Triangle Angle Bisector Theorem Worksheet
Are you a math teacher or a student in need of practice material for the Triangle Angle Bisector Theorem? Look no further as we have a comprehensive worksheet that will help solidify your understanding of this important geometric concept. Designed for high school students, this worksheet features a variety of exercises to test your knowledge and mastery of the theorem. Get ready to sharpen your geometry skills with this engaging resource!
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
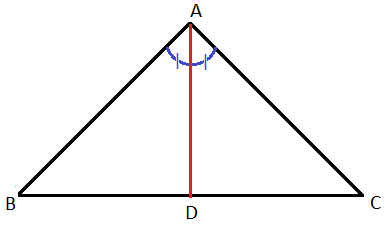
What is the Triangle Angle Bisector Theorem?
The Triangle Angle Bisector Theorem states that in a triangle, an angle bisector divides the opposite side of the triangle into segments that are proportional to the lengths of the two other sides of the triangle. In other words, if a line segment bisects an angle of a triangle, it divides the opposite side into two segments that are proportionate to the other two sides of the triangle.
How is the angle bisector of a triangle defined?
The angle bisector of a triangle is a line or ray that divides an angle of the triangle into two equal angles. In other words, it is a line segment that divides an angle into two congruent angles.
How does the theorem relate to the bisector dividing the opposite side into two segments?
The Angle Bisector Theorem states that an angle bisector divides the opposite side of a triangle into two segments that are proportional to the lengths of the other two sides. Specifically, the ratio of the lengths of the two segments is equal to the ratio of the lengths of the two sides forming the angle being bisected. This theorem helps us determine the lengths of segments in a triangle when the proportions of the sides and angles are known, providing a geometric relationship between the angle bisector and the segments on the opposite side.
What is the relationship between the lengths of the two segments formed by the angle bisector?
The relationship between the lengths of the two segments formed by an angle bisector is that they are proportional to the lengths of the two sides of the angle. Specifically, the segments are in proportion to the lengths of the sides that form the angle that is being bisected. This relationship can be expressed using the angle bisector theorem: the ratio of the length of one segment to the length of the other segment is equal to the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle being bisected to the length of the other side of the angle.
How does the angle bisector theorem help in solving triangle problems?
The angle bisector theorem states that in a triangle, an angle bisector divides the opposite side into segments that are proportional to the lengths of the other two sides. This property can be used to find missing side lengths or angles in a triangle by setting up ratios based on the lengths of the sides involved. By applying the angle bisector theorem, one can accurately determine unknown measurements in a triangle, making it a valuable tool in solving various triangle problems.
What are the conditions that must be met for the angle bisector theorem to be applicable?
For the angle bisector theorem to be applicable in a triangle, the conditions that must be met are that a line bisects an angle of the triangle and intersects the opposite side in a way that divides the side into segments that are proportional to the lengths of the other two sides of the triangle. This theorem holds true for any type of triangle, including equilateral, isosceles, and scalene triangles.
Can the angle bisector theorem be applied to any type of triangle?
Yes, the angle bisector theorem can be applied to any type of triangle, whether it is scalene, isosceles, or equilateral. The theorem states that in a triangle, the angle bisector intersects the opposite side in a proportional manner, meaning that the lengths of the two segments are proportional to the lengths of the other two sides.
How can the angle bisector theorem be proved?
The angle bisector theorem can be proved using similar triangles. By drawing a line parallel to one side of a triangle that intersects the other two sides, two smaller similar triangles are formed. By comparing the ratios of the sides of these triangles, one can derive the angle bisector theorem, which states that the angle bisector of a triangle divides the opposite side into segments that are proportional to the lengths of the other two sides of the triangle.
Can the angle bisector theorem be used to find missing angles in a triangle?
Yes, the angle bisector theorem can be used to find missing angles in a triangle. By using this theorem, you can find the measures of angles in a triangle by knowing the lengths of the sides that the angle bisector intersects. The theorem states that in a triangle, an angle bisector divides the opposite side into segments that are proportional to the adjacent sides. By setting up proportions based on this theorem, you can solve for unknown angles in the triangle.
In what real-life situations can the angle bisector theorem be useful?
The angle bisector theorem can be useful in various real-life situations, such as architecture and engineering, where it can help in accurately dividing angles in structures to ensure balance and stability. It can also be applied in navigation, surveying, and cartography for determining directions and distances. Additionally, the angle bisector theorem can be used in photography for achieving symmetry and balance in composition, and in game design for creating visually appealing and realistic environments.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
































Comments