Wave Worksheets with Answers
Are you searching for a resource that can help your students grasp the concept of waves in a clear and concise manner? Look no further! With our wave worksheets that come with answers, teaching and learning about waves has never been easier. From identifying the different types of waves to understanding wave properties and behaviors, these worksheets cover a wide range of topics and are designed to engage and challenge students of all levels. Get ready to make waves in your classroom with these invaluable educational resources.
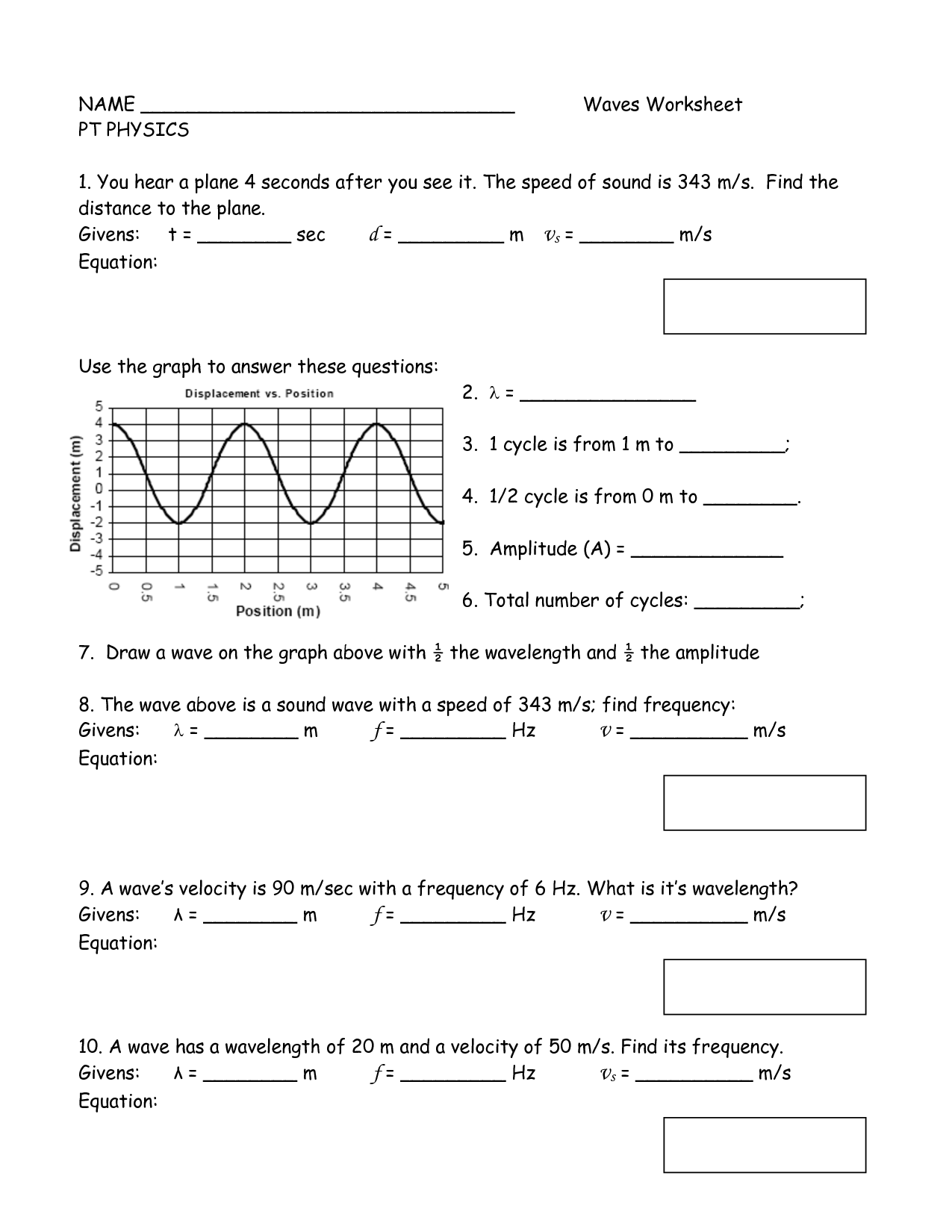
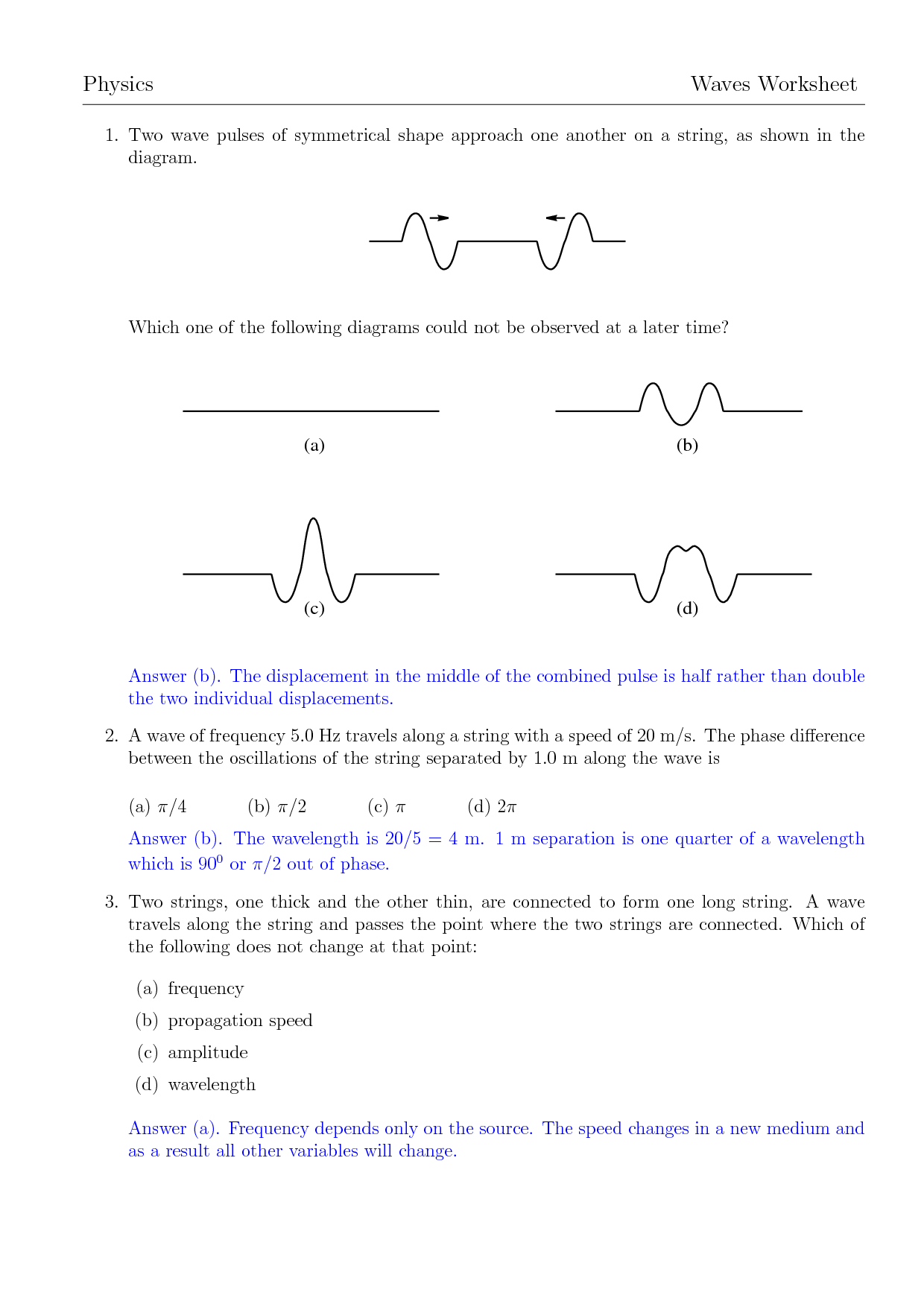
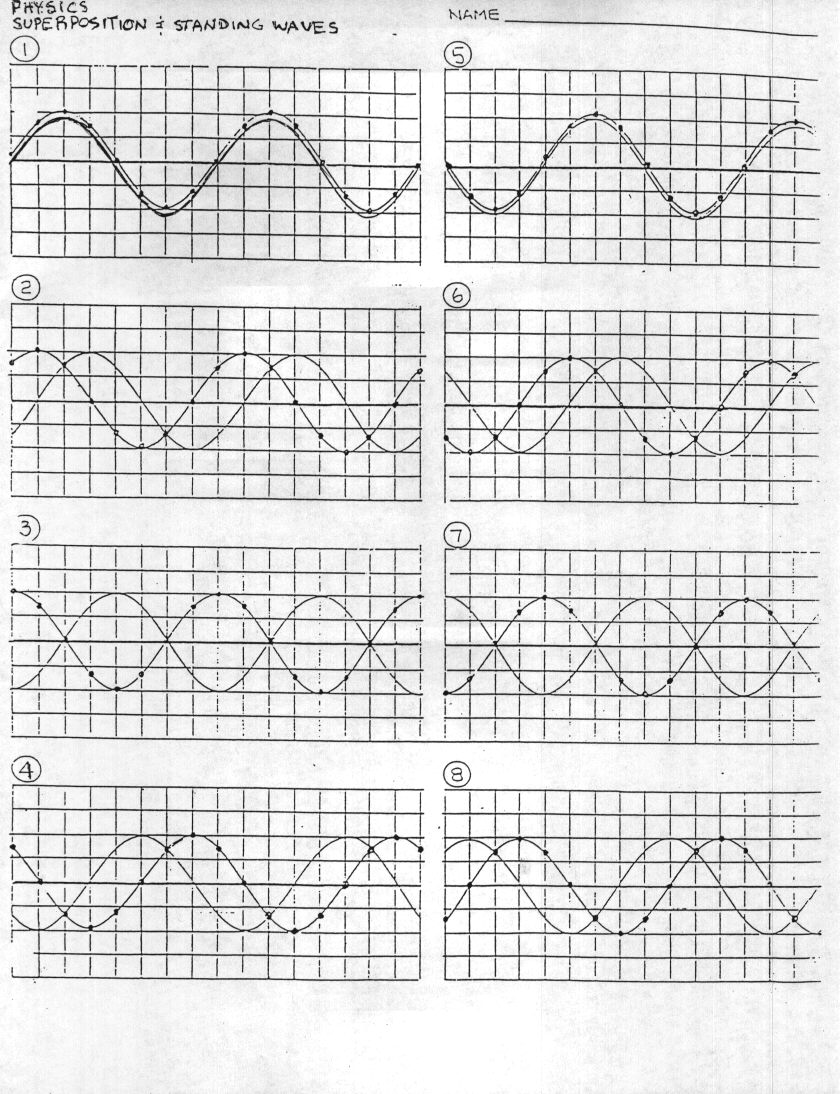
Table of Images 👆
- Sound Wave Worksheet Answer
- Labeling Waves Worksheet Answer Key
- Waves Worksheet Answer Key
- Waves and Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers
- Speed Wavelength Frequency Energy Worksheet Answers
- Wave Properties Worksheet Answers
- Sound Waves Worksheet
- Physics Waves Worksheets
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers
- Standing Waves Worksheet Answers
- Electron Configuration Worksheet Answer Key
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is a wave?
A wave is a disturbance that carries energy through a medium or space without transferring matter. Waves can be categorized as mechanical waves, which require a medium to propagate, like sound waves and water waves, or electromagnetic waves, which can travel through a vacuum, like light and radio waves. Waves exhibit properties such as amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and speed, allowing them to transmit energy over long distances without the physical displacement of material particles.
What is the difference between a transverse and longitudinal wave?
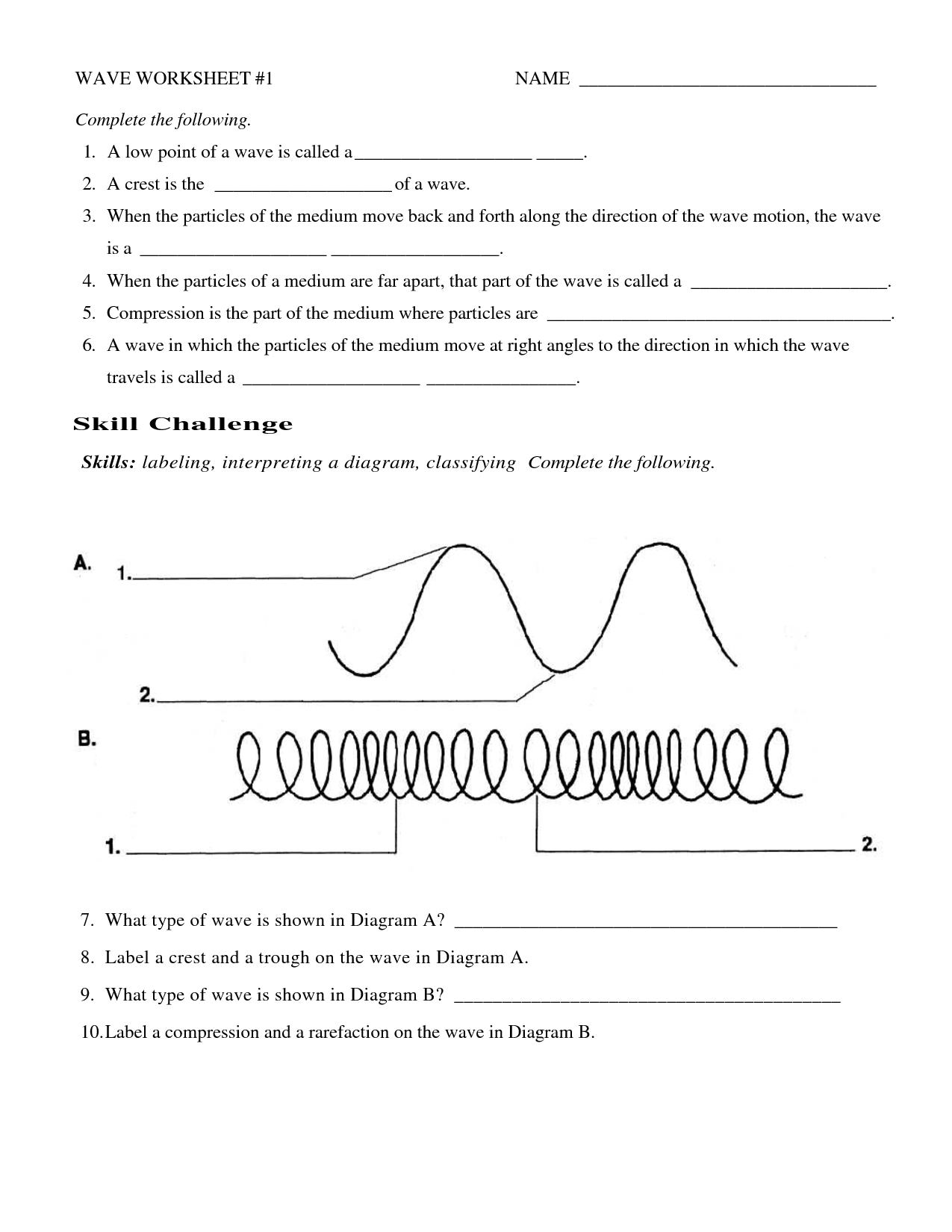
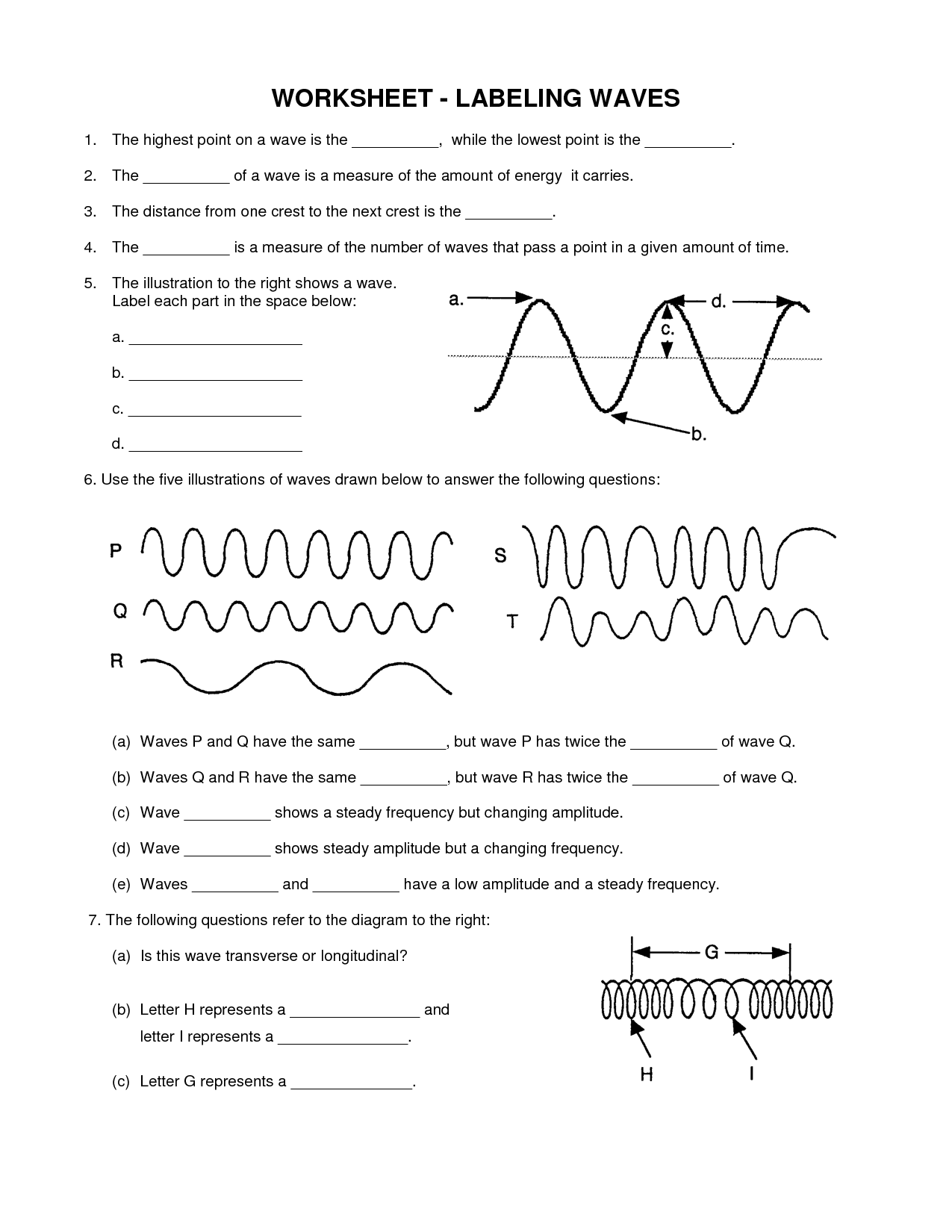
The main difference between a transverse and longitudinal wave lies in the direction of the wave's oscillation in relation to the direction of energy propagation. In a transverse wave, the particles of the medium oscillate perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer, creating crests and troughs. On the other hand, in a longitudinal wave, the particles oscillate parallel to the direction of energy transfer, causing compressions and rarefactions in the medium. Examples of transverse waves include electromagnetic waves and water waves, while examples of longitudinal waves include sound waves.
What are the parts of a wave?
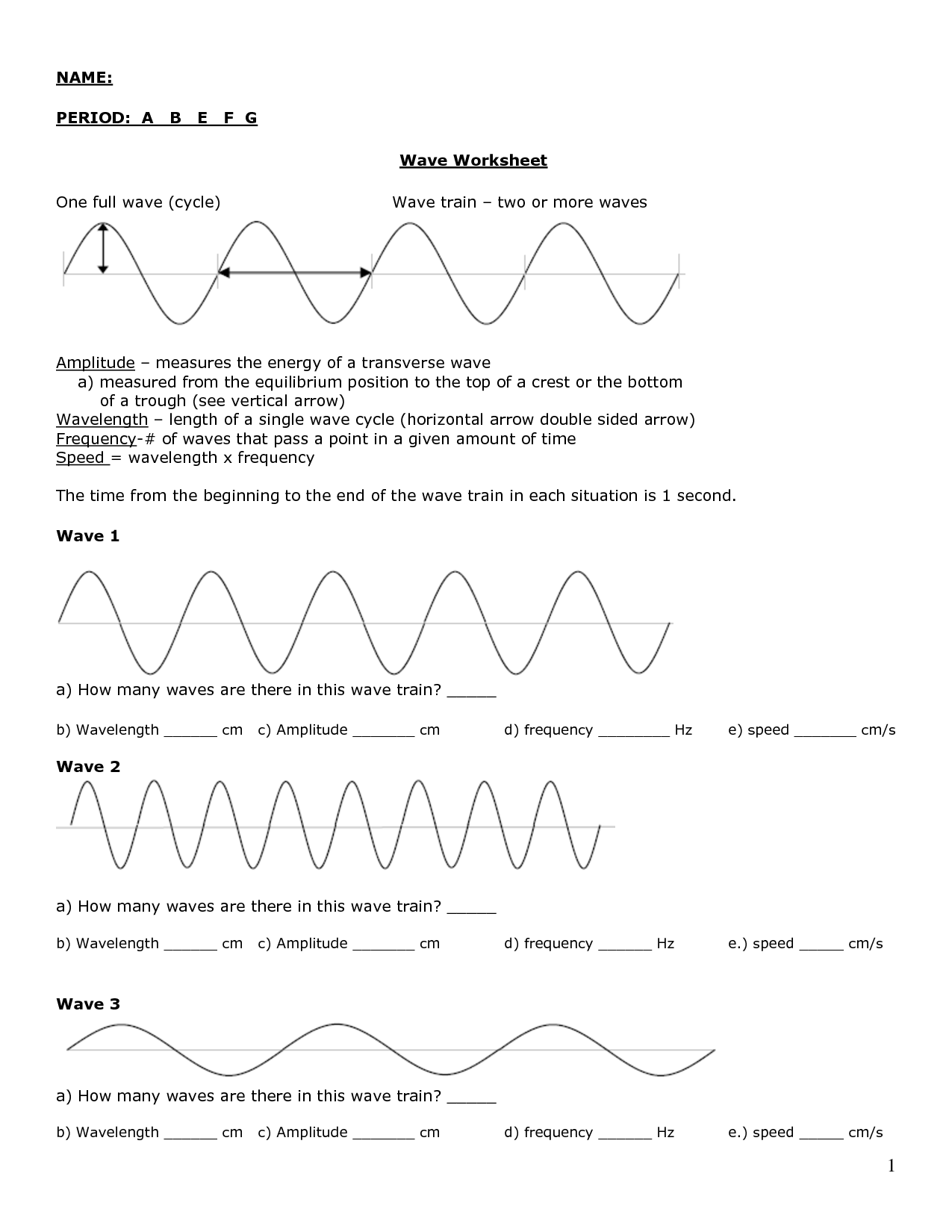
A wave has three main parts: the crest (the highest point of the wave), the trough (the lowest point of the wave), and the wavelength (the distance between two successive crests or troughs). These parts are essential in describing and understanding the behavior of waves in various mediums.
What is amplitude?
Amplitude is the maximum displacement or distance a wave varies from its rest position. It is a measure of the intensity or strength of a wave and is typically used to describe the size or height of a wave in various systems such as sound waves, light waves, and water waves. Increasing the amplitude of a wave generally results in a higher energy and a more intense wave.
What is frequency?
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It can be measured in Hertz (Hz), where one Hertz is equal to one cycle per second. The higher the frequency, the more frequently the event occurs within a given time frame.
What is wavelength?
Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive points of a wave that are in phase, such as the distance from one crest to the next crest or from one trough to the next trough. It is a fundamental characteristic of a wave and is commonly measured in meters or other units of length.
How does the speed of a wave relate to its frequency and wavelength?
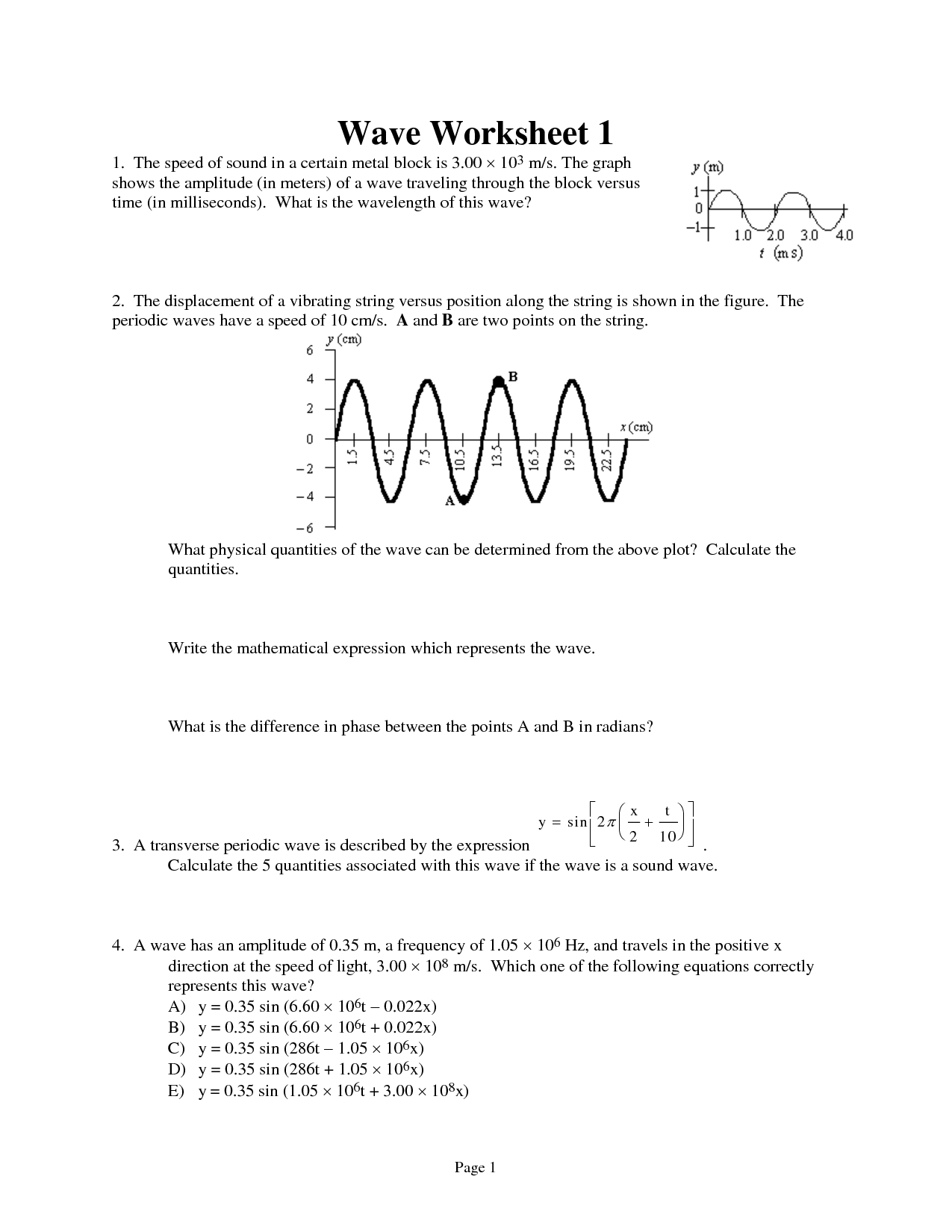
The speed of a wave is directly proportional to its frequency and wavelength. This is described by the equation: speed = frequency x wavelength. This means that as the frequency of a wave increases, its speed will also increase if the wavelength remains constant. Alternatively, if the wavelength increases, the speed of the wave will decrease if the frequency remains constant.
What is the formula for wave speed?
The formula for wave speed is: wave speed (v) = frequency (f) x wavelength (?).
What is reflection of a wave?
The reflection of a wave occurs when a wave encounters a boundary or interface and bounces back in the opposite direction. This phenomenon occurs because the wave cannot pass through the boundary or interface, causing it to reverse its direction of travel. The angle at which the wave reflects off the boundary is equal to the angle at which it approached the boundary, in accordance with the law of reflection. Reflection plays a crucial role in various aspects of wave behavior, including in optics, acoustics, and the behavior of seismic waves.
What is the principle of superposition?
The principle of superposition states that when two or more waves interact, the resulting wave is the sum of the individual waves. In other words, the displacement of a medium caused by two or more waves passing through it is the algebraic sum of the displacements that each individual wave would produce on its own. This principle is commonly used in the field of physics, particularly in the study of wave interactions and interference phenomena.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





























Comments