Transverse Wave Worksheet
Are you a science teacher or homeschooling parent searching for a comprehensive workspace for your students to practice their understanding of transverse waves? If so, this transverse wave worksheet is the perfect resource for you. Designed with the concept of entity in mind, this worksheet provides clear explanations and a variety of engaging questions on the subject.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
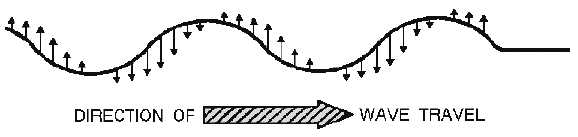
What is a transverse wave?
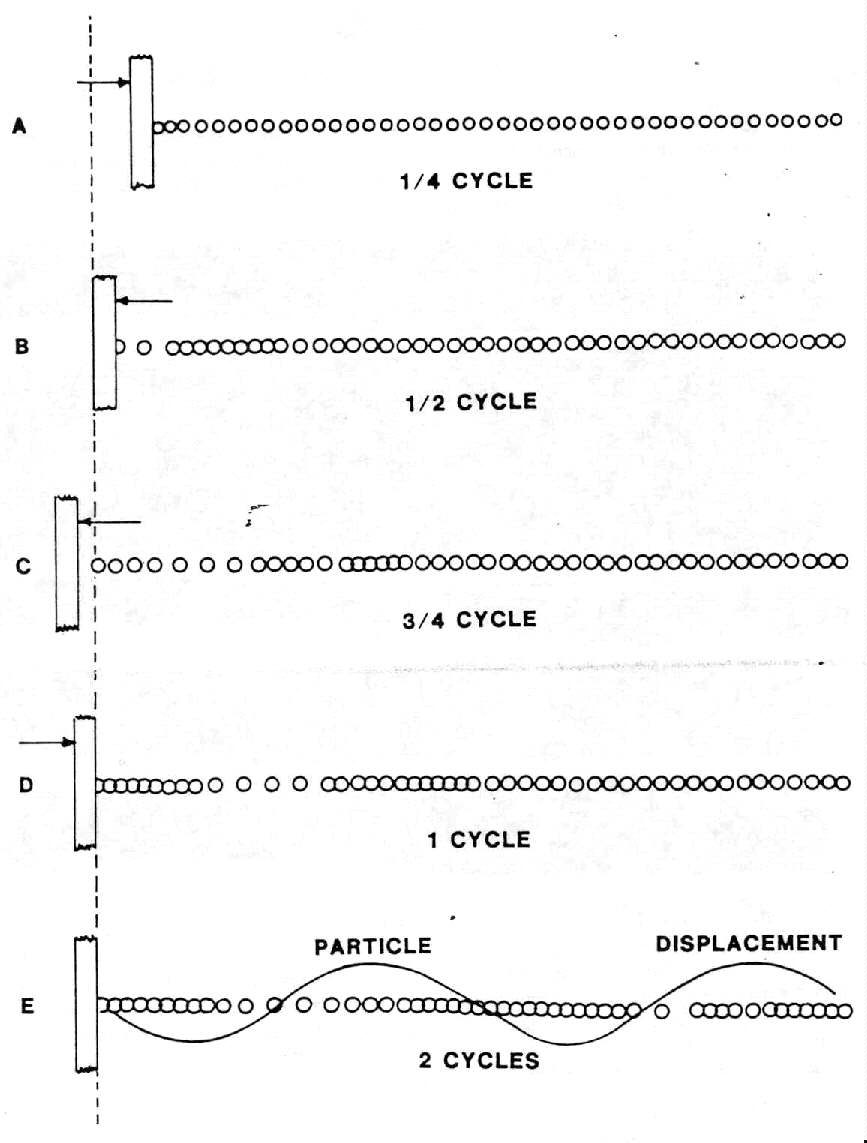
A transverse wave is a type of wave in which the oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer. The wave's particles move up and down or side to side in a perpendicular direction to the wave's direction of travel, creating a series of crests and troughs. Examples of transverse waves include electromagnetic waves (such as light) and waves on a string.
How does a transverse wave oscillate?
A transverse wave oscillates perpendicular to the direction of its propagation, moving up and down or side to side in a wave-like pattern. This oscillation is characterized by the particles of the medium moving at right angles to the direction of energy transfer. The amplitude of the wave represents the maximum displacement of a particle from its equilibrium position as it oscillates.
What are the characteristics of a transverse wave?
Transverse waves exhibit oscillations perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, with particles moving in a direction perpendicular to the wave itself. They have crests and troughs, show properties such as wavelength, amplitude, frequency, and speed, do not require a medium to propagate, and are found in various phenomena like electromagnetic waves, seismic S-waves, and light.
Give examples of transverse waves in everyday life.
Some examples of transverse waves in everyday life include light waves, water waves, and seismic waves. Light waves move through the air or space as vibrations perpendicular to the direction of their propagation, allowing us to see objects and colors. Water waves at the beach or in a pond move up and down as they travel horizontally, creating the ripple effect we see. Finally, seismic waves produced by earthquakes propagate through the Earth's crust in a transverse motion, causing the ground to shake side to side or up and down.
How is the motion of particles in a transverse wave different from the direction of wave propagation?
In a transverse wave, the particles move perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. This means that as the wave travels horizontally (or in any other specific direction), the particles oscillate up and down (or in a perpendicular direction). This is different from longitudinal waves, where the particles move parallel to the direction of wave propagation.
How is the amplitude of a transverse wave measured?
The amplitude of a transverse wave is typically measured by determining the maximum displacement of a point on the wave from its equilibrium position. This value represents the height of the wave crest (or depth of the trough) with respect to the equilibrium position and indicates the maximum distance that a particle of the medium moves away from its rest position due to the passage of the wave.
What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength in a transverse wave?
The relationship between frequency and wavelength in a transverse wave is inverse. This means that as the frequency of a wave increases, its wavelength decreases, and vice versa. This relationship is defined by the formula: speed of wave = frequency × wavelength. This relationship is important in understanding how characteristics of a wave, such as its speed, frequency, and wavelength, are interrelated in transverse waves.
How does the speed of a transverse wave depend on the tension in the medium?
The speed of a transverse wave in a medium is directly proportional to the tension in the medium. This means that as the tension in the medium increases, the speed of the transverse wave will also increase. Conversely, if the tension decreases, the speed of the wave will decrease as well. This relationship is described by the equation v = ?(T/?), where v is the speed of the wave, T is the tension in the medium, and ? is the mass per unit length of the medium.
Explain the concept of polarization in transverse waves.
Polarization in transverse waves refers to the orientation of the oscillations of the wave with respect to the direction of wave propagation. Transverse waves exhibit perpendicular oscillations in a plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation. When a wave is polarized, all the oscillations of the wave occur in a specific orientation within that plane. This orientation can be vertical, horizontal, or any other angle. Polarization is an important characteristic of transverse waves and can have implications for various applications, such as in optics and communication systems.
What are some applications of transverse waves in various fields?
Transverse waves have various applications in different fields, such as in communication technologies like radio waves, microwaves, and light waves for transmitting information over long distances. In medicine, transverse waves are utilized in ultrasound imaging to visualize internal organs and tissues. Additionally, transverse waves play a crucial role in seismology for studying earthquakes and in the field of optics for creating lenses and mirrors for various optical instruments.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments