Weather Worksheets for 5th Grade
Weather worksheets are a valuable resource for 5th grade students to further their understanding of this scientific phenomenon. These worksheets provide an engaging way for students to explore topics such as climate patterns, weather instruments, and the water cycle. By completing these worksheets, students can strengthen their knowledge and develop a solid foundation in the subject of weather.
Table of Images 👆
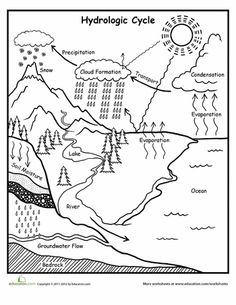
- Earth Water Cycle Worksheets 5th Grade
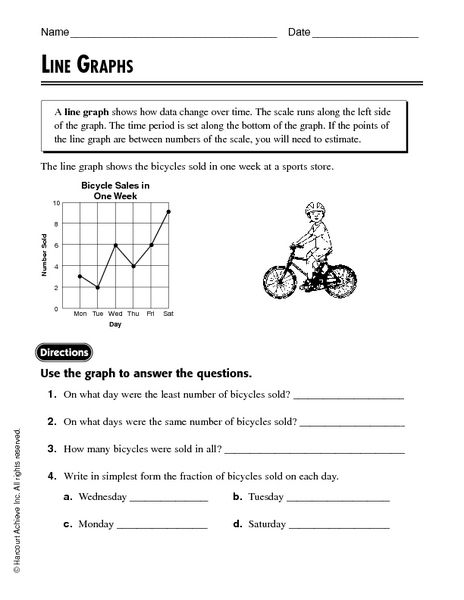
- Line Plot Graph Worksheets 3rd Grade
- States of Matter 6th Grade Science Worksheets
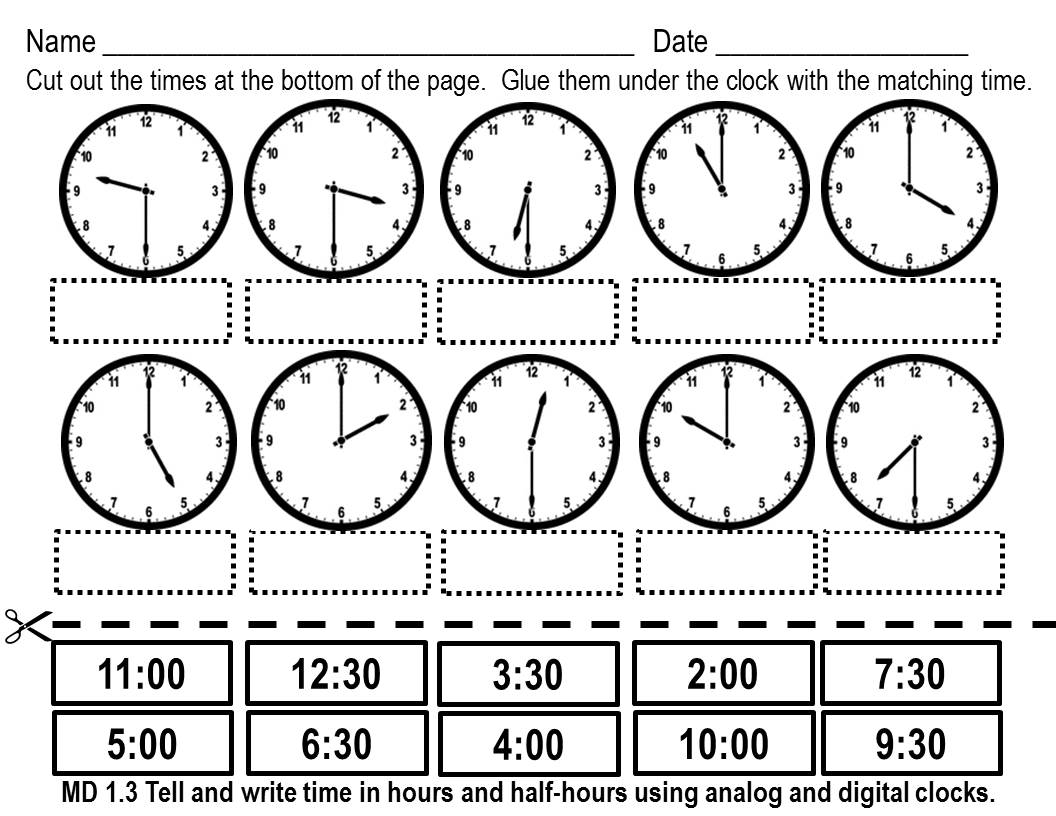
- Cut and Paste Telling Time Worksheets
- 1st Grade Halloween Math Worksheets
- Triangle Meaning
- Draw the Feeling Face Worksheet
- Water Cycle Worksheet Kindergarten
- Printable Preschool Worksheets Number 3
More 5th Grade Worksheets
5th Grade Math Worksheets PrintableMultiplication Worksheets for 5th Grade
Constitution Worksheets for 5th Grade
Coordinates Worksheets 5th Grade
United States Worksheets 5th Grade
Free Division Worksheets for 5th Grade
Poetry Terms 5th Grade Worksheets
5th Grade Social Studies Printable Worksheets
What is weather?
Weather refers to the atmospheric conditions present in a specific place at a specific time, including aspects such as temperature, humidity, precipitation, wind, and atmospheric pressure. It is influenced by factors such as the Earth's rotation, the sun, and air masses, and can vary significantly from day to day and season to season.
How is weather different from climate?
Weather refers to the short-term conditions of the atmosphere in a specific location, such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and precipitation, that change frequently. Climate, on the other hand, refers to the long-term patterns and averages of weather conditions in a particular region over an extended period, typically 30 years or more. While weather can change from day to day or even hour to hour, climate represents the overall picture of a region's typical weather patterns and trends.
What are the four main components of weather?
The four main components of weather are temperature, humidity, precipitation, and wind. These factors work together to determine the atmospheric conditions that we experience on a day-to-day basis.
How are clouds formed?
Clouds are formed when water vapor in the air condenses into tiny water droplets or ice crystals around particles like dust, pollen, or salt in the atmosphere. As more of these droplets or crystals come together, they form a visible mass of suspended water or ice particles that we see as clouds. Changes in temperature, humidity, and air pressure all play a role in the formation and appearance of clouds in the sky.
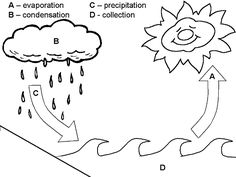
What is the water cycle and how does it affect weather?
The water cycle is the continuous process in which water evaporates from bodies of water, condenses into clouds, falls back to Earth as precipitation, and then flows back into bodies of water. This cycle plays a crucial role in shaping weather patterns by distributing water across the Earth's surface, which influences temperature and humidity levels, cloud formation, and precipitation amounts. The water cycle contributes to the formation of different weather phenomena such as rain, snow, and thunderstorms, impacting local and global weather patterns.
How do air masses and fronts influence weather patterns?
Air masses and fronts play a crucial role in influencing weather patterns. Air masses are large bodies of air with consistent temperature and humidity characteristics that form over a particular region. When different air masses collide at fronts, such as cold fronts, warm fronts, or stationary fronts, it can lead to changes in weather conditions. The interaction between air masses can result in the formation of storms, precipitation, and temperature fluctuations. The movement and interactions of air masses and fronts are key factors in determining the weather patterns in a specific area.
What are the different types of precipitation?
The different types of precipitation are rain, snow, sleet, and hail. Rain is liquid water droplets falling from clouds, snow is ice crystals or snowflakes that fall to the ground, sleet is a mix of rain and snow that partially melts before reaching the ground, and hail is ice pellets that form in strong thunderstorms and fall to the ground.
How does temperature affect weather?
Temperature plays a critical role in shaping weather patterns. Warmer temperatures typically lead to the expansion of air, causing it to rise and create areas of low pressure, which can result in the formation of clouds and precipitation. Cooler temperatures, on the other hand, lead to the contraction of air, creating areas of high pressure that often bring fair weather. Additionally, temperature differences between regions drive the movement of air masses, resulting in the formation of weather systems such as fronts, storms, and wind patterns. In summary, temperature influences many aspects of weather, from cloud formation to wind circulation, ultimately shaping the conditions we experience on a day-to-day basis.
How do meteorologists use weather instruments to collect data?
Meteorologists use a variety of weather instruments such as thermometers, barometers, anemometers, hygrometers, and weather satellites to collect data. These instruments measure parameters like temperature, air pressure, wind speed, humidity, and cloud cover. The data collected by these instruments helps meteorologists forecast weather patterns and make informed predictions about potential weather events such as storms or heatwaves.
How does severe weather, such as hurricanes or tornadoes, form?
Severe weather, like hurricanes and tornadoes, form due to a combination of specific atmospheric conditions. Hurricanes form over warm ocean waters, where low pressure systems develop and feed off the heat and moisture, creating strong winds and rotating clouds. Tornadoes typically develop from supercell thunderstorms, where rotating updrafts create a funnel cloud that descends to the ground. Both types of severe weather require a delicate balance of factors like temperature, humidity, and wind patterns to create the destructive forces that we see.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



















Comments