Volcano Worksheets for Students
Are you searching for engaging and informative worksheets on volcanoes? Look no further! Our volcano worksheets are designed to captivate students' attention while providing valuable knowledge on this fascinating geological phenomenon. Whether you are an educator looking to supplement your lessons or a parent seeking educational resources for your child, our volcano worksheets are the perfect tools to enhance understanding and retention.
Table of Images 👆
More Student Worksheets
Middle School Student Goals WorksheetWho I AM Student Worksheet
High School Student Information Worksheet
Student Art Critique Worksheet
Student Getting to Know You Worksheet
Daily Journal Worksheet for Students
Star Student Printable Worksheet
Self-Esteem Worksheets for Students
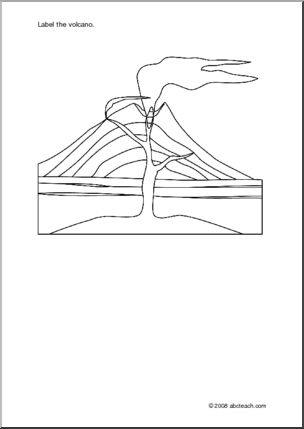
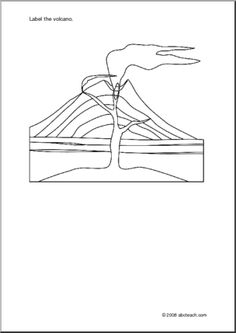
What is a volcano?
A volcano is a geological landform created by the eruption of molten rock, ash, and gases from deep within the Earth's crust. When pressure builds up within a pocket of magma below the surface, it can lead to a volcanic eruption, releasing lava, ash, and volcanic gases onto the Earth's surface. This process can result in the formation of a cone-shaped mountain with a crater at the summit, through which the volcanic material is expelled.
How are volcanoes formed?
Volcanoes are formed through the movement of tectonic plates beneath the Earth's surface. When these plates collide or separate, magma from the mantle can rise to the surface, creating volcanic activity. As the magma erupts through the Earth's crust, it forms a volcano. Over time, repeated eruptions can build up layers of hardened lava and ash, shaping the volcano's characteristic cone structure.
What are the different types of volcanoes?
The main types of volcanoes are stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, and lava dome volcanoes. Stratovolcanoes, also known as composite volcanoes, are tall and steep with explosive eruptions. Shield volcanoes are broad with gentle slopes, formed by low-viscosity lava flows. Cinder cone volcanoes are small and made of pyroclastic debris, resulting in short-lived eruptions. Lava dome volcanoes have viscous lava that piles up near the vent, often leading to explosive eruptions.
What is the Ring of Fire?
The Ring of Fire is a horseshoe-shaped area in the Pacific Ocean basin where a large number of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur due to the movement of tectonic plates. This region is known for its high seismic and volcanic activity, with the majority of the world's earthquakes and volcanic eruptions happening along this belt, which extends from the coasts of South America, North America, Asia, and Oceania.
How do volcanic eruptions occur?
Volcanic eruptions occur when magma from within the Earth's mantle rises to the surface, leading to pressure build-up in magma chambers beneath the volcano. As the pressure becomes too great, it causes the rock surrounding the magma to fracture and break, allowing the magma to escape in the form of lava, ash, and gases. This release of pressure results in explosive eruptions, spewing molten rock and debris into the air and shaping the landscape around the volcano.
What are the main hazards associated with volcanic eruptions?
The main hazards associated with volcanic eruptions include pyroclastic flows (fast-moving currents of hot gas and volcanic debris), lahars (mudflows of volcanic material mixed with water), ash fall (fine particles that can disrupt transportation and pose respiratory health risks), lava flows (destroying infrastructure and potentially harming nearby communities), and volcanic gases (such as sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide, which can be harmful to health and the environment). Additionally, volcanic eruptions can trigger secondary hazards like landslides, tsunamis, and earthquakes.
How do volcanologists monitor and predict volcanic activity?
Volcanologists monitor and predict volcanic activity using various tools and techniques such as seismometers to detect earthquakes, gas sensors to measure gas emissions, satellite imagery to track ground deformation, and thermal cameras to monitor changes in temperature. By analyzing data collected from these instruments, along with studying historical activity and geological features, volcanologists can assess the level of risk and make predictions about potential eruptions, helping to mitigate hazards and protect surrounding communities.
What is volcanic ash and how does it impact the environment?
Volcanic ash consists of tiny, glass-like particles created during volcanic eruptions. When ash is released into the atmosphere, it can have significant impacts on the environment, including reduced air quality, disruptions to ecosystems, and damage to agriculture. Ash can also pose health risks to humans and animals through respiratory issues and skin irritations. Additionally, when ash settles on land and water surfaces, it can smother vegetation, contaminate water sources, and disrupt transportation systems.
How do volcanoes affect climate change?
Volcanoes can both cool and warm the Earth's climate. Large volcanic eruptions can release sulfur dioxide and ash into the atmosphere, which can block sunlight and lower temperatures, leading to short-term cooling effects. However, the release of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases during eruptions can contribute to long-term global warming. Overall, the impact of volcanoes on climate change depends on the type and scale of the eruption.
What are some famous volcanoes around the world?
Some famous volcanoes around the world include Mount Vesuvius in Italy, Mount Etna in Italy, Mount Fuji in Japan, Mount St. Helens in the USA, Krakatoa in Indonesia, and Mauna Loa in Hawaii, USA. These volcanoes are known for their historical eruptions, geological significance, and iconic profiles on the global landscape.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments