Year 9 Science Worksheets Basic
Year 9 Science Worksheets are a valuable resource for students looking to reinforce their understanding of foundational concepts in the subject. These worksheets offer a range of engaging activities that cover key topics such as chemistry, biology, and physics. With clear instructions and thoughtfully designed exercises, these worksheets provide an effective way for students to practice and review what they have learned in class. Whether you are a student seeking extra practice or a teacher looking for supplementary materials, these worksheets are an invaluable tool for enhancing knowledge and comprehension in Year 9 Science.
Table of Images 👆
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
What is the difference between an element and a compound?
An element is a pure substance made up of only one type of atom, such as oxygen or gold, while a compound is a substance made up of two or more different types of atoms chemically bonded together, such as water (H2O) or sodium chloride (NaCl). Elements cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means, whereas compounds can be broken down into their component elements through chemical reactions.
How does energy transfer occur in solid, liquid, and gas?
In solids, energy transfer occurs mainly through vibrations of atoms and electrons. In liquids, energy is transferred through the movement of molecules, conduction, and convection. In gases, energy transfer occurs through collisions of molecules, conduction, convection, and radiation. Overall, energy transfer in all three states involves a combination of these mechanisms depending on the specific properties of the substance and the conditions involved.
What are the three types of heat transfer?
The three types of heat transfer are conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact of particles or materials, convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids (liquids or gases), and radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves.
How does the structure of a plant cell differ from that of an animal cell?
Plant cells have a rigid cell wall mainly composed of cellulose for structural support and protection, while animal cells lack a cell wall. Plant cells also contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis, a large central vacuole for storage and maintaining cell turgidity, and plastids responsible for pigment production. Additionally, plant cells have a rectangular shape due to the presence of a fixed cell wall, whereas animal cells are round or irregular in shape.
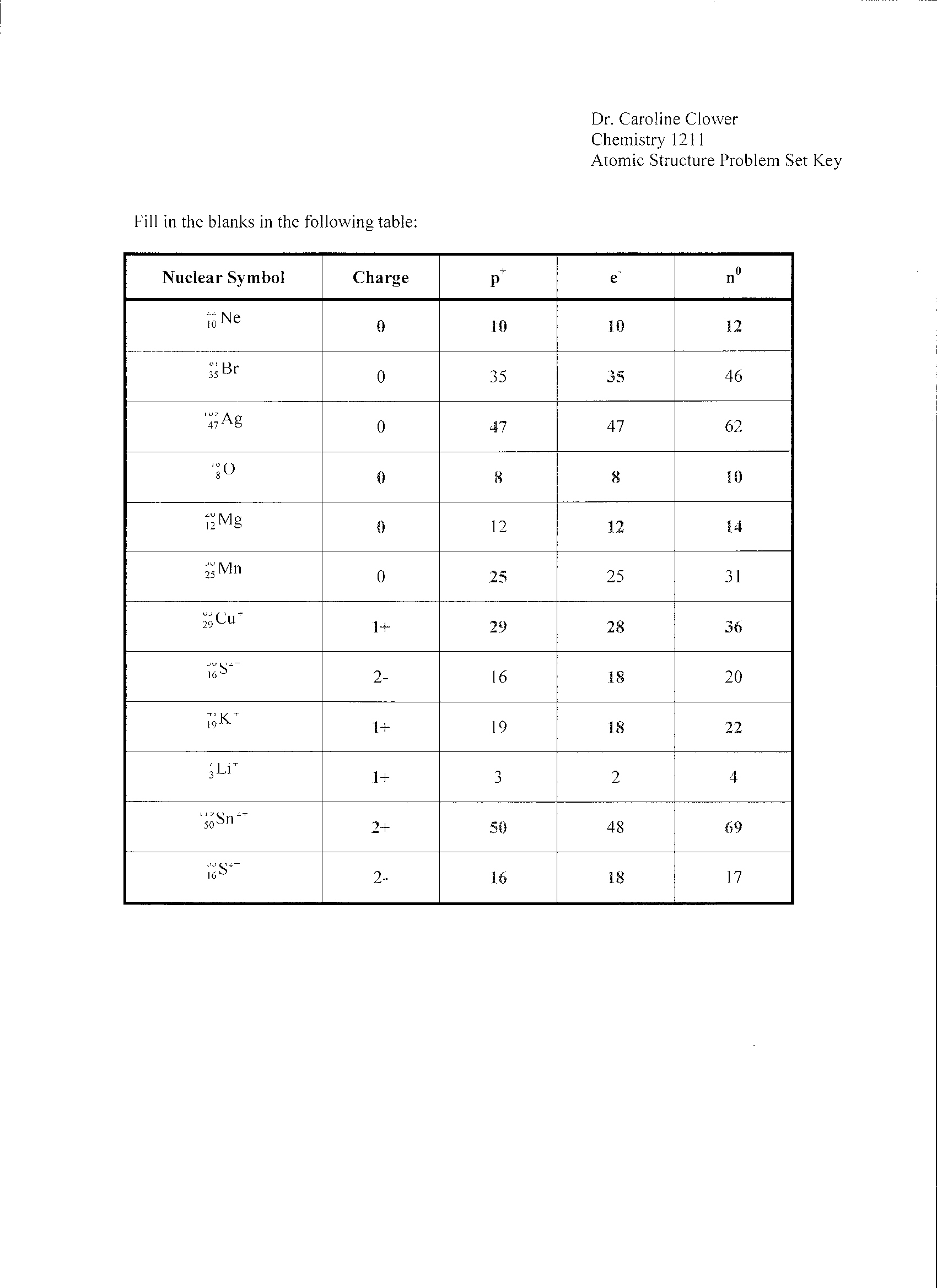
What are the three particles that make up an atom and their charges?
The three particles that make up an atom are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons have a positive charge, electrons have a negative charge, and neutrons have no charge (they are neutral).
What is the difference between a physical and chemical change?
A physical change is a change in the appearance or state of a substance without changing its chemical composition, such as melting, freezing, or dissolving. On the other hand, a chemical change involves the rearrangement of atoms to form one or more new substances with different properties, such as burning wood or rusting of iron.
How does the process of photosynthesis occur in plants?
Photosynthesis in plants occurs in chloroplasts, where sunlight is absorbed by chlorophyll to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. The light-dependent reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes, where light energy is used to split water molecules into oxygen and electrons. The electrons move through the electron transport chain, creating ATP and NADPH. The Calvin cycle then uses these products to fix carbon dioxide into glucose in the stroma of the chloroplast. This process enables plants to produce their own food and release oxygen as a byproduct.
How does the human respiratory system work?
The human respiratory system works by inhaling air through the nose or mouth, which then travels down the trachea into the lungs. In the lungs, the air passes through smaller tubes called bronchi and bronchioles until it reaches the alveoli, where oxygen is transferred into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide is removed. The diaphragm and intercostal muscles help with the process of breathing by expanding and contracting the chest cavity to create changes in air pressure, allowing air to be drawn into and expelled from the lungs. This exchange of gases is essential for the body to obtain oxygen for cellular respiration and to remove waste carbon dioxide.
What factors affect the rate of reaction in a chemical reaction?
Several factors affect the rate of a chemical reaction, such as the nature of the reactants and their concentrations, temperature, pressure, surface area of the reactants, presence of a catalyst, and the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. Additionally, the physical state of the reactants and the presence of any inhibitors or contaminants can also influence the rate of reaction.
How do magnets produce a magnetic field?
Magnets produce a magnetic field due to the alignment of their individual magnetic moments at the atomic level. Within a magnet, the magnetic moments of the atoms point in the same direction, creating a net magnetic field. This alignment results in the magnet having a north and south pole, with magnetic field lines extending from the north pole to the south pole, creating the characteristic magnetic field around the magnet.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments