The 12 Cell Review Worksheet Answers Biology
This blog post aims to provide biology students with a helpful resource: the 12 Cell Review Worksheet Answers. These answers will assist students in better understanding the topics covered in their biology classes and will serve as a valuable tool for reviewing key concepts.
Table of Images 👆
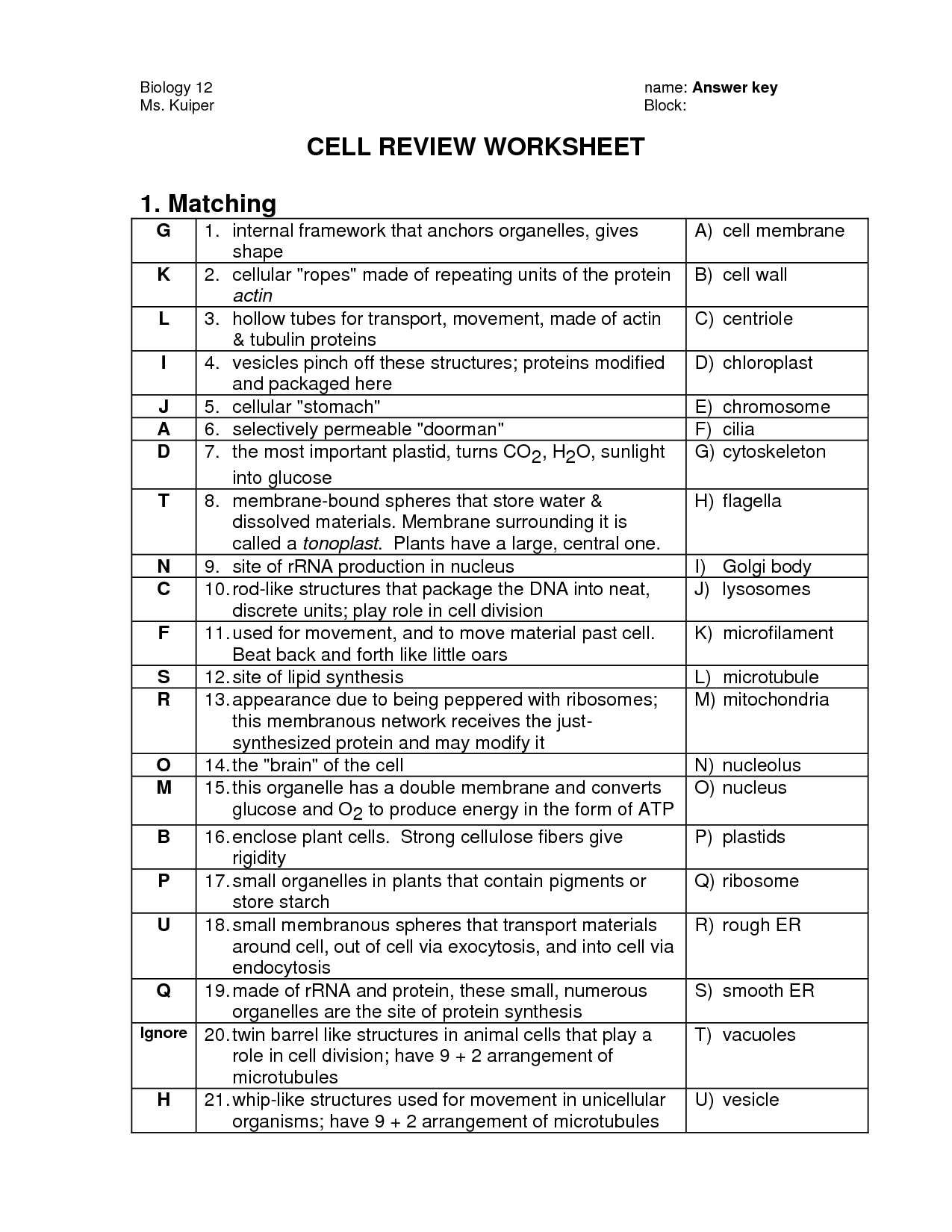
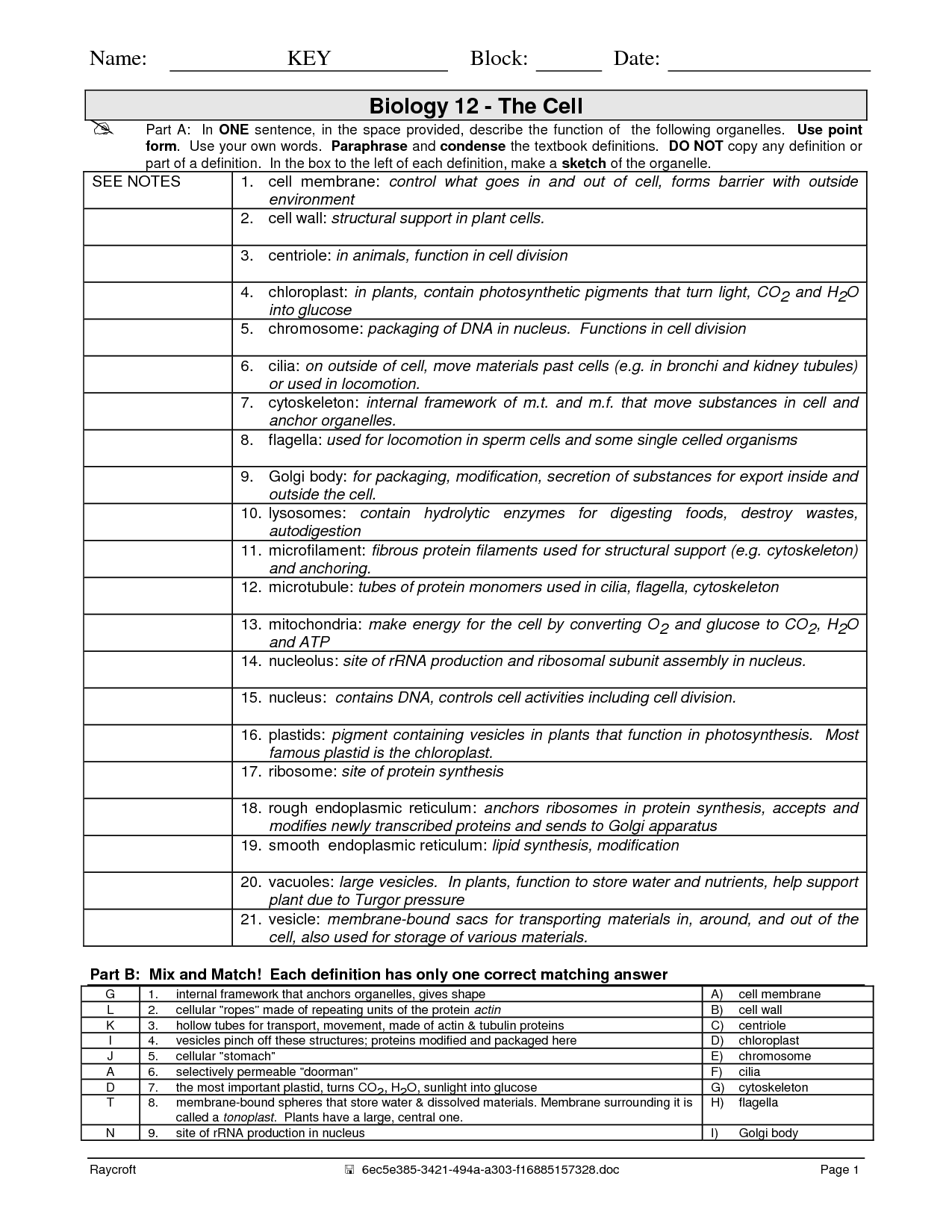
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Answer Key
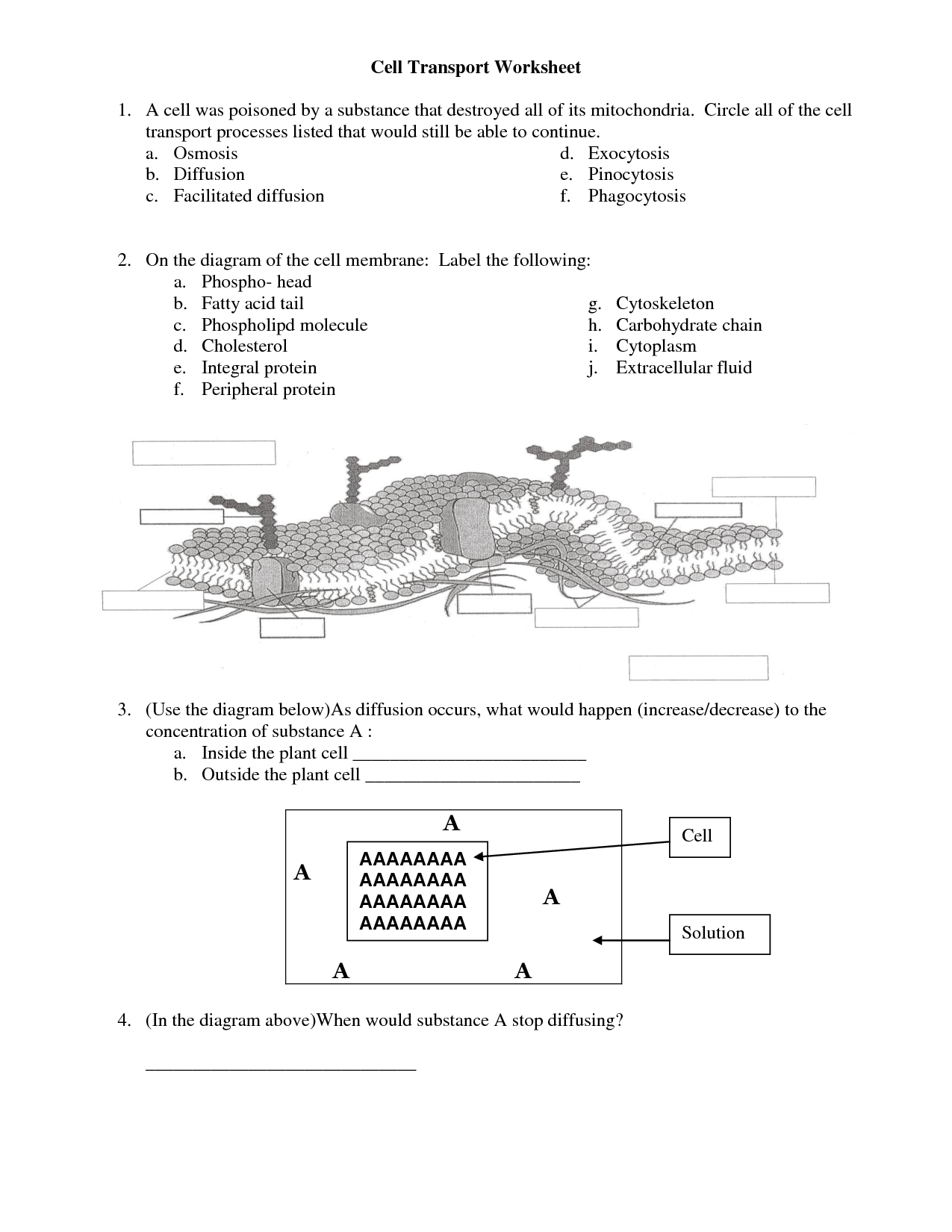
- Cell Transport Worksheet Answer Key Review
- Biology Cell Reproduction Worksheets Answers
- Cell Structure and Function Worksheets Answer Key
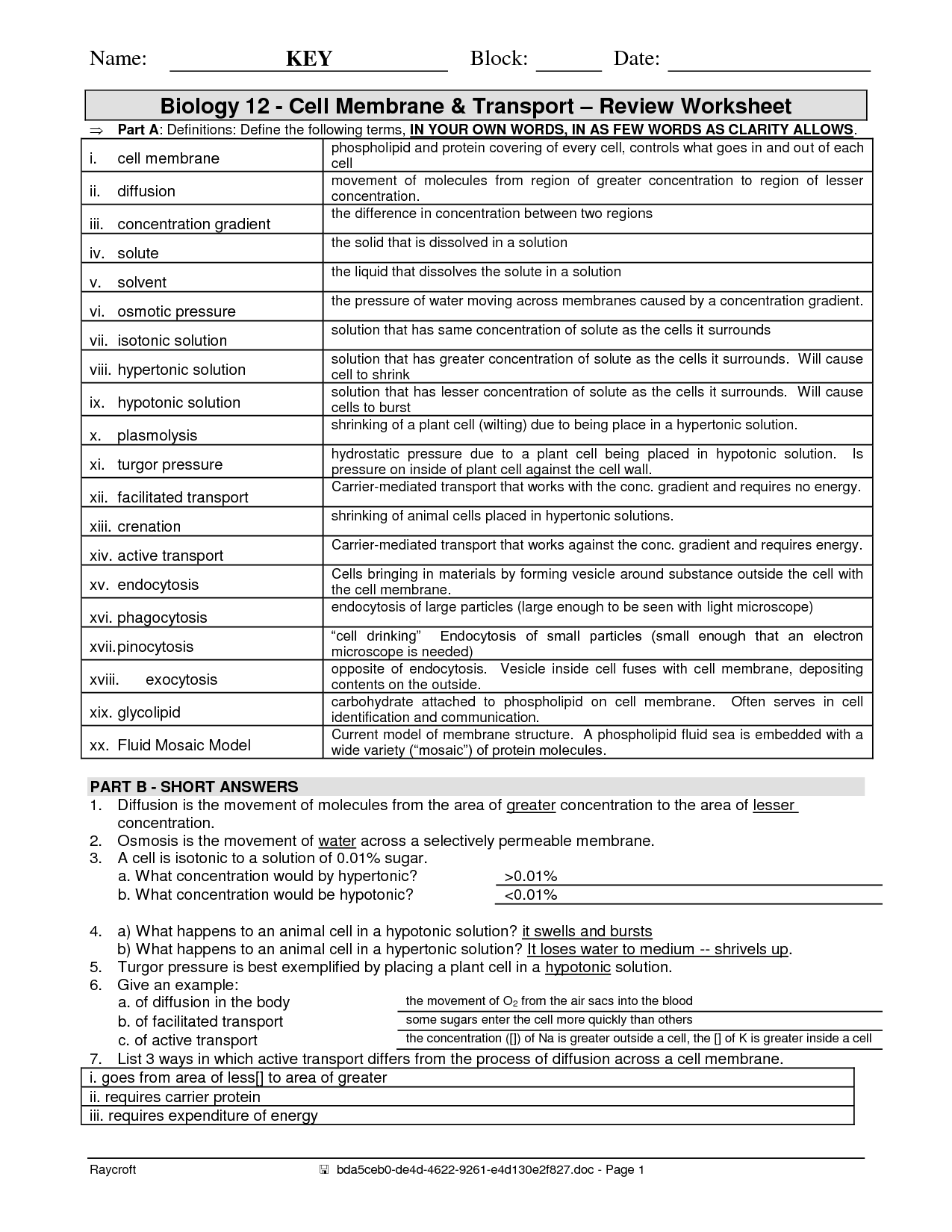
- Cell Membrane Transport Worksheet
- Osmosis and Tonicity Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Transport Worksheet Answer Key
- Biology If8765 Worksheet Answer Key
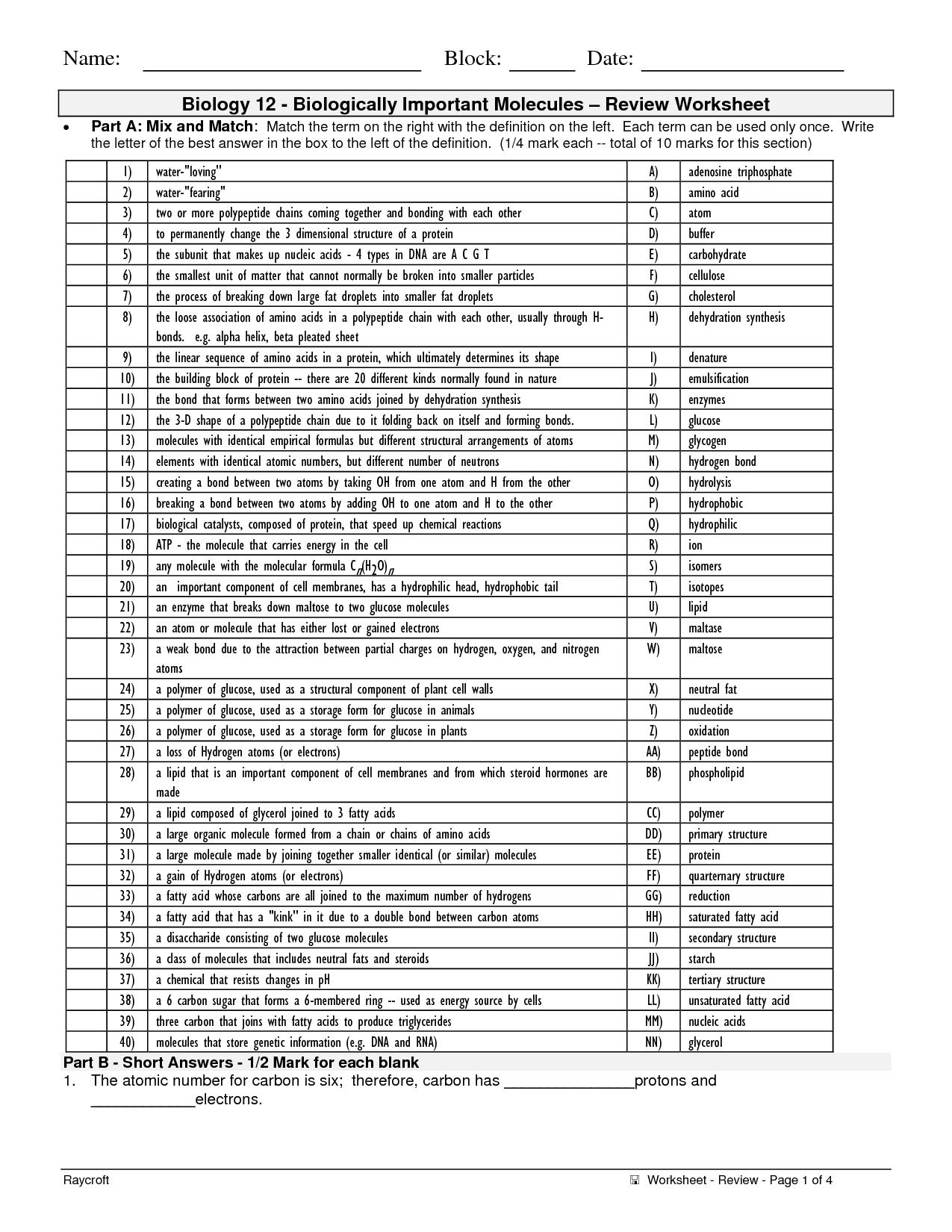
- Organic Compound Worksheet Answers Biology
- Pearson Biology Workbook a Answer Key Chapter 16
- Cell Cycle Review Worksheet Answers
- Cell Review Worksheet Chapter 3
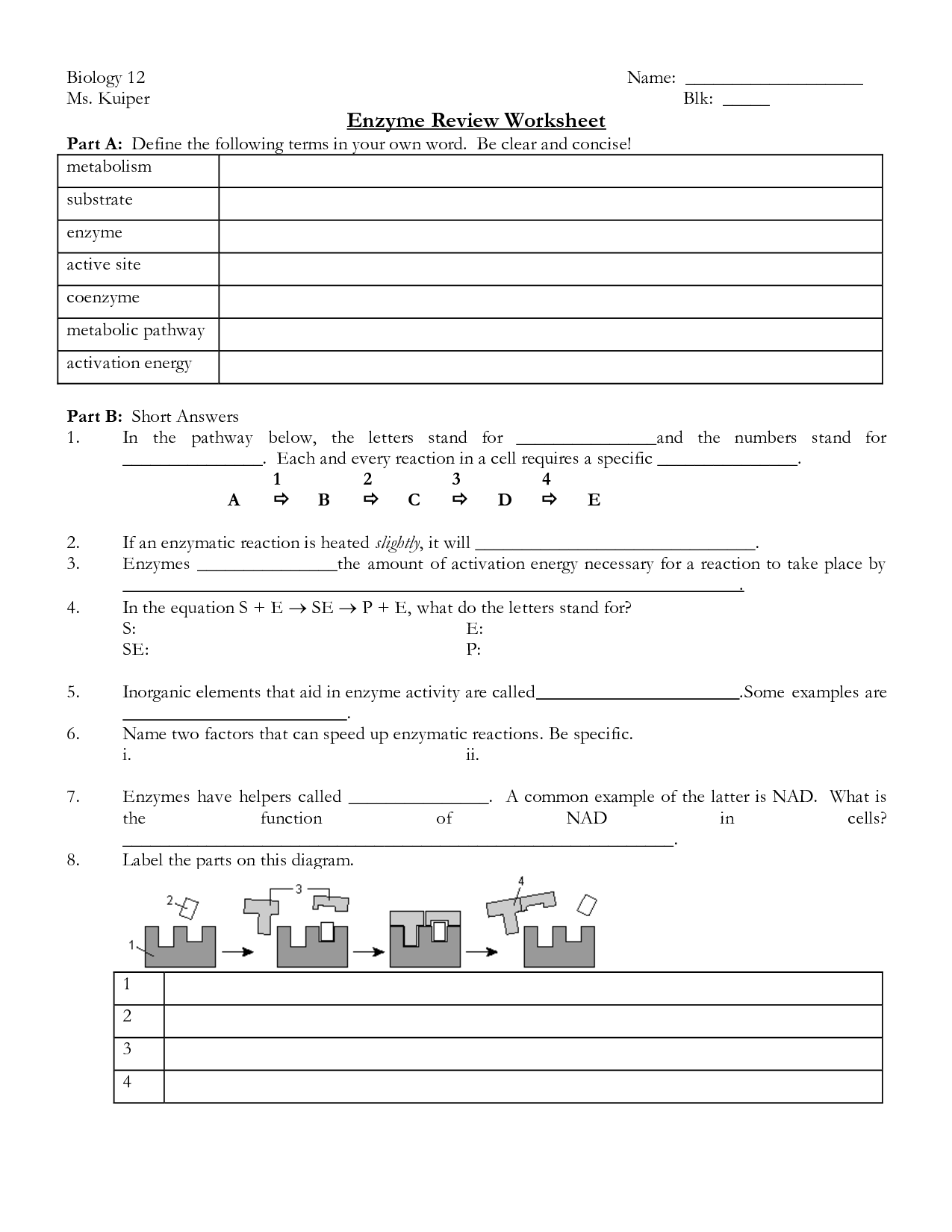
- Biology Enzyme Worksheet
- AP Biology Photosynthesis Worksheet Answers
- Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answer Key
- Biology Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
What role do cells play in living organisms?
Cells are the basic structural and functional units of living organisms. They carry out essential processes such as growth, reproduction, and metabolism. Cells also perform specialized functions in different tissues and organs to ensure the proper functioning of the organism. From maintaining homeostasis to responding to stimuli, cells are integral to the survival and functioning of all living organisms.
How are prokaryotic cells different from eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have a defined nucleus and various membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum. Prokaryotic cells are typically smaller and simpler in structure, with circular DNA in the nucleoid region, while eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex, with linear DNA in the nucleus. Additionally, prokaryotic cells reproduce through binary fission, whereas eukaryotic cells reproduce through mitosis or meiosis.
What are the main components of a cell membrane?
The main components of a cell membrane are phospholipid bilayer, proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrate chains. The phospholipid bilayer forms the basic structure of the membrane, while proteins play crucial roles in transport, signaling, and cell adhesion. Cholesterol helps maintain the fluidity and stability of the membrane, and carbohydrate chains attached to proteins and lipids play a role in cell-cell recognition and communication.
Describe the structure and function of the mitochondria.
The mitochondria are membrane-bound organelles found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. They serve as the powerhouse of the cell, responsible for producing the majority of the cell's adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through the process of cellular respiration. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure, with an outer membrane and an inner membrane that is highly folded into structures called cristae. The inner membrane houses the proteins and enzymes involved in the electron transport chain and ATP synthesis. Mitochondria also contain their own DNA and ribosomes, allowing them to partially control their own replication and protein synthesis.
What is the purpose of the endoplasmic reticulum in a eukaryotic cell?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in a eukaryotic cell has a crucial role in protein and lipid synthesis, modification, and transport. It provides a large surface area for these cellular processes to occur, producing proteins and lipids for various cellular functions. The ER also plays a role in detoxification and calcium storage within the cell.
Explain the process of photosynthesis and where it occurs in a plant cell.
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy in the form of glucose. It takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells, specifically in the grana of the chloroplasts. During photosynthesis, chlorophyll in the chloroplasts captures sunlight and uses it to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This process is crucial for the survival of plants and other organisms that depend on them for food and oxygen.
What is the function of the golgi apparatus in a cell?
The Golgi apparatus in a cell functions as a packaging and distribution center, processing proteins and lipids synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum and directing them to specific destinations within and outside the cell. It modifies, sorts, and packages these molecules into vesicles for transport to their appropriate locations, playing a crucial role in intracellular trafficking and maintaining cellular functionality.
Describe the structure and function of a lysosome.
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles found in animal cells that contain digestive enzymes responsible for breaking down waste materials, cellular debris, and foreign invaders such as bacteria. These enzymes are active at an acidic pH, which is maintained within the lysosome. Lysosomes play a crucial role in cellular digestion, recycling of cellular components, and programmed cell death (apoptosis). They are involved in various cellular processes, including nutrient sensing, cell signaling, and autophagy.
How do cells maintain homeostasis?
Cells maintain homeostasis through processes like active transport, passive transport, and feedback mechanisms. Active transport pumps ions or molecules across the cell membrane to maintain proper concentration gradients, while passive transport allows molecules to move across the membrane in response to concentration gradients. Feedback mechanisms, such as negative feedback loops, regulate cell processes by detecting changes in internal conditions and triggering responses to restore balance. Together, these processes help cells maintain stable internal environments despite external changes.
What is the significance of cell division and why is it important for living organisms?
Cell division is crucial for living organisms as it plays a key role in growth, development, repair, and reproduction. It enables cells to multiply and renew tissues, allowing organisms to grow larger and mature. Through cell division, damaged or old cells can be replaced with new, healthy cells to maintain the overall function and integrity of the organism. Additionally, cell division is essential for passing on genetic information from one generation to the next during reproduction, ensuring the continuation of a species.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments