Transcription Protein Synthesis Worksheet
Are you a biology student eager to dive into the intricate world of transcription and protein synthesis? If so, you're in luck! In this blog post, we will explore the benefits of using worksheets as a valuable learning tool for mastering this complex subject. Designed to enhance your understanding of the entity and subject of transcription and protein synthesis, worksheets offer a structured approach to reinforce concepts and practice essential skills for success in your studies.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
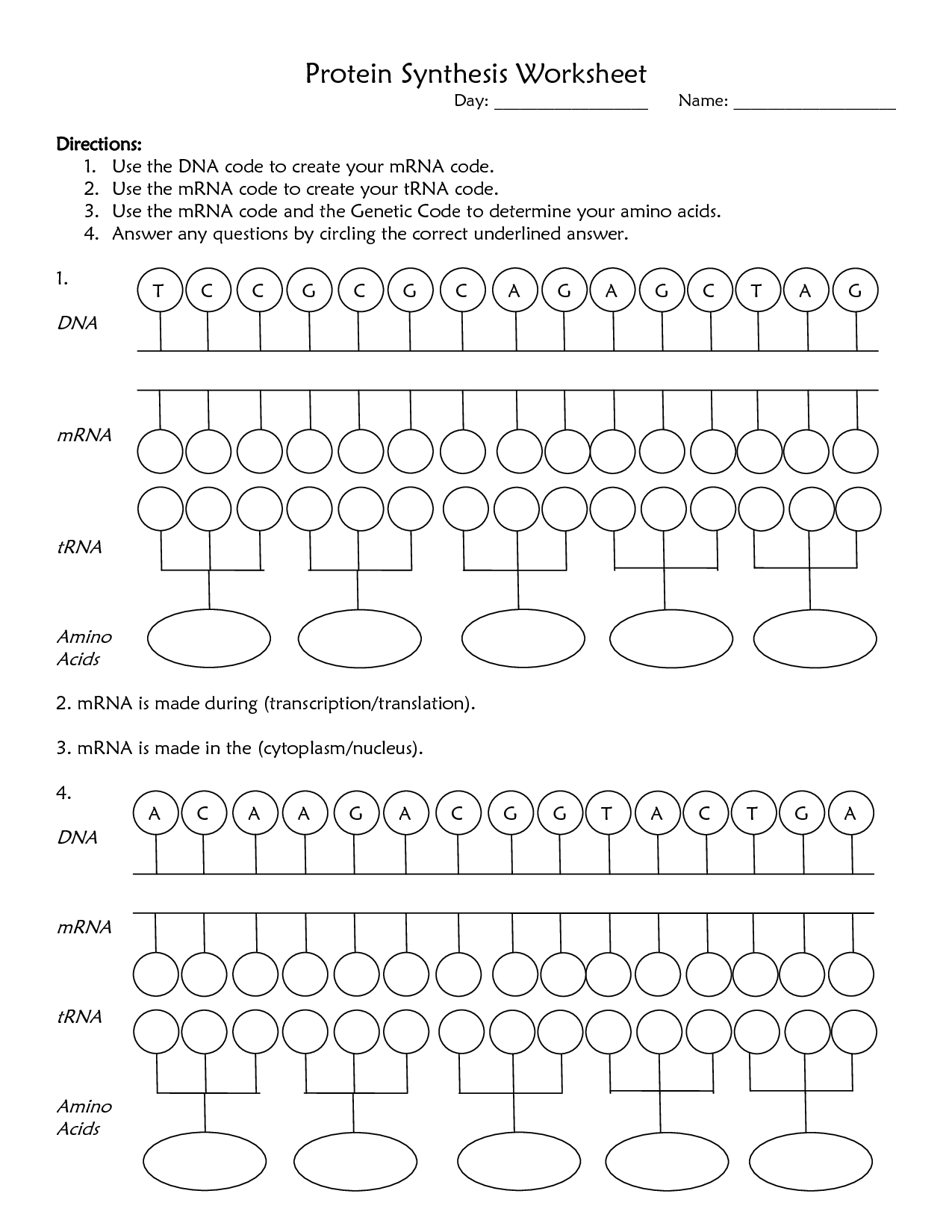
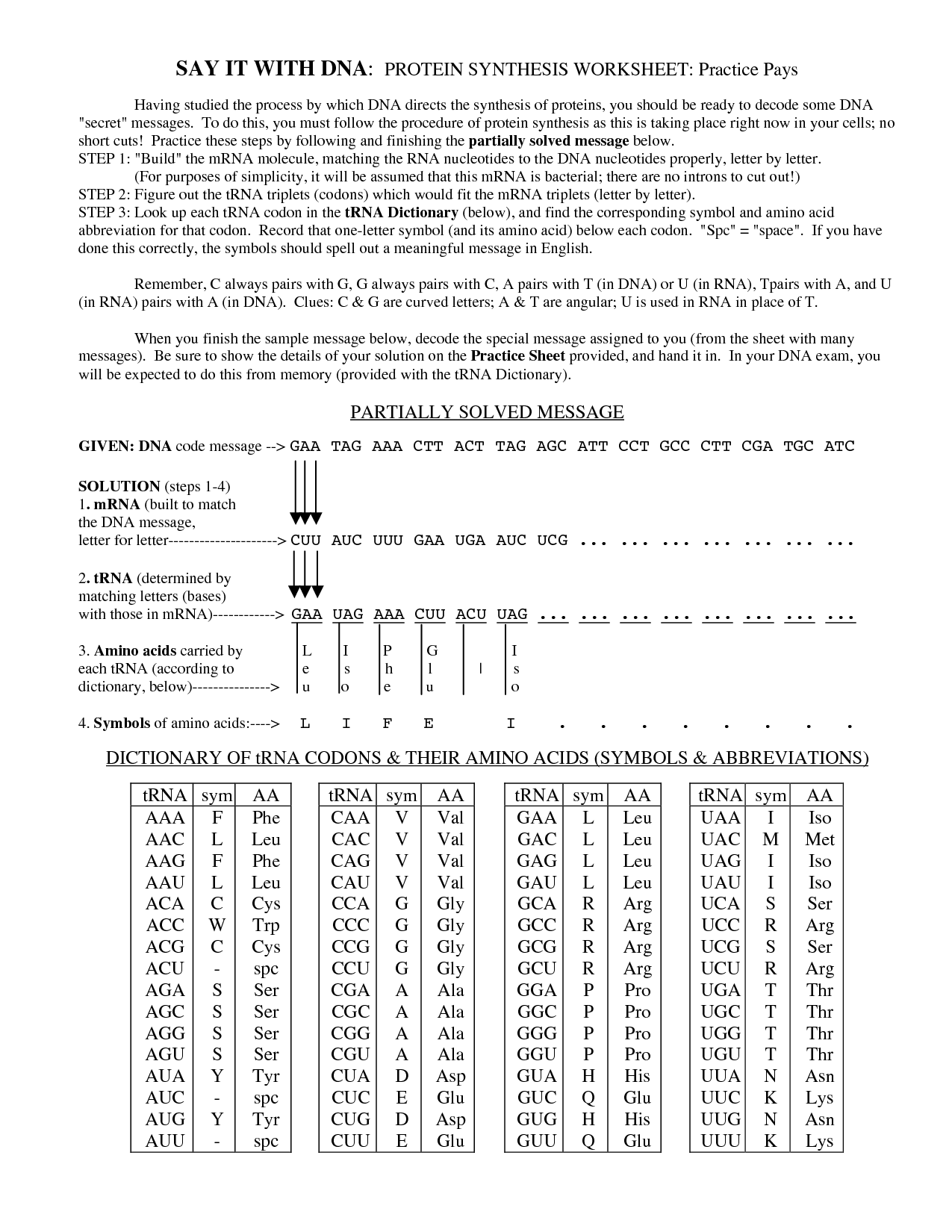
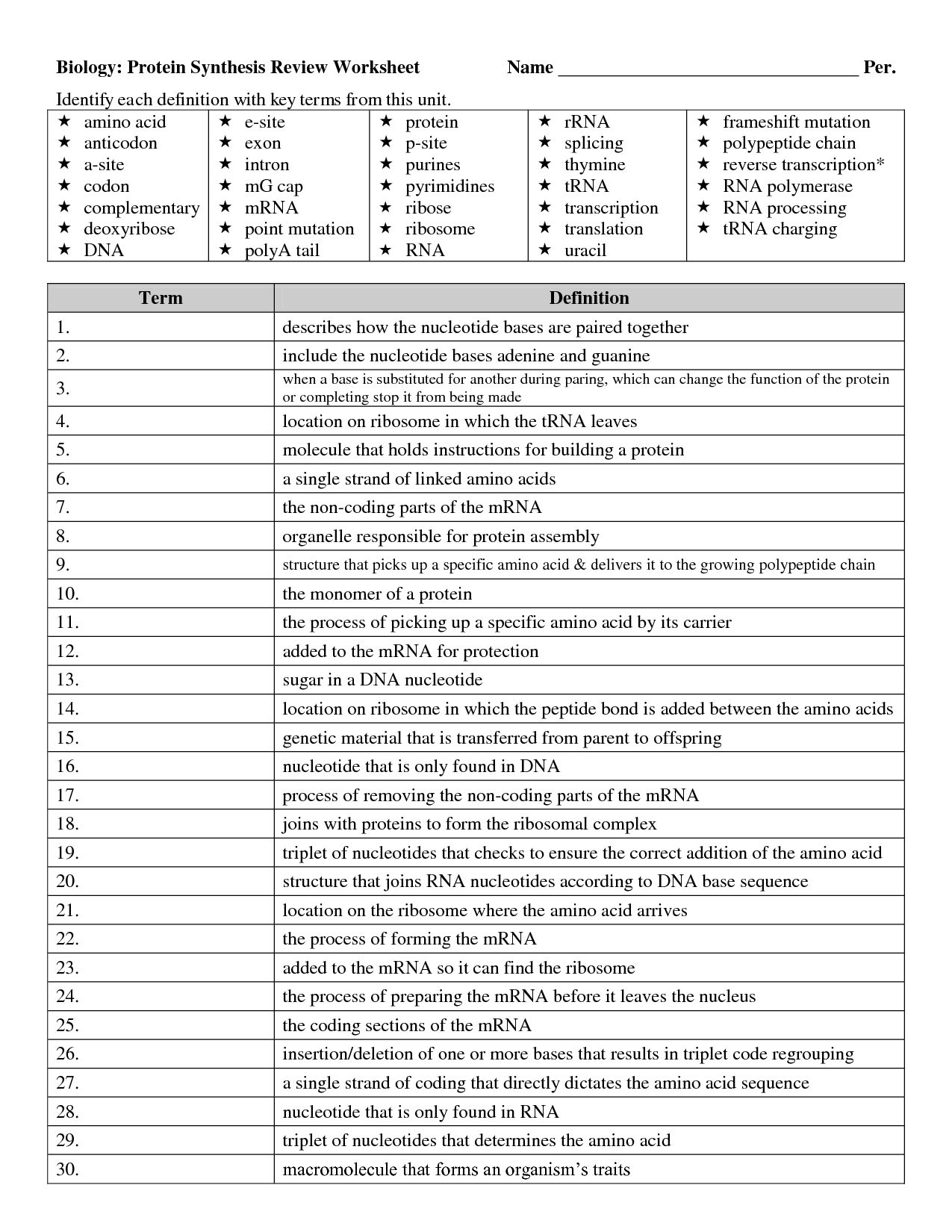
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is transcription?
Transcription is the process through which genetic information stored in DNA is copied into a complementary RNA molecule by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. This RNA molecule can then be used as a template for protein synthesis or perform other cellular functions.
Where does transcription take place in a cell?
Transcription takes place in the nucleus of a cell.
What is the purpose of transcription in protein synthesis?
The purpose of transcription in protein synthesis is to create a single-stranded RNA copy of a gene's DNA sequence. This RNA molecule, known as messenger RNA (mRNA), serves as a template for translation, where the information encoded in the mRNA is used to assemble a specific sequence of amino acids, ultimately forming a protein. Transcription is crucial as it ensures that the genetic information stored in the DNA can be used to guide the production of proteins essential for various biological functions in the cell.
What are the three main steps involved in transcription?
Transcription involves three main steps: initiation, where RNA polymerase binds to a promoter region on the DNA and unwinds the double helix; elongation, where the RNA polymerase synthesizes a complementary RNA strand using the DNA template; and termination, where RNA polymerase and the newly formed RNA strand are released from the DNA once a termination signal is reached.
What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription?
RNA polymerase is responsible for catalyzing the synthesis of RNA molecules from a DNA template during transcription. It binds to the DNA at specific sequences called promoters, separates the DNA strands, and then moves along the template strand, adding complementary RNA nucleotides to the growing RNA chain. It plays a crucial role in copying genetic information from the DNA to produce mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA molecules essential for protein synthesis in cells.
What is the difference between the coding strand and the template strand in DNA?
The coding strand, also known as the sense strand, is the DNA strand that has the same sequence as the mRNA transcript (except T is replaced with U in mRNA). It is not directly involved in transcription but serves as a convenient reference for determining the sequence of the mRNA transcript. On the other hand, the template strand, also known as the antisense strand, is the complementary DNA strand that is used as a template for the synthesis of mRNA during transcription. RNA polymerase binds to the template strand and reads it in the 3' to 5' direction, synthesizing the mRNA in the 5' to 3' direction.
What is a promoter and why is it important in transcription?
A promoter is a region of DNA that initiates the process of transcription by providing a binding site for RNA polymerase and transcription factors. It is important in transcription because it regulates the transcription of specific genes by determining when and how much mRNA is produced. Promoters play a crucial role in controlling the expression of genes and are essential for the accurate and timely synthesis of proteins in a cell.
What is the function of transcription factors in gene expression?
Transcription factors are proteins that play a crucial role in gene expression by binding to specific DNA sequences near a gene and either activating or repressing its transcription. They regulate the rate of transcription by recruiting RNA polymerase to the gene, thus influencing the production of mRNA and ultimately protein synthesis. Transcription factors help control when and where a gene is expressed, allowing for the precise regulation of cellular processes and responses to external stimuli.
How does the process of transcription terminate?
Transcription process terminates in prokaryotes when the RNA polymerase reaches a termination sequence on the DNA template that causes the RNA polymerase to detach along with the newly synthesized mRNA. In eukaryotes, transcription termination involves the recognition of specific termination sequences by proteins that trigger the release of the RNA polymerase from the DNA template, allowing the synthesized mRNA to be further processed and translated by the cellular machinery.
How is the primary transcript modified after transcription to become a functional mRNA molecule?
The primary transcript undergoes several modifications to become a functional mRNA molecule. These include capping at the 5' end with a methylated guanine cap, addition of a poly-A tail at the 3' end, and removal of noncoding introns through splicing. Additionally, RNA editing can occur to alter the nucleotide sequence, and other modifications such as methylation or pseudouridylation can also take place to regulate mRNA stability, localization, or translation efficiency. These post-transcriptional modifications result in a mature, processed mRNA molecule that can be translated into a protein by the ribosome.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments