Unit Circle Worksheet
The unit circle worksheet is a valuable resource for students studying trigonometry and calculus. Designed to enhance understanding and mastery of the unit circle, this worksheet provides an organized and comprehensive approach to tackling this important mathematical concept. By focusing on entities and subjects within the unit circle, students can thoroughly grasp the relationships between angles and their corresponding trigonometric functions.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is a unit circle?
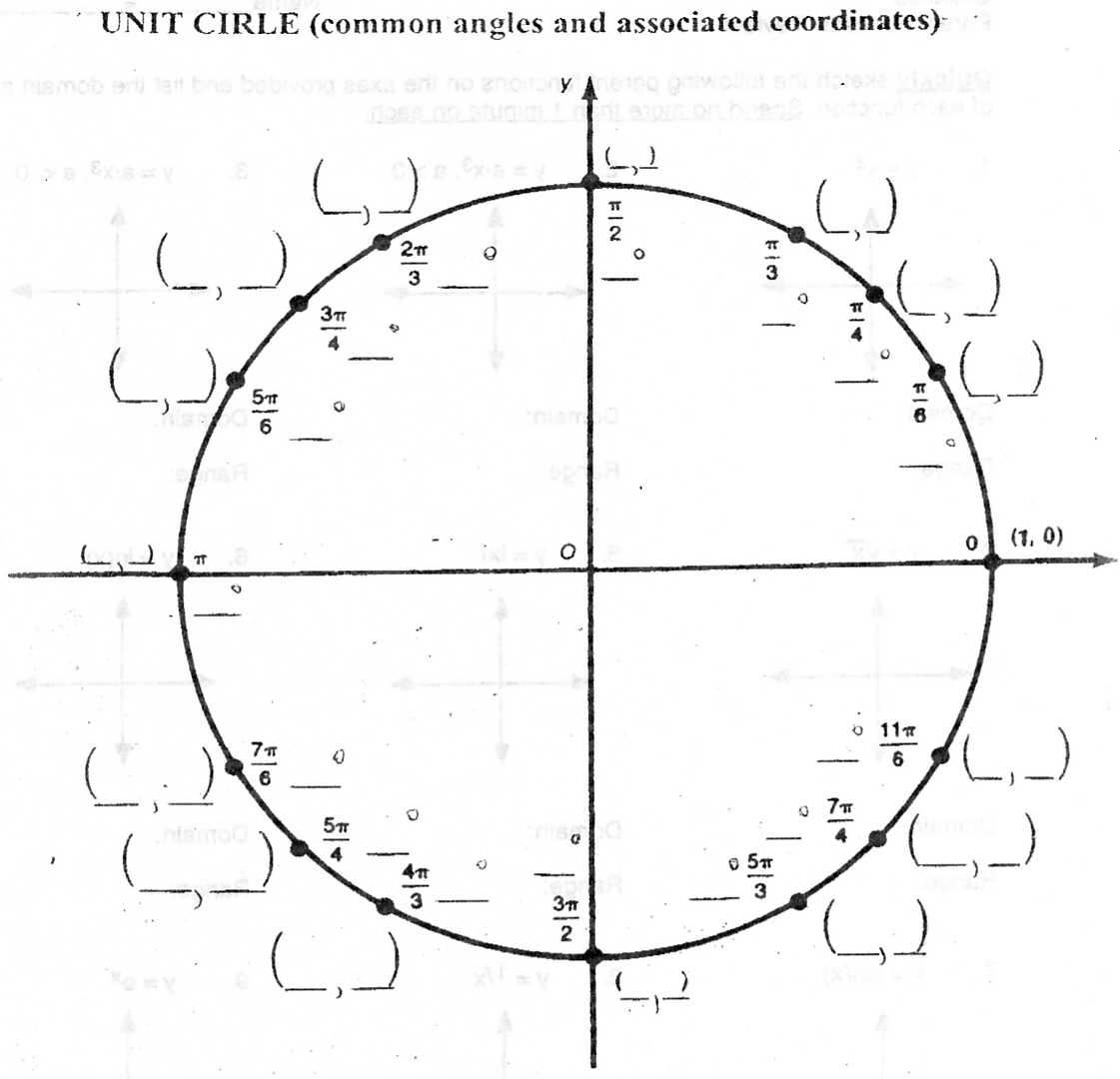
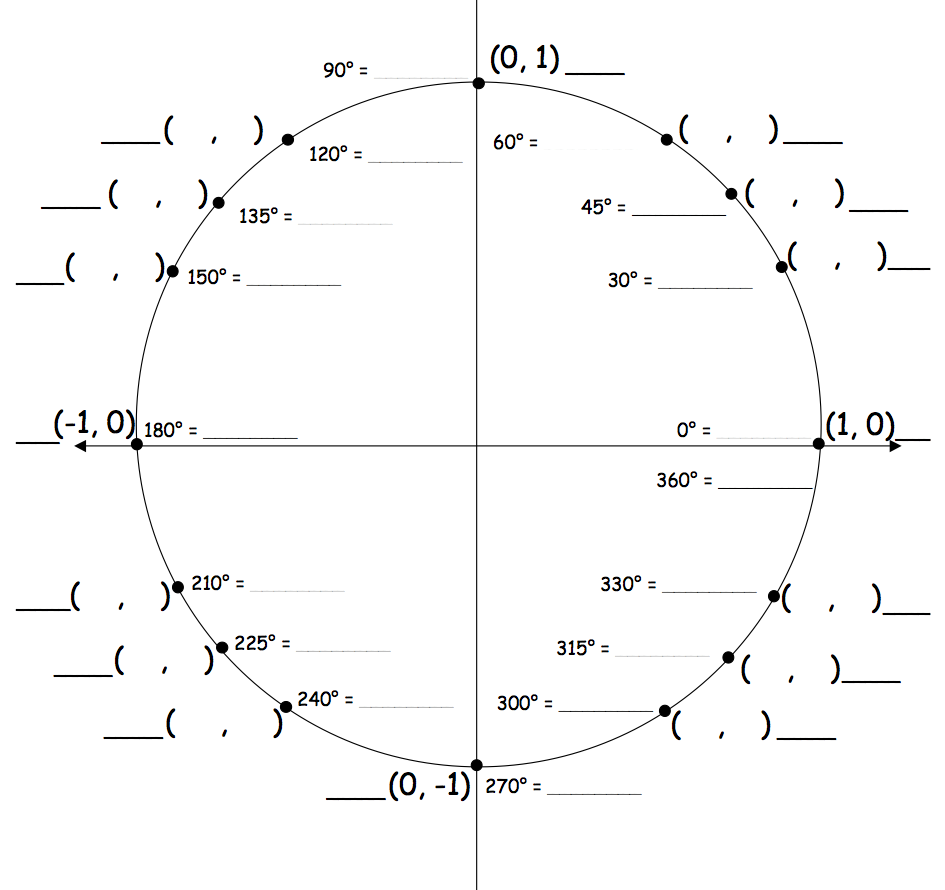
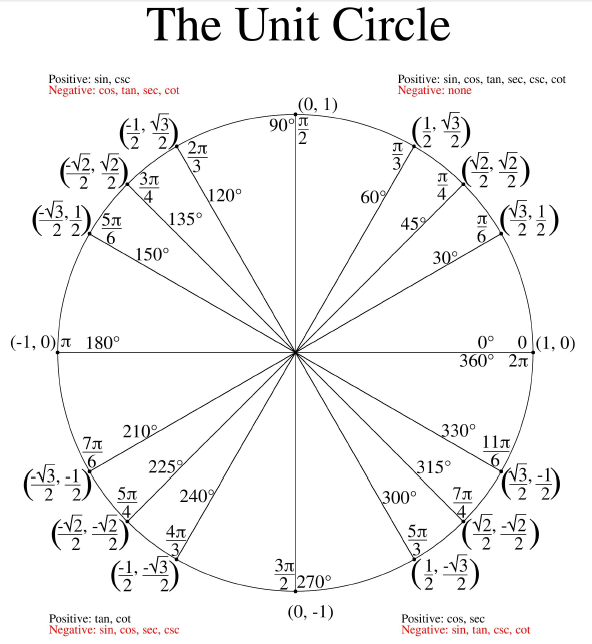
A unit circle is a circle with a radius of 1 unit, centered at the origin of a coordinate system. It is commonly used in mathematics, particularly in trigonometry, to represent the values of trigonometric functions at various angles. The unit circle is a fundamental tool for understanding and solving problems involving angles, triangles, and periodic functions.
How is the unit circle divided into quadrants?
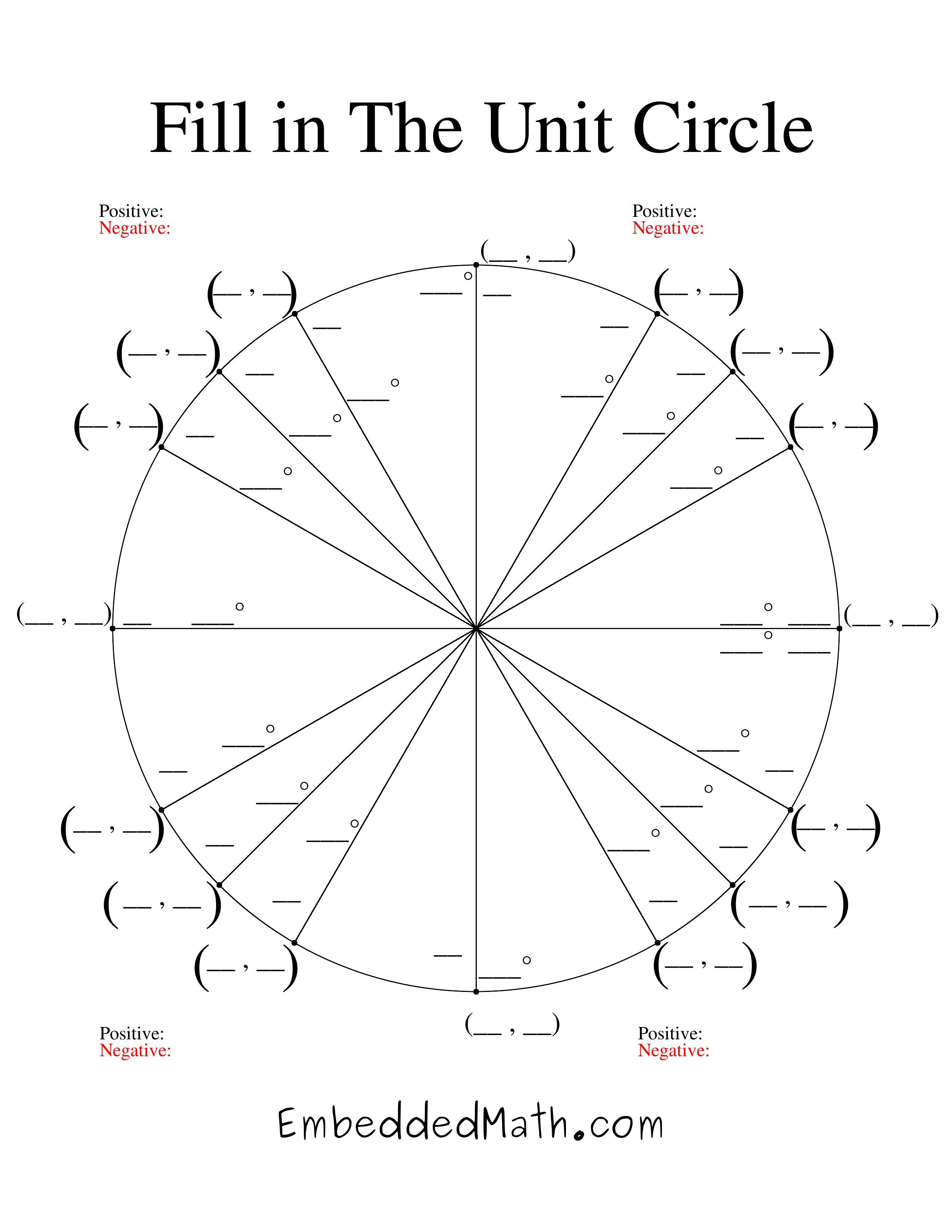
The unit circle is divided into four quadrants, starting from the positive x-axis and moving counterclockwise. The first quadrant is in the top right with positive values for both x and y coordinates. The second quadrant is in the top left with negative x values and positive y values. The third quadrant is in the bottom left with negative values for both x and y coordinates. The fourth quadrant is in the bottom right with positive x values and negative y values.
Explain the concept of radians on the unit circle.
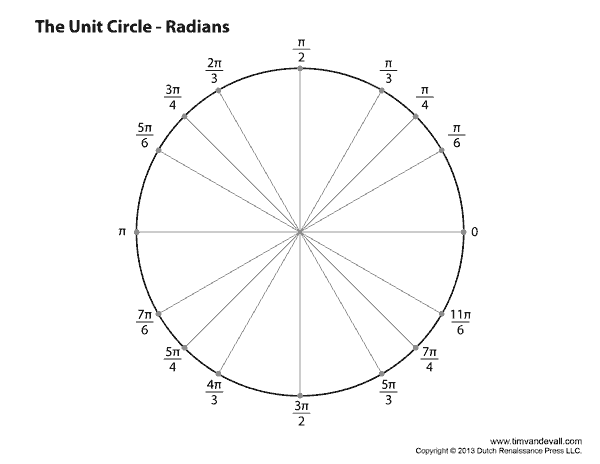
Radian is a unit of angular measurement used in mathematics and physics to specify angles. It is defined based on the radius of a circle. One radian is the angle subtended when the arc length on the unit circle is equal to its radius. This means that an angle of 1 radian corresponds to an arc length equal to the radius of the circle. Radians offer a more natural and consistent way of measuring angles compared to degrees since they directly relate to the geometry of the circle. The unit circle is a circle with a radius of 1, making it a convenient tool for measuring angles in radians.
What is the purpose of labeling the angles on the unit circle?
Labeling the angles on the unit circle serves the purpose of easily identifying and measuring the values of trigonometric functions such as sine, cosine, and tangent for specific angles. It provides a convenient way to visualize and understand the relationship between angles and the coordinates of points on the unit circle, aiding in calculations and problem-solving in trigonometry.
How can you find the coordinates of a point on the unit circle?
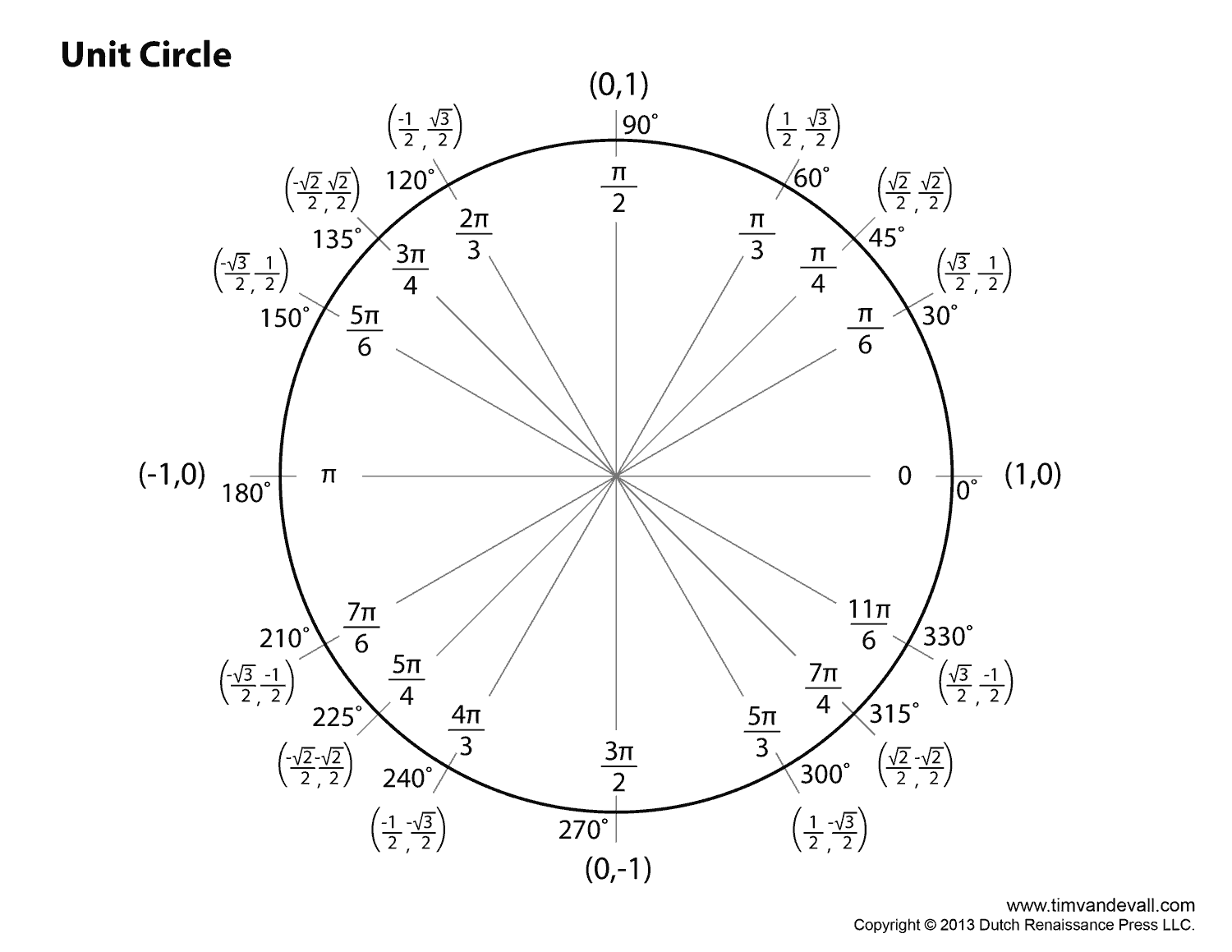
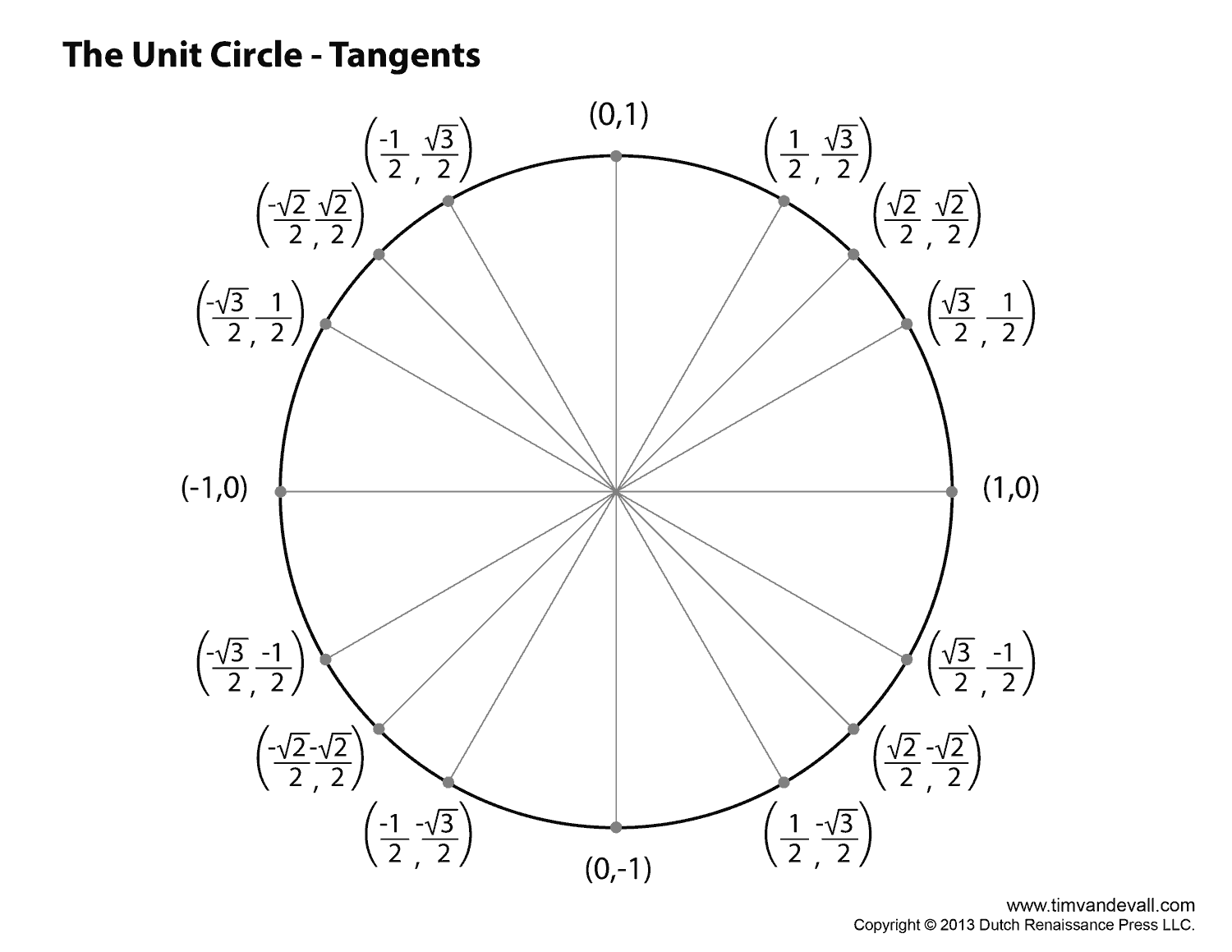
To find the coordinates of a point on the unit circle, you can use trigonometric functions sine and cosine. For a point at an angle ? on the unit circle, the x-coordinate is cos(?) and the y-coordinate is sin(?). Simply substitute the angle in radians into these equations to calculate the coordinates of the point on the unit circle.
How are the values of sine and cosine calculated on the unit circle?
The values of sine and cosine on the unit circle are calculated by considering the coordinates of a point on the circle, where the angle formed by the point with the positive x-axis determines the values of sine and cosine. The sine of an angle is equal to the y-coordinate of the point, while the cosine is equal to the x-coordinate. By using this relationship between the coordinates and trigonometric functions, we can determine the values of sine and cosine for any angle on the unit circle.
What is the relationship between the angle measure and the coordinates on the unit circle?
The relationship between the angle measure and the coordinates on the unit circle is that the coordinates (x, y) of a point on the unit circle are determined by the trigonometric functions sine and cosine of the angle formed by the point and the positive x-axis. Specifically, if the angle measured counterclockwise from the positive x-axis is ?, then the coordinates of the point are (cos(?), sin(?)). This relationship is fundamental in trigonometry and is used to find the values of sine, cosine, and tangent at any given angle measure on the unit circle.
How does the unit circle help in solving trigonometric equations?
The unit circle is a powerful tool in solving trigonometric equations because it provides a visual representation of the relationship between the trigonometric functions and the angle measure. By understanding the unit circle and the trigonometric functions associated with it (sine, cosine, and tangent), we can easily identify the values of these functions for different angles and use them to solve trigonometric equations more efficiently. The unit circle helps in converting trigonometric equations into geometric relationships, making it easier to find solutions by using the properties of the unit circle.
In which trigonometric identities does the unit circle play a significant role?
The unit circle plays a significant role in many trigonometric identities, most notably the relationship between trigonometric functions and right triangles. By setting a circle with radius 1 on the coordinate plane, trigonometric functions can be defined as ratios of the sides of right triangles inscribed in the unit circle. This forms the basis for several fundamental identities such as sine and cosine functions, Pythagorean identities, and the conversion formulas between trigonometric functions.
How does understanding the unit circle contribute to solving real-world problems involving angles and trigonometry?
Understanding the unit circle is essential for solving real-world problems involving angles and trigonometry as it provides a visual representation of the relationships between angles, coordinates, and trigonometric functions. By utilizing the unit circle, one can easily determine the exact values of sine, cosine, and tangent for various angles, enabling accurate calculations in fields such as physics, engineering, and navigation. The unit circle serves as a fundamental tool for solving problems involving angles and trigonometry by providing a clear and concise framework for understanding these concepts and their applications in real-world scenarios.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments