Wave Worksheet Activity
Worksheets are a valuable tool for educators looking to engage their students in hands-on learning. With a wide range of subjects and topics covered, worksheets provide an organized and structured approach to teaching important skills. Whether you're an elementary school teacher looking for a creative way to explore the concept of waves in science class or a homeschooling parent seeking educational activities that promote critical thinking, our wave worksheet activity is designed to engage and educate learners of all ages.
Table of Images 👆
- Free Printable Cutting Lines
- All About Me Graphic Organizer
- Science Homework Worksheets
- Sound and Light Energy Worksheet
- 4th Grade Science Sound Worksheets
- Wave Speed Equation Worksheet
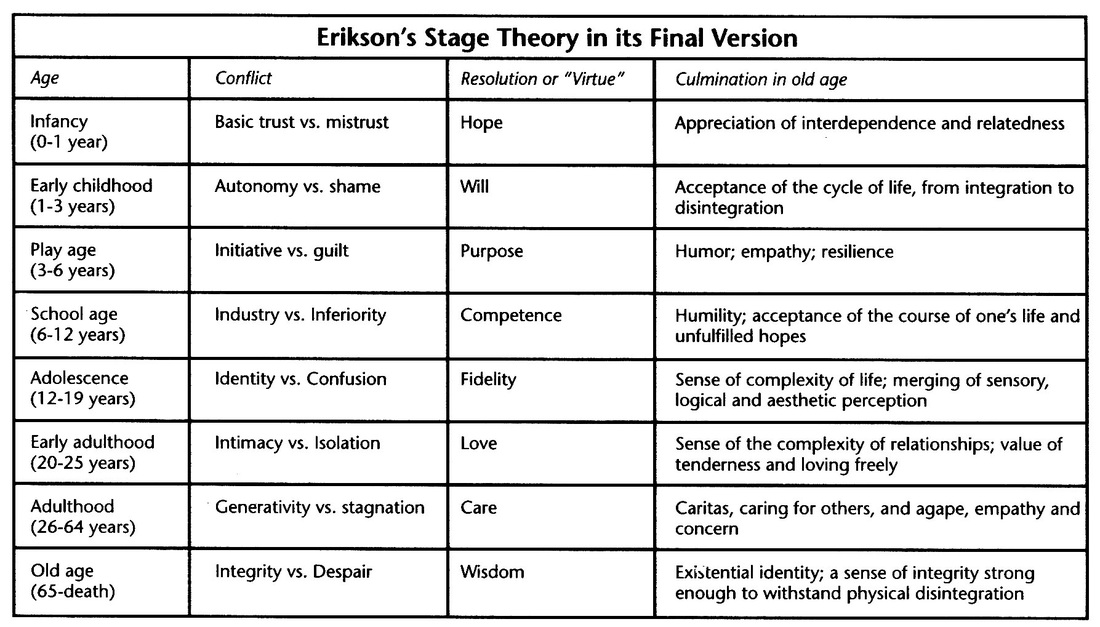
- Erik Eriksons Stages of Development
- Sound and Light Worksheets 4th Grade
- Apple Tree Life Cycle Worksheet
- Mother and Daughter Coloring Pages
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is a wave?
A wave is a form of disturbance or oscillation that transfers energy through a medium or space without permanently displacing the medium itself. Waves can take many forms, such as sound waves, water waves, light waves, and seismic waves, and they exhibit characteristics like frequency, amplitude, wavelength, and speed. Waves play a crucial role in various natural phenomena and technological applications.
What are the two main types of waves?
The two main types of waves are transverse waves and longitudinal waves. Transverse waves occur when particles move perpendicular to the direction of the wave, while longitudinal waves occur when particles move parallel to the direction of the wave.
How does a transverse wave differ from a longitudinal wave?
A transverse wave differs from a longitudinal wave in the direction of particle oscillation and wave propagation. In a transverse wave, particles oscillate perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, creating crests and troughs. In contrast, in a longitudinal wave, particles oscillate parallel to the direction of wave propagation, compressing and expanding in the same direction as the wave.
What is the amplitude of a wave?
The amplitude of a wave is the maximum displacement of a particle in the medium from its equilibrium position as the wave passes through it. It determines the intensity or loudness of the wave for sound waves, the brightness of the wave for light waves, and the strength of the wave for seismic waves, with larger amplitudes corresponding to more intense waves.
How is wavelength defined?
Wavelength is defined as the distance between two corresponding points on a wave, such as the distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs. It is a measurement of the length of one complete cycle of a wave and is typically measured in meters.
Define frequency in relation to waves.
Frequency in relation to waves is the number of complete cycles or vibrations of a wave that occur in a given amount of time, usually measured in hertz (Hz). It represents how many times a wave oscillates or repeats its pattern in one second. A higher frequency corresponds to a shorter wavelength and higher energy waves, while a lower frequency corresponds to a longer wavelength and lower energy waves.
What is the equation for wave speed?
The equation for wave speed is given by v = ?f, where v is the wave speed, ? is the wavelength of the wave, and f is the frequency of the wave.
What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength?
Frequency and wavelength are inversely related to each other. This means that as the frequency of a wave increases, its wavelength decreases, and vice versa. This is described by the formula: speed of light = frequency x wavelength. Therefore, if the frequency of a wave increases, its wavelength decreases, and if the frequency decreases, the wavelength increases.
Explain the concept of wave reflection.
Wave reflection is the phenomenon where waves bounce off a boundary or obstacle instead of passing through it. When a wave encounters a new medium or a surface that does not allow it to pass through, some or all of the wave energy is reflected back in the direction it came from. The angle at which the wave strikes the boundary or obstacle determines the angle at which it is reflected, following the law of reflection. This process plays a significant role in various natural phenomena and practical applications, such as sound waves reflecting off walls or light waves reflecting off mirrors.
How does wave refraction occur?
Wave refraction occurs when waves approach a shoreline at an angle. As the waves enter shallower water, the part of the wave in deeper water moves faster than the part in shallower water. This speed difference causes the wave to bend and change direction, with the part of the wave in shallower water slowing down and the part in deeper water continuing at its original speed. This bending effect is what causes wave refraction, resulting in waves breaking more parallel to the shoreline rather than perpendicular to it.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments