Sound Waves and Energy Worksheet
Have you ever wondered about the fascinating world of sound waves and energy? If you're a curious student looking to deepen your understanding of this topic, you're in luck! We have the perfect resource for you - the Sound Waves and Energy Worksheet.
Table of Images 👆
More Energy Worksheets
Light and Heat Energy WorksheetsTypes of Energy Transfer Worksheet
Energy Light Heat Sound Worksheets
3 Forms of Energy Worksheets
Energy Worksheets for Third Grade
What is a sound wave?
A sound wave is a type of mechanical wave that carries energy through a medium by causing particles in the medium to vibrate back and forth in a series of compressions and rarefactions. These vibrations are transmitted through the medium, such as air or water, and are perceived by our ears as sound.
How does a sound wave travel through a medium?
Sound waves travel through a medium by causing particles in the medium to vibrate in the same direction as the wave's propagation. As sound is created, it compresses air molecules which then collide with neighboring molecules, transferring the wave's energy. This process continues along the medium until the sound wave reaches its destination, where it is then perceived by our ears as sound.
What is the wavelength of a sound wave?
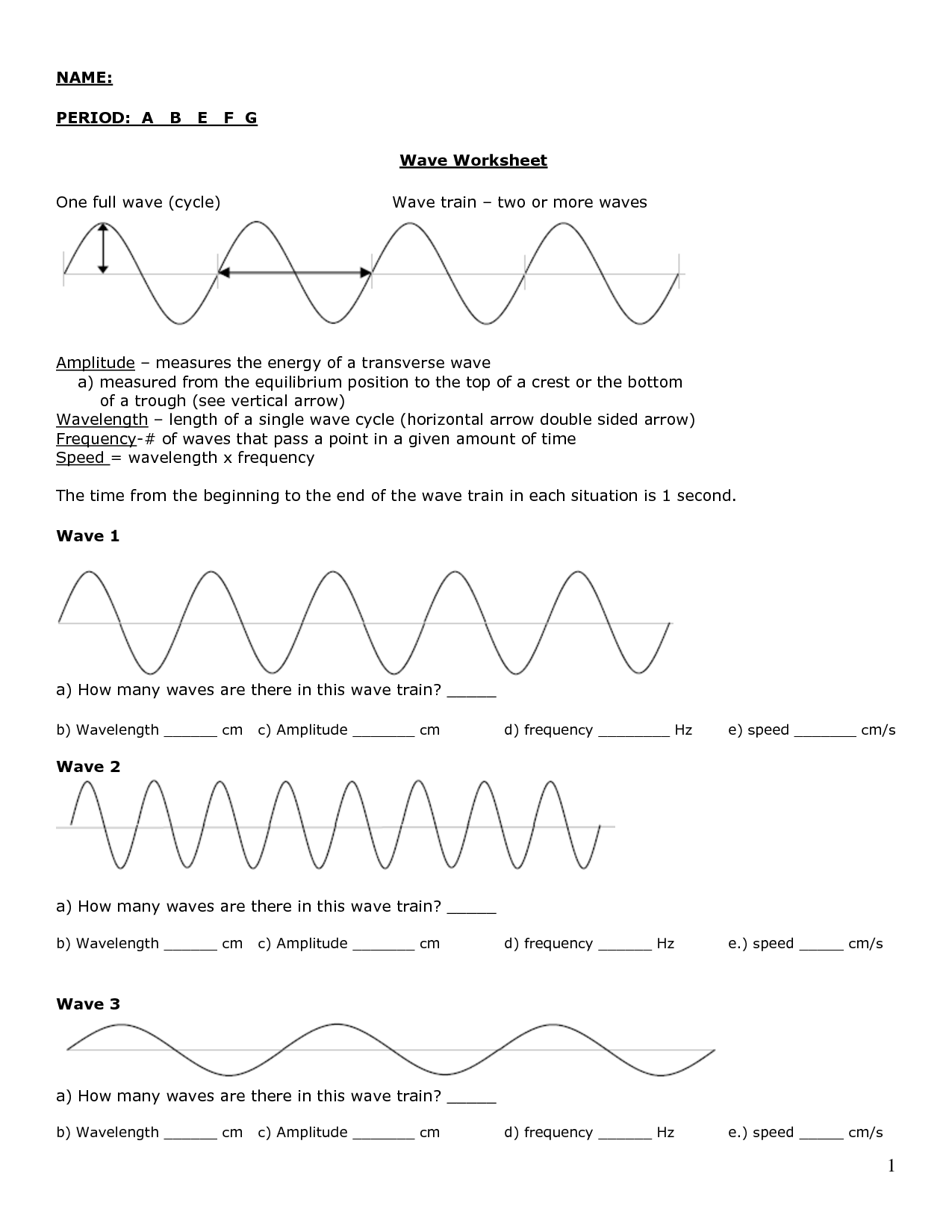
The wavelength of a sound wave is the distance between two consecutive points in a wave that are in phase with each other, such as between two crests or two troughs. It is typically measured in meters and is inversely proportional to the frequency of the sound wave, meaning that as the frequency increases, the wavelength decreases.
How is the amplitude of a sound wave related to its perceived loudness?
The amplitude of a sound wave is directly related to its perceived loudness. In simple terms, the greater the amplitude of a sound wave, the louder the sound will be perceived by our ears. This is because larger amplitudes result in more energy being transferred to our ears, causing the sensation of increased volume.
What is the frequency of a sound wave?
The frequency of a sound wave refers to the number of complete oscillations or cycles that occur in one second and is measured in Hertz (Hz). The higher the frequency, the higher the pitch of the sound.
What determines the pitch of a sound wave?
The pitch of a sound wave is determined by its frequency, which is the number of vibrations or cycles that occur per second. Higher frequencies result in higher pitch sounds, while lower frequencies produce lower pitch sounds. The human ear perceives frequencies as different musical notes, ranging from low frequency bass sounds to high frequency treble sounds.
How does the speed of sound change in different mediums?
The speed of sound varies in different mediums due to differences in the molecular structure and density of the medium. In general, sound travels faster in solids, such as metals, due to the tightly packed molecules allowing for quicker transmission of vibrations. In liquids, the speed of sound is slower than in solids but faster than in gases, as the molecules are still closer together but not as tightly packed as in solids. Gases have the slowest speed of sound due to the greater distance between molecules.
What is the relationship between wavelength, frequency, and speed of sound?
The relationship between wavelength, frequency, and speed of sound is defined by the equation v = ?f, where v is the speed of sound, ? is the wavelength, and f is the frequency. This equation states that the speed of sound is equal to the product of the wavelength and the frequency. As wavelength increases, frequency decreases, and vice versa, while the speed of sound remains constant in a given medium. This relationship is fundamental in understanding how sound behaves and propagates through different mediums.
How does the Doppler effect affect the perceived frequency of a moving sound source?
The Doppler effect causes the perceived frequency of a moving sound source to change based on the relative motion between the source and the observer. When the source is moving toward the observer, the perceived frequency is higher than the actual frequency (known as a blueshift), and when the source is moving away, the perceived frequency is lower than the actual frequency (known as a redshift). This effect is commonly experienced when a siren of an approaching emergency vehicle sounds higher in pitch as it gets closer and lower in pitch as it moves away.
What is the principle of superposition as it relates to sound waves?
The principle of superposition states that when two or more waves overlap, the resulting wave is the sum of the individual waves. In the context of sound waves, this means that when multiple sound waves meet at a point in space, they combine to create a new wave with an amplitude that is the sum of the amplitudes of the individual waves. This principle helps to explain phenomena such as interference and standing waves in sound.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments