Work and Power Practice Problems Worksheet
If you find yourself in need of extra practice with work and power concepts, look no further than our comprehensive Work and Power Practice Problems Worksheet. Designed for students learning about these subjects, this worksheet provides a variety of exercises to reinforce understanding and allow for focused skill development.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
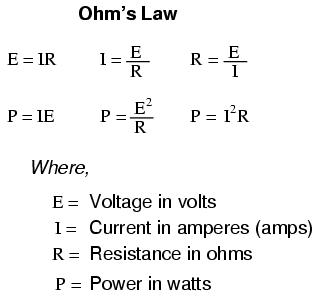
How do you calculate work?
Work can be calculated by multiplying the force applied to an object by the distance over which the force is applied in the direction of the force. The formula for work is: work = force x distance x cos(theta), where theta is the angle between the force and the direction of motion. Work is typically measured in joules (J) in the International System of Units (SI).
What is the SI unit for work?
The SI unit for work is the joule (J).
What is the formula for calculating power?
The formula for calculating power is P = W/t, where P represents power in watts (W), W represents work done in joules (J), and t represents time in seconds (s).
What is the unit for power?
The unit for power is the watt, which is symbolized by the letter "W.
What is the difference between work and power?
Work is the transfer of energy that results in an object being displaced over a distance, while power is the rate at which work is done or the rate at which energy is transferred or converted. In simpler terms, work is a measure of the total energy transferred, while power is a measure of how quickly that energy is transferred.
How can you increase the power output of a machine?
To increase the power output of a machine, you can consider the following options: optimize the machine's design for efficiency, upgrade its components to higher capacity ones, enhance its cooling system to prevent overheating, increase the input energy source such as using a higher voltage power supply, and potentially consider adding supplementary power sources like a motor or engine to work in conjunction with the machine.
How does the weight of an object affect the amount of work done?
The weight of an object does not directly affect the amount of work done. Work is calculated by multiplying the force applied to an object by the distance over which the force is applied. While weight is a measure of the force of gravity acting on an object, it is the distance over which the force is applied that determines the amount of work done. So, the weight of an object may affect the force required to lift it, but the actual work done depends on the force applied over a certain distance.
Can work be negative? Explain.
Yes, work can be negative in the context of physics. In physics, work is defined as the transfer of energy that results in a displacement of an object in the direction of the force applied. When the force and the displacement are in opposite directions, the work done is considered negative. This means that the force is acting in a direction that opposes the displacement of the object, resulting in a negative value for the work done.
How does the angle between the force and displacement affect the amount of work done?
The amount of work done is directly proportional to the component of the force acting in the direction of the displacement. When the force and displacement are in the same direction, the angle between them is zero degrees, resulting in maximum work done. Conversely, if the force is perpendicular to the displacement (angle of 90 degrees), no work is done. Therefore, the angle between the force and displacement affects the work done by determining how much of the force is actually contributing to the displacement.
In what scenarios is no work being done?
No work is being done when there is no force being applied to an object or when the object does not move, even if a force is being applied. Work is only done when a force causes an object to move in the direction of the force being applied. Additionally, if the force being applied is perpendicular to the direction of motion, no work is done as the force does not contribute to the movement of the object.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments