Weather Fronts Worksheet Activity
Weather fronts are an essential concept to understand for anyone interested in meteorology or wanting to learn more about the weather. A weather front is the boundary between two air masses with different temperatures and humidity levels. In this blog post, we will explore a worksheet activity that focuses on weather fronts, intended for science enthusiasts or students looking to enhance their understanding of meteorological phenomena.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
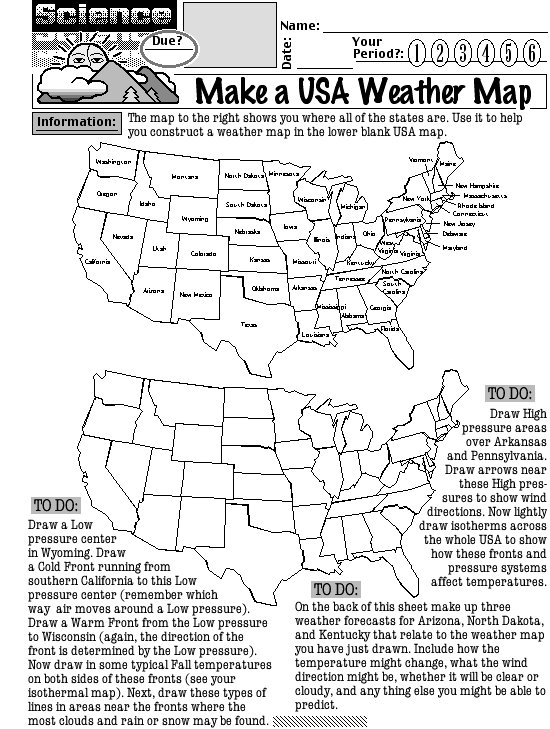
What is a weather front?
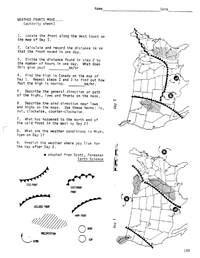
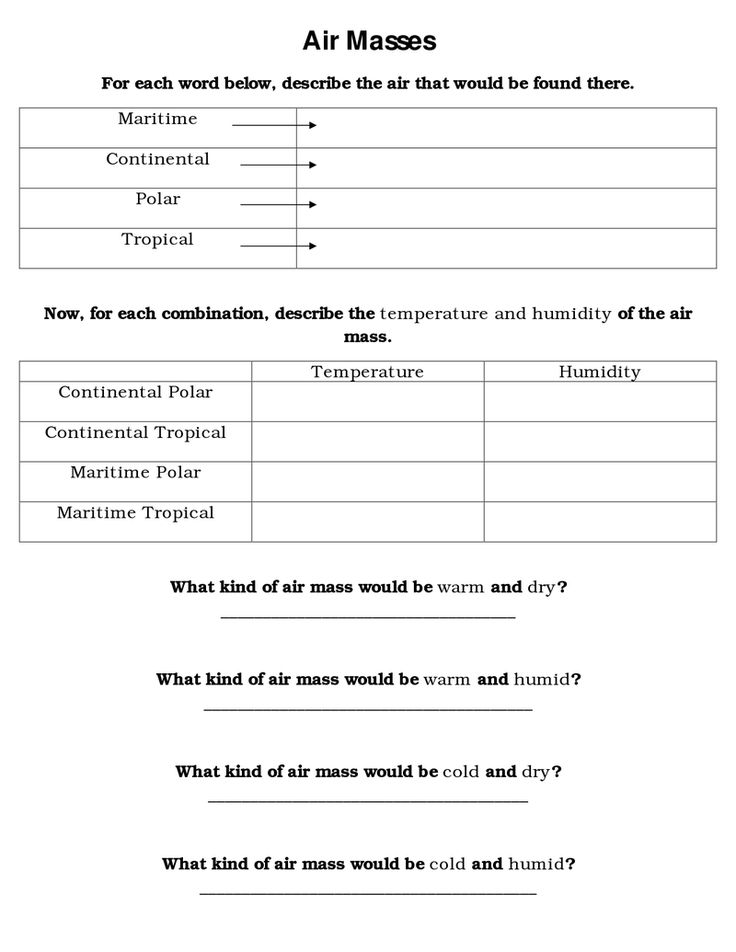
A weather front is a boundary between two air masses with different temperatures and moisture levels. When these air masses meet, they can create changes in weather conditions, such as precipitation, changes in temperature, and shifts in wind direction. There are four main types of weather fronts: cold fronts, warm fronts, stationary fronts, and occluded fronts.
What causes a weather front to form?
A weather front forms when two air masses with different temperatures, humidity levels, and densities meet. The warmer, less dense air rises over the cooler, denser air, creating a boundary between the two air masses known as a front. As the air masses interact, they can lead to changes in weather conditions such as precipitation, thunderstorms, or temperature fluctuations.
How are weather fronts classified?
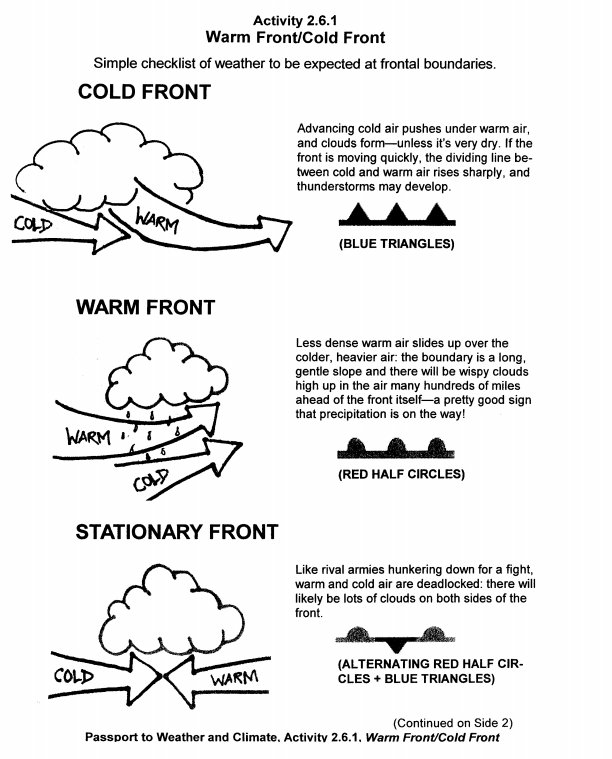
Weather fronts can be classified into four main types based on the temperature and density of air masses involved: cold fronts, warm fronts, stationary fronts, and occluded fronts. Cold fronts occur when a cold air mass advances on a warm air mass, causing the warm air to rise and cool rapidly. Warm fronts form when warm air moves over a cold air mass, creating gradual lifting and generally more gentle weather changes. Stationary fronts occur when neither air mass advances, leading to prolonged periods of cloudy and potentially rainy weather. Occluded fronts happen when a fast-moving cold front overtakes a slower-moving warm front, resulting in complex weather conditions.
Describe the characteristics of a warm front.
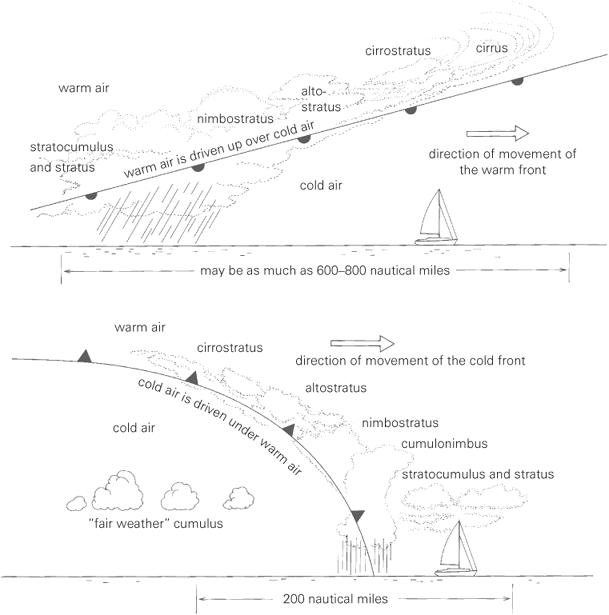
A warm front is a boundary where warm air mass moves over and replaces a colder air mass, leading to warmer temperatures. This front is typically associated with steady precipitation over a broad area, which can last for an extended period. As the warm front approaches, it brings increasing cloud cover and gentle, steady rain that may persist even after the front has passed. Warm fronts often result in a gradual increase in temperature and humidity, creating a more stable and less turbulent weather pattern compared to cold fronts.
Describe the characteristics of a cold front.
A cold front is characterized by the boundary where cold, dense air advances and replaces warmer air. This transition zone is typically associated with abrupt changes in weather conditions, such as plummeting temperatures, gusty winds, and often heavy precipitation. Cloud formations like cumulonimbus clouds, thunderstorms, and sometimes tornadoes can develop along a cold front. Additionally, the pressure drops sharply as the front moves through an area, leading to a rapid change in weather patterns.
What type of weather is typically associated with a warm front?
A warm front is typically associated with warmer temperatures, rising humidity levels, and light precipitation that can last for an extended period. It brings in a gradual transition from colder to milder conditions, often leading to overcast skies and scattered showers or drizzle as the warm air mass overtakes the cooler air mass.
What type of weather is typically associated with a cold front?
A cold front is typically associated with localized storms, heavy rain showers, cooler temperatures, and sometimes strong winds. This weather pattern occurs when a mass of cold air advances and displaces warmer air, leading to a sudden drop in temperature and atmospheric instability, which can contribute to the development of thunderstorms and gusty winds.
Explain why weather fronts often bring changes in temperature and air pressure.
Weather fronts, which are boundaries between air masses with different characteristics, bring changes in temperature and air pressure because of the interactions between these contrasting air masses. When a cold front approaches, colder, denser air pushes under warmer, less dense air, causing the warmer air to rise rapidly. As the warm air cools, condenses, and forms clouds, it can lead to storms and a drop in temperature. On the other hand, a warm front occurs when warmer air replaces cooler air. The warm air gradually rises over the denser cold air, leading to gradual warming and potential precipitation. These interactions between air masses cause changes in temperature and air pressure, resulting in shifts in weather conditions along the front.
How do stationary fronts differ from warm and cold fronts?
Stationary fronts differ from warm and cold fronts in that they do not have a distinct movement or displacement. While warm and cold fronts move and bring changes in weather conditions as they displace, stationary fronts remain nearly stationary and act as a boundary between different air masses with no significant movement. This can lead to prolonged periods of unsettled weather along the front as the opposing air masses interact and create potential for prolonged precipitation events.
Provide an example of a weather event that is commonly associated with a particular type of front.
One example is a thunderstorm associated with a cold front. As a cold front moves in, the denser, cooler air lifts the warm, moist air ahead of it rapidly, leading to the formation of cumulonimbus clouds and potentially severe weather such as heavy rain, thunder, lightning, hail, and gusty winds.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments