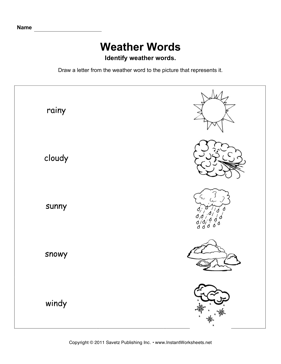
Weather Worksheets Kindergarten Activities
Kindergarten weather worksheets offer young learners engaging activities to explore the fascinating topic of weather. Designed specifically for this age group, these worksheets provide an excellent opportunity for children to become familiar with various weather elements and concepts.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is weather?
Weather refers to the atmospheric conditions, such as temperature, humidity, precipitation, wind, and cloud cover, in a specific location at a particular time. It is the day-to-day changes in the atmosphere that people experience and can impact activities like farming, travel, and outdoor events.
How do we measure temperature?
Temperature can be measured using various instruments such as thermometers, infrared thermometers, thermocouples, and thermal imaging cameras. These instruments detect the heat energy or thermal radiation emitted by an object or environment, converting that information into a numerical value that represents the temperature. The most common unit for measuring temperature is degrees Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F), with scientific researchers often using Kelvin (K).
What is precipitation?
Precipitation is the release of water, in liquid or solid form, from the atmosphere to the earth's surface. This includes rain, snow, sleet, and hail, which are all forms of water that fall from clouds due to condensation of water vapor in the atmosphere.
What are the four seasons?
The four seasons are spring, summer, autumn (fall), and winter. Each season is characterized by distinct weather patterns and changes in temperature, daylight hours, and natural landscapes.
How does the weather change during different seasons?
Weather changes during different seasons due to the tilt of the Earth's axis and its orbit around the sun. In winter, the hemisphere is tilted away from the sun, resulting in colder temperatures and shorter days. In summer, the hemisphere is tilted towards the sun, leading to warmer temperatures and longer days. Spring and autumn are transition periods with milder temperatures as the Earth's axis is neither pointing towards nor away from the sun. These seasonal changes impact factors like temperature, precipitation, and daylight hours.
What are some examples of extreme weather conditions?
Some examples of extreme weather conditions include hurricanes, tornadoes, blizzards, heatwaves, droughts, floods, wildfires, and severe thunderstorms. These extreme weather events can cause significant damage to property, infrastructure, and can also pose threats to human lives and the environment.
How do clouds form?
Clouds form when warm, moist air rises and cools, causing the water vapor in the air to condense into water droplets or ice crystals. These tiny droplets or crystals then gather together to form visible clouds in the sky. The process of cloud formation can also involve factors such as air pressure, temperature, and the presence of particles (like dust or pollution) that serve as nuclei for water droplets to form around.
What is the water cycle?
The water cycle is the continuous process in which water evaporates from bodies of water, turns into water vapor, condenses into clouds, precipitates as rain or snow, and then flows back into bodies of water or infiltrates into the ground to replenish groundwater reserves. This cycle is driven by solar energy and helps to distribute water across the Earth, sustaining life and ecosystems.
How does wind form?
Wind is formed when air moves from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure, creating air circulation patterns. This movement is driven by the uneven heating of the Earth's surface by the sun, causing changes in air temperature and pressure. Additionally, the rotation of the Earth contributes to the horizontal movement of air masses, resulting in the formation of wind patterns on a global scale.
How does the sun affect weather patterns?
The sun plays a critical role in driving Earth's weather patterns through the process of heating the atmosphere and Earth's surface. Solar energy warms the Earth unevenly, creating temperature gradients that lead to the movement of air masses and the formation of wind currents. This energy also evaporates water from oceans, lakes, and land, leading to the formation of clouds and precipitation. Additionally, the sun's heat is responsible for creating atmospheric pressure differences that drive the circulation of air masses, influencing weather patterns such as high and low-pressure systems, storms, and the overall climate of different regions.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments