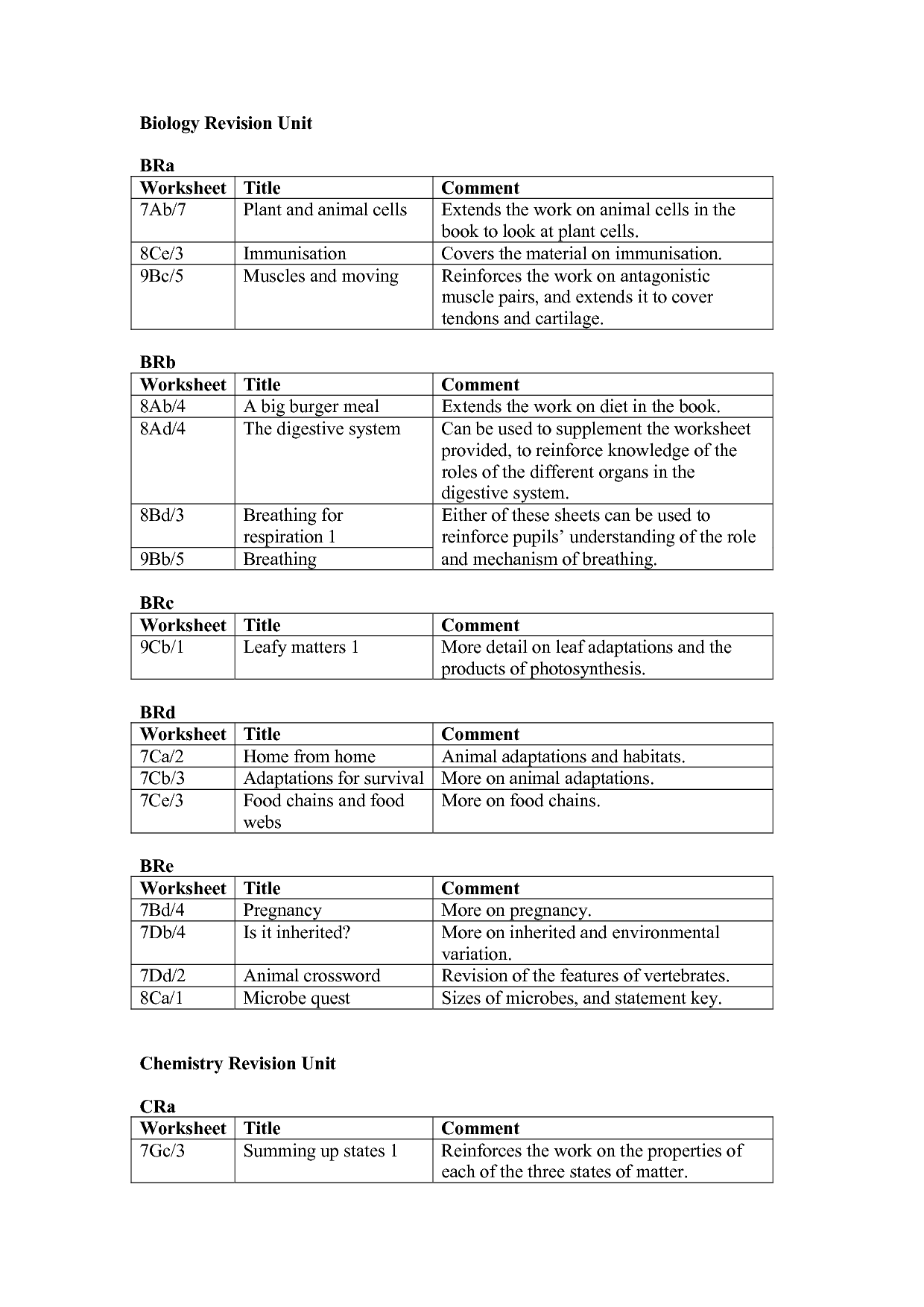
- Biology Plant and Animal Cell Worksheets
- Enzymes Worksheet Answer Key
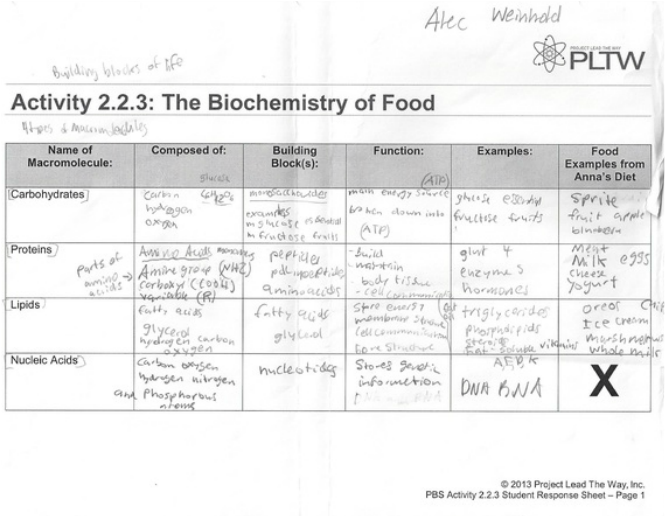
- Macromolecules Chart Answers
- Evolution Review Worksheet Answer Key
- Chemical Reaction Types Worksheet
- Chemistry Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
- Rabbit Population By Season Gizmo Answer Key
- Blank Concept Map Macromolecules
- Enzyme and Substrate Complex
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers
- Biology 310 Worksheet Chapter 4 Worksheet Key Concepts -Protein Structure
- Cellular Respiration Lab Report On
- Macromolecule Worksheet with Answers
More Chemistry Worksheets
What is a biomolecule?
A biomolecule is a molecule that is present in living organisms, such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. These molecules play crucial roles in various biological processes, including metabolism, energy production, and cell structure. They are essential for the functioning and regulation of cells, tissues, and organs within an organism.
Define biochemistry.
Biochemistry is a branch of science that explores the chemical processes and compounds that occur within living organisms. It focuses on understanding the structure and function of biological molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids, as well as the metabolic pathways that regulate energy production, growth, and response to stimuli in cells and organisms.
What are enzymes?
Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions in living organisms by lowering the amount of energy required for the reactions to occur. They are highly specific in their action, targeting specific substrates to catalyze the conversion of these substrates into products. Enzymes play a crucial role in various biological processes, such as metabolism, digestion, and synthesis of molecules within cells.
Explain the structure of an enzyme.
Enzymes are typically proteins that are made up of long chains of amino acids folded into specific three-dimensional shapes. This structure includes an active site where the enzyme interacts with its substrate, allowing for the catalysis of biochemical reactions. The active site contains specific amino acids that are crucial for binding the substrate and facilitating the reaction. Enzymes can also have other structural components, such as cofactors or coenzymes, that aid in their function. Overall, the structure of an enzyme is crucial for its ability to perform its biological role as a catalyst in various cellular processes.
How do enzymes catalyze chemical reactions?
Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur, thus speeding up the reaction. They achieve this by binding to the reactant molecules and bringing them into close proximity, providing an alternative pathway for the reaction to occur. Enzymes can also stabilize the transition state of the reaction, making it easier for the reaction to proceed. This ability to lower the activation energy makes enzyme-catalyzed reactions more efficient and allows for the rapid turnover of substrates into products.
What is an active site?
An active site is a region on an enzyme where the substrate binds and where the chemical reaction catalyzed by the enzyme takes place. This site contains specific amino acid residues that interact with the substrate to facilitate the reaction, ultimately leading to the formation of products.
Describe the process of enzyme-substrate specificity.
Enzyme-substrate specificity refers to the concept that enzymes are highly selective in recognizing and binding only to specific substrates. This specificity is determined by the precise shapes and chemical properties of both the enzyme's active site and the substrate molecule. When a substrate molecule fits into the active site of the enzyme, it forms an enzyme-substrate complex, which allows for the catalysis of a specific biochemical reaction. The specificity of this interaction is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and accuracy of many biological processes.
What factors can affect enzyme activity?
Several factors can affect enzyme activity, including temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and enzyme concentration. Temperature can affect the speed at which enzymes work, with most enzymes having an optimal temperature at which they function best. pH levels can influence the shape and charge of the enzyme, thus affecting its activity. Substrate concentration can impact the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions up to a certain point where all enzyme active sites are saturated. Finally, enzyme concentration can also affect the rate of reaction, with higher enzyme concentrations leading to faster reaction rates until substrate saturation is reached.
What is enzyme regulation and why is it important?
Enzyme regulation is the process by which enzymes are controlled and directed to carry out specific biological functions in response to various internal and external stimuli. This regulation is crucial for maintaining metabolic pathways, controlling biochemical reactions, and ensuring that cellular processes operate efficiently. By regulating enzymes, cells can adapt to changing environments, coordinate metabolic activities, and conserve energy resources, ultimately supporting overall cellular function and homeostasis.
How do inhibitors affect enzyme activity?
Inhibitors can affect enzyme activity by either binding to the active site of the enzyme, hindering substrate binding and catalysis, or by binding to a different location on the enzyme, changing its shape and preventing substrate binding. This can result in a decrease or complete loss of enzyme activity, leading to a reduction in the rate of the catalyzed reaction.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments