Transcription and Translation Coloring Worksheet Colored
Are you in search of a creative and engaging way to reinforce your understanding of transcription and translation? Look no further! Our Transcription and Translation Coloring Worksheet is the perfect tool for students who want to explore these complex scientific concepts while unleashing their creative side. This worksheet provides a unique and captivating approach to learning, ensuring that your understanding of these crucial processes is solidified while having fun at the same time.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Coloring Transcription and Translation
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- The DNA Double Helix Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Coloring Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- DNA Coloring Transcription and Translation Answer Key
- DNA Structure Coloring Worksheet
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- Transcription Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- Transcription and Translation Practice Worksheet
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- Protein Synthesis Transcription and Translation Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the purpose of the Transcription and Translation Coloring Worksheet?
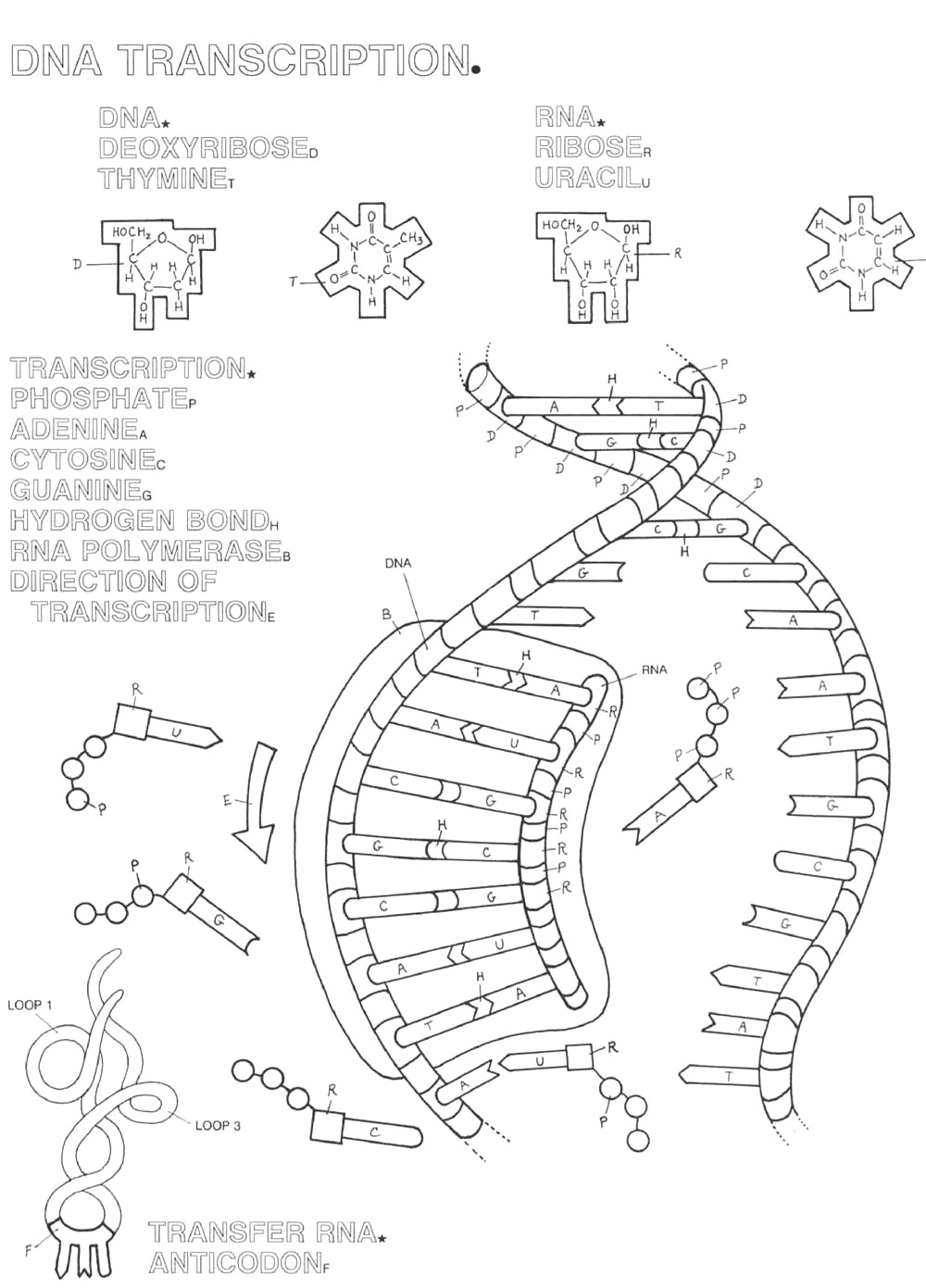
The purpose of the Transcription and Translation Coloring Worksheet is to help students understand and visualize the processes of transcription and translation in molecular biology. By coloring different components of the DNA, RNA, and protein molecules involved in these processes, students can better grasp the sequence of events and how genetic information is transferred from DNA to RNA to protein.
How does transcription differ from translation?
Transcription is the process of synthesizing messenger RNA (mRNA) from a DNA template in the cell nucleus, while translation is the process of synthesizing a polypeptide chain from mRNA in the ribosome. In other words, transcription involves the copying of genetic information from DNA to mRNA, whereas translation involves decoding the mRNA sequence to produce a specific protein by linking amino acids together.
What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription?
RNA polymerase is the enzyme responsible for catalyzing the process of transcription in cells. It binds to the DNA template strand and synthesizes a complementary RNA strand by adding nucleotides one by one. This process is crucial for converting the genetic information stored in the DNA into RNA, which can then be used for protein synthesis. RNA polymerase plays a central role in gene expression by transcribing specific genes into messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules.
What are the three main types of RNA molecules involved in transcription and translation?
The three main types of RNA molecules involved in transcription and translation are messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). mRNA carries genetic information from the DNA to the ribosome for protein synthesis, tRNA helps in bringing specific amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis, and rRNA forms the structural and catalytic core of the ribosome where protein synthesis takes place.
Describe the process of transcription from start to finish.
Transcription is the process in which the genetic information in a strand of DNA is copied into a complementary strand of RNA by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. It begins with the RNA polymerase binding to the promoter region of the DNA molecule. The enzyme then unwinds the double helix of DNA and starts assembling a complementary RNA strand by pairing RNA nucleotides with their corresponding DNA nucleotides. As RNA polymerase moves along the DNA strand, it reads the genetic code and creates a single-stranded RNA molecule. Once the entire gene is transcribed, RNA polymerase reaches the termination sequence and detaches from the DNA, releasing the newly synthesized RNA strand. This RNA molecule can then undergo further processing and translation to produce proteins.
What is the function of the ribosome in translation?
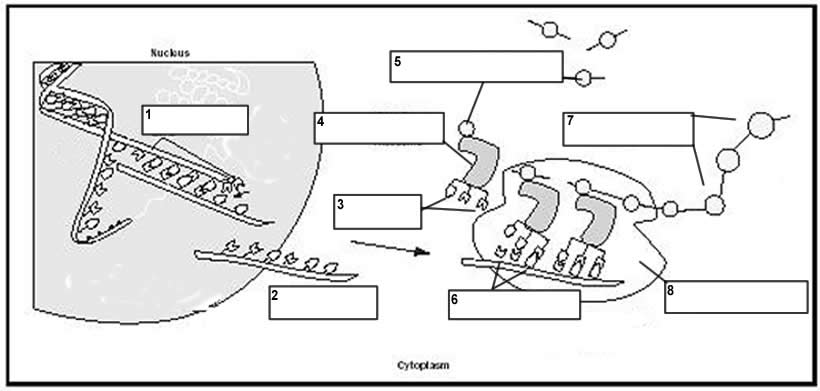
The function of the ribosome in translation is to synthesize proteins by translating the genetic code carried by messenger RNA (mRNA) into a specific sequence of amino acids. The ribosome acts as a molecular machine that reads the information encoded in the mRNA and catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between the amino acids, thereby building a polypeptide chain that will ultimately fold into a functional protein.
What is a codon and how does it relate to translation?
A codon is a sequence of three nucleotides in mRNA that codes for a specific amino acid during protein synthesis. During translation, the ribosome reads these codons and matches them with the appropriate transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules carrying the corresponding amino acids. This process ensures that the correct sequence of amino acids is assembled to form a protein based on the instructions encoded in the mRNA. So, codons essentially serve as the genetic code language that dictates the specific amino acid sequence in a protein.
How is the genetic code read during translation?
During translation, the genetic code is read by ribosomes. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring amino acids to the ribosome according to the sequence of three mRNA nucleotides called codons. The ribosome matches the codons on the mRNA with complementary anticodons on the tRNA molecules, and as a result, the amino acids are linked together to form a protein according to the genetic information encoded in the mRNA.
Briefly explain the process of protein synthesis.
Protein synthesis begins with the transcription of DNA into messenger RNA (mRNA) in the nucleus. This mRNA then moves to the cytoplasm where ribosomes translate the mRNA sequence into a specific amino acid sequence, forming a protein. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring the corresponding amino acids to the ribosome based on the mRNA sequence, where they are linked together to form a polypeptide chain. This chain undergoes folding and post-translational modifications to become a functional protein.
How do mutations in DNA affect transcription and translation?
Mutations in DNA can affect transcription and translation by changing the sequence of nucleotides, which can result in the production of a non-functional or altered protein. This can occur by causing changes in the amino acid sequence during translation, disrupting the formation of functional protein structures, or affecting the regulation of gene expression during transcription. Ultimately, mutations can lead to various genetic disorders and diseases by altering the normal functioning of the protein produced.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments