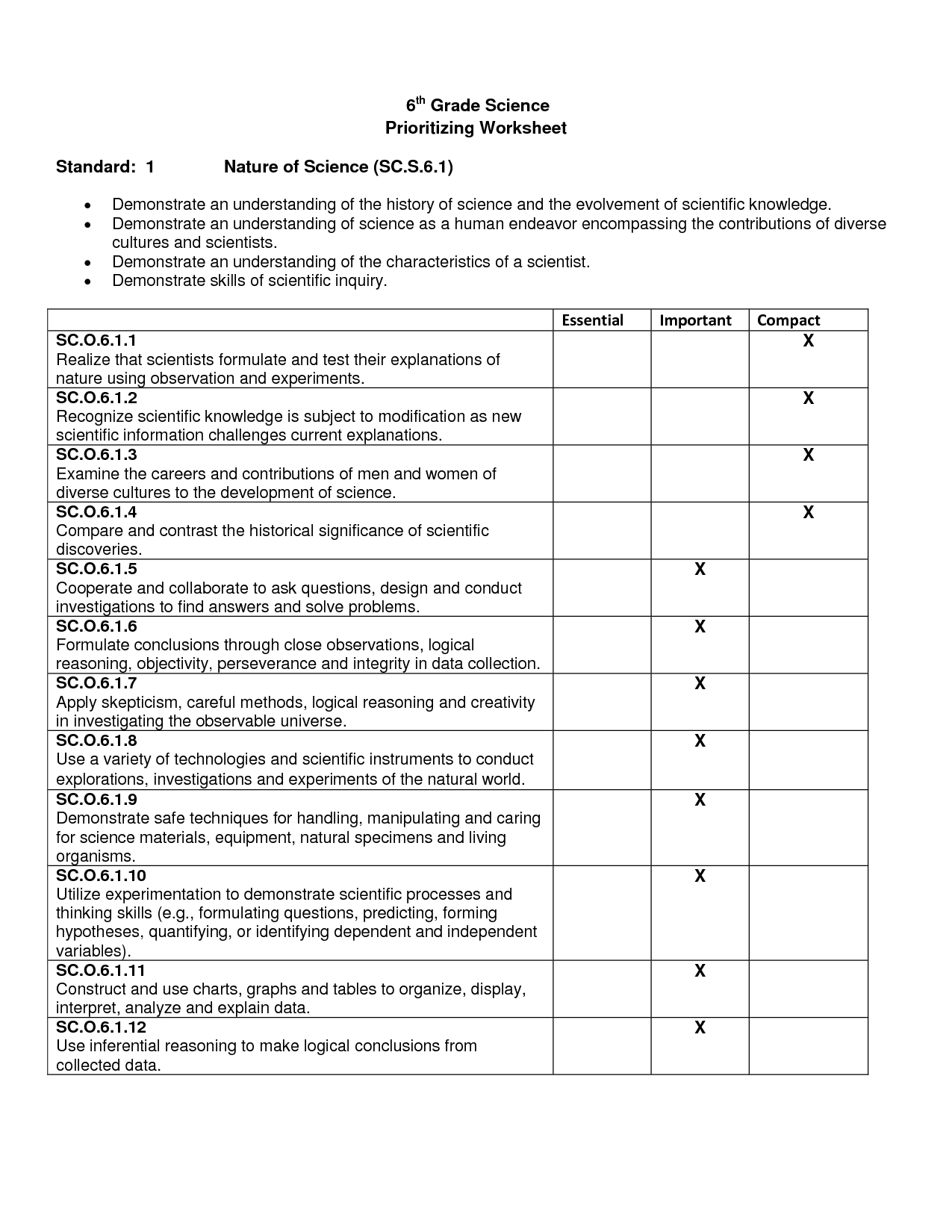
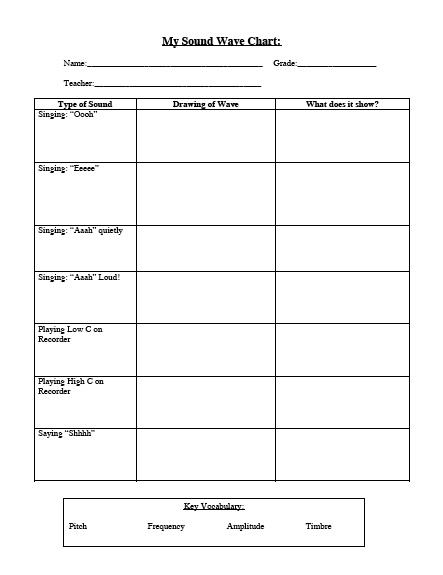
Sound Wave Worksheet Answer
Worksheets are a valuable learning tool that offer a structured approach to reinforce and solidify understanding of a specific subject. For individuals seeking to enhance their knowledge and comprehension of sound waves, a sound wave worksheet can provide a comprehensive and organized way to practice and apply concepts.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
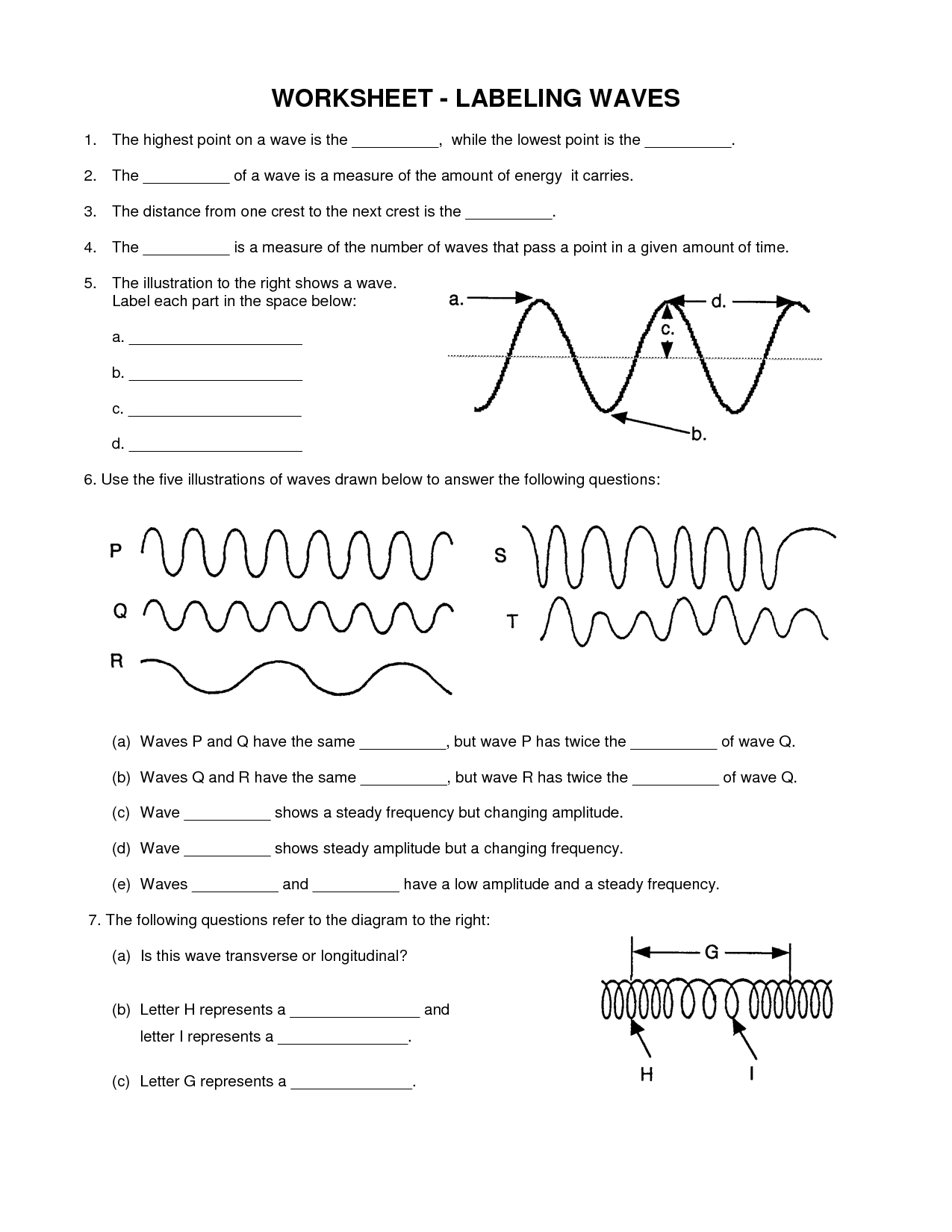
What is a sound wave?
A sound wave is a type of mechanical wave that carries energy through a medium such as air, water, or solids by the vibration of particles. These waves create variations in air pressure that our ears perceive as sound. Sound waves can vary in frequency and amplitude, resulting in different pitches and volumes of sound.
How is sound produced?
Sound is produced when an object vibrates, causing the air particles around it to also vibrate. These vibrations create waves that travel through the air and reach our ears, where they are detected and processed by the brain as sound. Various factors such as the frequency and amplitude of the vibrations determine the characteristics of the sound, such as pitch and volume.
What is the role of a medium in sound wave propagation?
The role of a medium in sound wave propagation is to serve as a material through which the sound wave can travel. Sound waves require a medium, such as air, water, or a solid material, in order to propagate and transmit energy from one location to another. The particles of the medium vibrate in response to the sound wave, transferring the energy along by colliding with adjacent particles and passing on the wave. Without a medium, such as in a vacuum, sound waves cannot propagate because there are no particles to transfer energy.
What is the frequency of a sound wave?
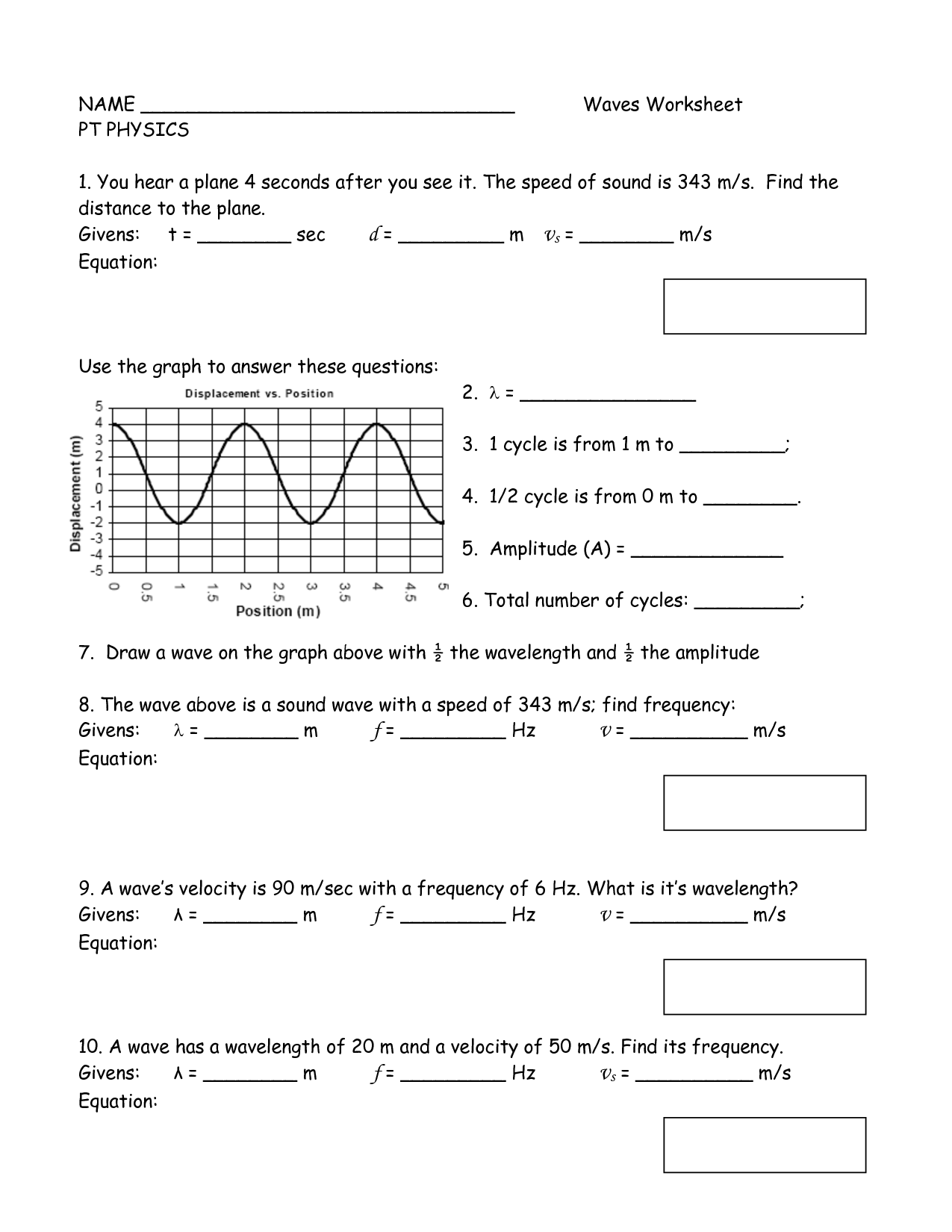
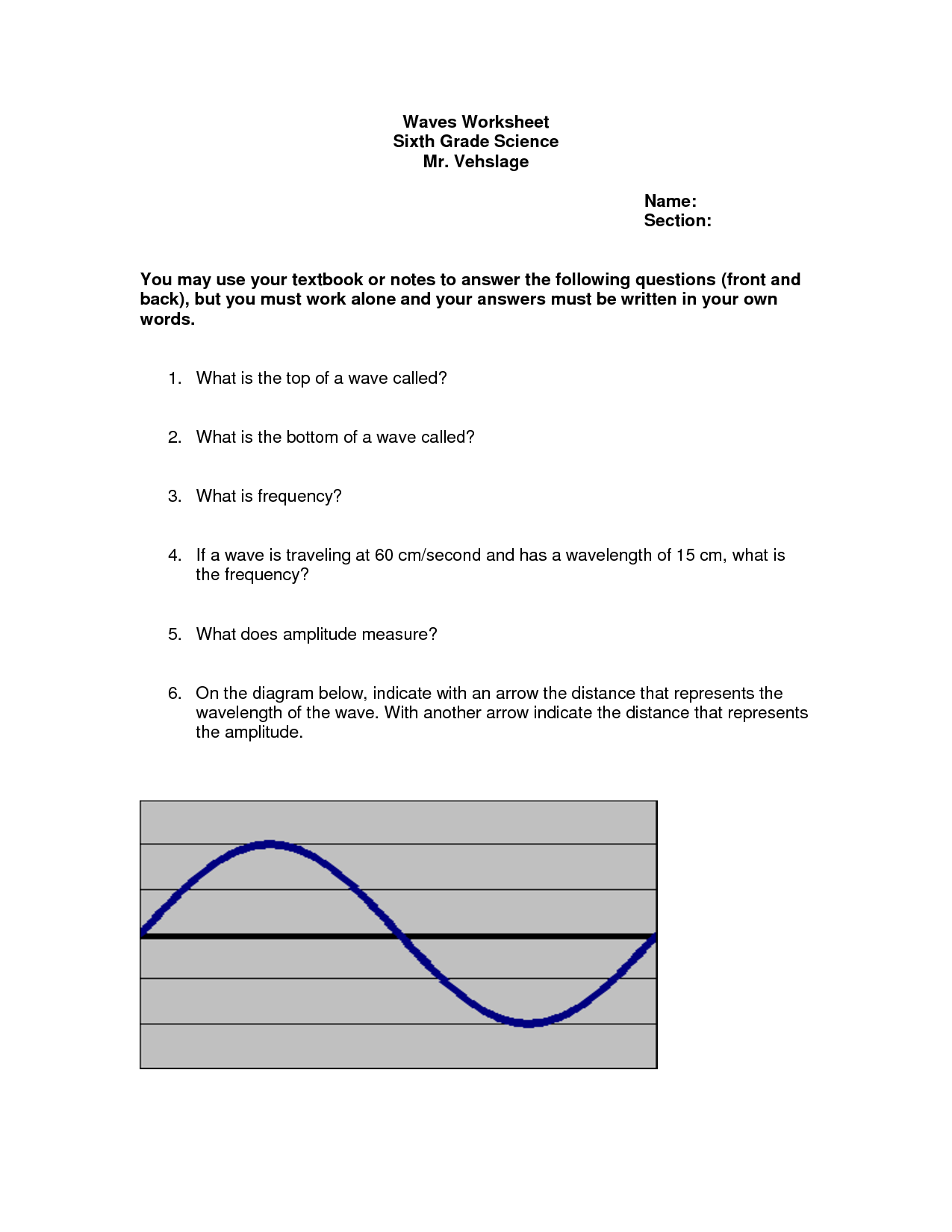
The frequency of a sound wave is the number of complete cycles of a wave that pass a point in a second, measured in hertz (Hz). It determines the pitch of the sound, with higher frequencies corresponding to higher-pitched sounds and lower frequencies to lower-pitched sounds.
How does amplitude affect the perception of sound?
Amplitude, or the intensity of a sound wave, affects the perceived loudness of a sound. A higher amplitude corresponds to a louder sound, while a lower amplitude produces a softer sound. This relationship is due to the way our ears and brain process sound waves, with greater amplitudes causing more intense vibrations in the ear and triggering a stronger neural response that we interpret as louder sound.
What is the speed of sound in air?
The speed of sound in air is approximately 343 meters per second (1235 kilometers per hour) at room temperature and normal atmospheric pressure.
How does the wavelength relate to the frequency of a sound wave?
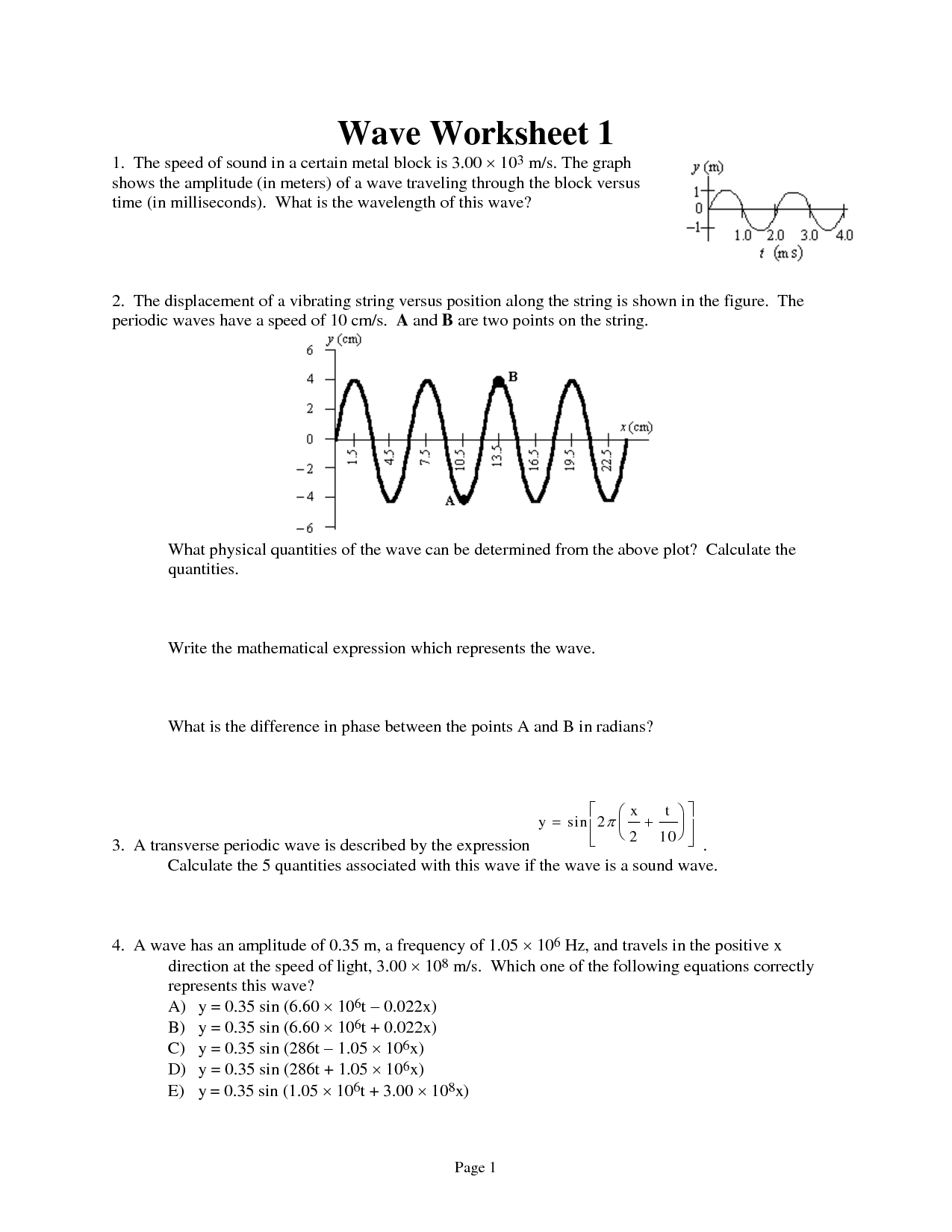
The wavelength of a sound wave is inversely related to its frequency. This means that as the frequency of a sound wave increases, its wavelength decreases, and vice versa. In other words, a sound wave with a higher frequency will have a shorter wavelength, while a sound wave with a lower frequency will have a longer wavelength.
What is the difference between a transverse and longitudinal wave?
The main difference between a transverse and longitudinal wave lies in the direction of the wave propagation and the oscillation of the particles within the medium through which the wave travels. In a transverse wave, the oscillation of particles is perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, creating crests and troughs along the wave. On the other hand, in a longitudinal wave, the oscillation of particles moves parallel to the direction of wave propagation, resulting in compressions and rarefactions along the wave.
How do sound waves travel through different mediums?
Sound waves travel through different mediums by creating vibrations in the particles of the medium they are passing through. In solids, such as metal or wood, sound waves travel faster and more efficiently because the particles are closely packed together. In liquids, like water, and gases, such as air, sound waves move through the medium by causing the particles to vibrate in a wave-like motion. The speed of sound in a medium depends on the density and elasticity of the material, with denser and more elastic materials allowing sound waves to travel faster.
What is the Doppler effect in relation to sound waves?
The Doppler effect in relation to sound waves refers to the change in frequency of a sound wave as either the source of the sound or the observer moves relative to each other. If the source and observer move towards each other, the frequency increases, resulting in a higher pitch sound. Conversely, if they move away from each other, the frequency decreases, resulting in a lower pitch sound. This phenomenon is commonly experienced when a vehicle passes by, causing the sound of its horn to change in pitch as it approaches and then moves away.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments