Transcription and Translation Summary Worksheet
The Transcription and Translation Summary Worksheet is a valuable tool for biology students studying the complex processes of gene expression. This worksheet focuses on providing a clear and concise summary of the key concepts and steps involved in both transcription and translation. Designed to enhance understanding and reinforce learning, this worksheet is a helpful resource for students seeking a comprehensive overview of this fundamental topic in molecular biology.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- DNA Coloring Transcription and Translation
- And Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA RNA Transcription Translation Worksheets
- Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answer Key
- Transcription and RNA Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Coloring Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- Transcription Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is transcription?
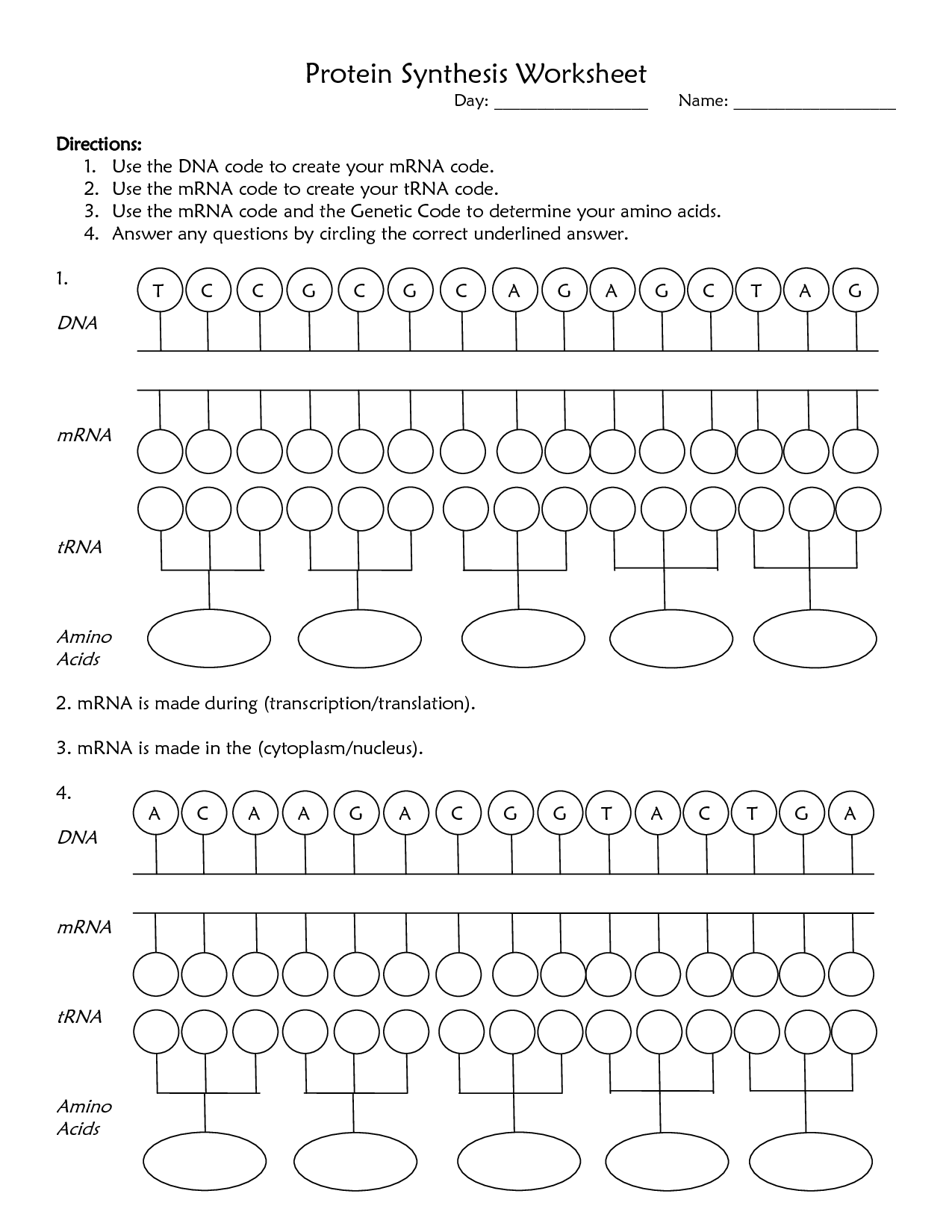
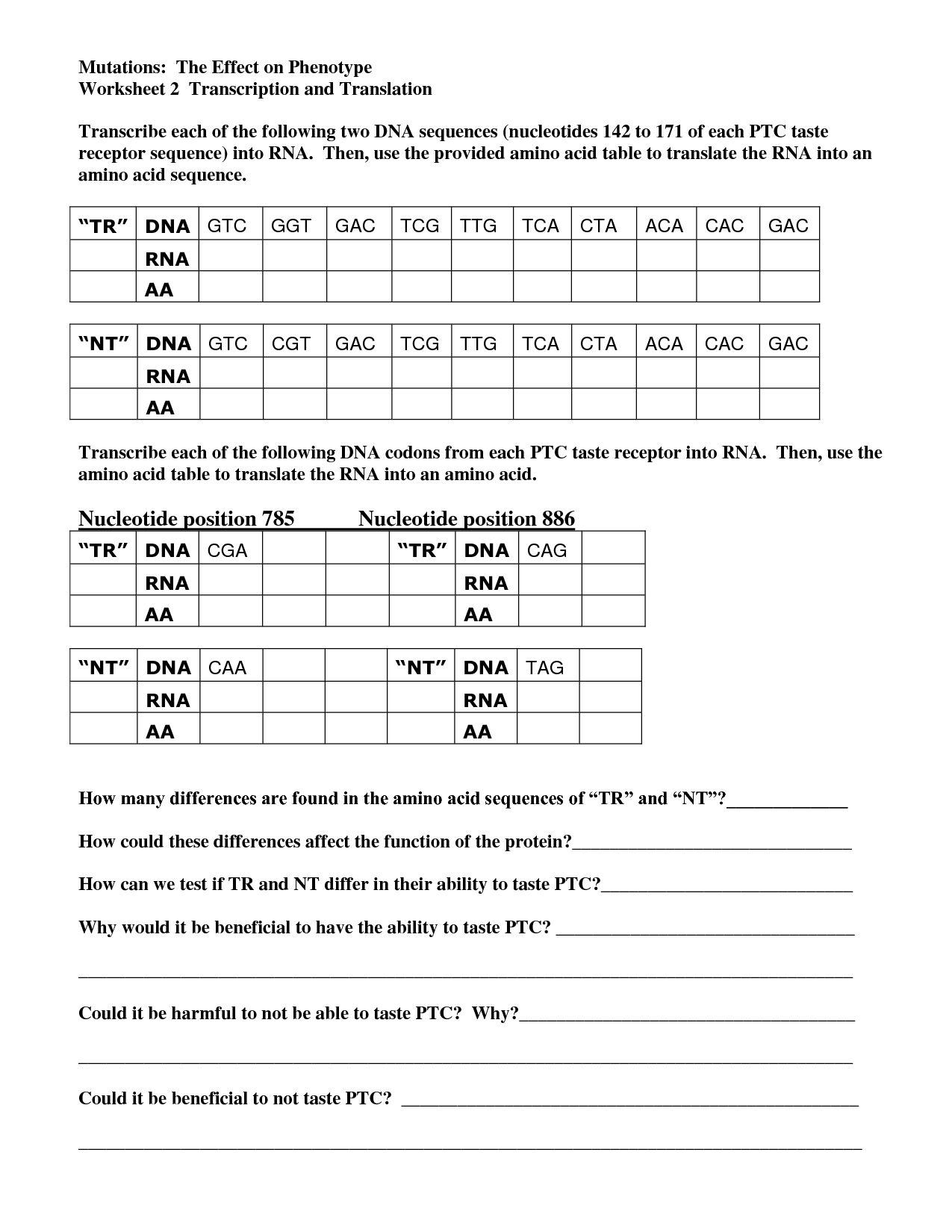
Transcription is the process in which the information stored in a gene's DNA is copied into mRNA (messenger RNA) by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. This mRNA molecule carries the genetic instructions from the DNA in the cell's nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where it serves as a template for protein synthesis.
What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription?
RNA polymerase is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in transcription by catalyzing the synthesis of a complementary RNA strand from a DNA template. It binds to the promoter region of the DNA and unwinds the DNA double helix, allowing for the formation of a RNA strand by adding nucleotides in a sequence that is complementary to the template DNA strand. This process ultimately results in the production of messenger RNA (mRNA) that carries the genetic information from the DNA to the ribosomes for protein synthesis.
How does transcription differ in prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes differs mainly in the complexity of the process. In prokaryotes, transcription occurs in the cytoplasm since they lack a nucleus, while in eukaryotes it takes place in the nucleus. Prokaryotic transcription involves a single RNA polymerase enzyme, whereas eukaryotes have three different RNA polymerases that transcribe different types of RNA molecules. Additionally, eukaryotic transcription includes more regulatory factors and complex processes such as RNA splicing, capping, and polyadenylation compared to prokaryotic transcription, which is more straightforward.
What is the purpose of the promoter region in transcription?
The promoter region in transcription serves as a recognition site for RNA polymerase to bind and initiate the transcription process. It signals the start of a gene sequence and helps regulate gene expression by determining when and how frequently a gene is transcribed. Additionally, the promoter region can contain specific sequences that influence the efficiency and accuracy of transcription initiation.
What is the role of transcription factors?
Transcription factors are proteins that play a crucial role in gene expression by binding to specific DNA sequences near genes and either promoting or inhibiting the transcription of those genes into RNA. By regulating gene expression, transcription factors control the production of proteins essential for various cellular processes, development, and responses to environmental stimuli. They act as molecular switches that help cells respond to signaling pathways and maintain proper gene regulation for normal cellular function.
What is splicing and why is it important in transcription?
Splicing is a process in molecular biology where non-coding sequences are removed from pre-mRNA molecules and the remaining coding sequences are joined together to form mature mRNA. Splicing is crucial in transcription because it allows cells to produce a variety of proteins from a limited number of genes through alternative splicing. This process enhances the diversity of proteins that can be synthesized, enabling cells to perform various functions and respond to different stimuli effectively.
What are the three main types of RNA involved in transcription?
The three main types of RNA involved in transcription are messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). mRNA carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosome for protein synthesis, tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome based on the mRNA sequence, and rRNA is a structural component of the ribosome where protein synthesis takes place.
What is translation?
Translation is the process of converting written or spoken text from one language into another while maintaining the original meaning, style, and context as closely as possible. This involves understanding the source language and culture, and effectively transferring that information into the target language to ensure accurate and clear communication.
What is the role of ribosomes in translation?
Ribosomes play a crucial role in translation as they are responsible for reading the mRNA (messenger RNA) sequence and synthesizing proteins. They interact with tRNA (transfer RNA) molecules carrying specific amino acids, which are then linked together in the correct order to form a protein chain. Ribosomes have two subunits that come together and move along the mRNA strand, decoding its information and building the corresponding protein.
How does the genetic code determine the sequence of amino acids in a protein?
The genetic code determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein through the process of translation. During translation, messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the genetic information from DNA to ribosomes, where transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring the corresponding amino acids based on the sequence of nucleotides in the mRNA. Each set of three nucleotides, called a codon, specifies a particular amino acid. This codon-amino acid correspondence is determined by the genetic code, which is a set of rules that relate each codon to a specific amino acid or a stop signal. As ribosomes move along the mRNA, tRNA molecules bring the correct amino acids to the ribosome in the order dictated by the mRNA sequence, ultimately leading to the synthesis of a specific protein with a unique sequence of amino acids.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

































Comments