Series Circuits Worksheet On Printable
Are you searching for a helpful resource to strengthen your understanding of series circuits? Look no further! In this blog post, we have curated a collection of printable worksheets that focus specifically on series circuits. Designed for students at intermediate levels, these worksheets offer a comprehensive set of problems to enhance your knowledge of entity and subjects within series circuits.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
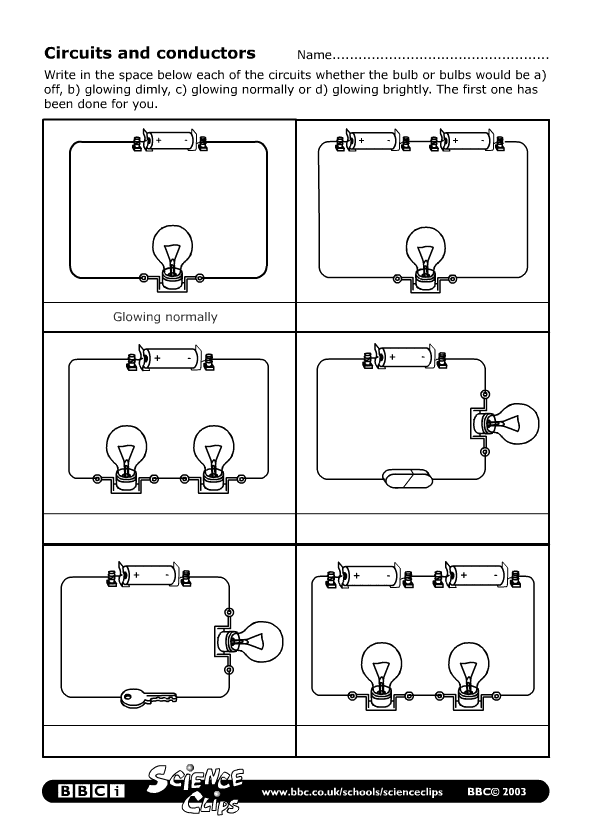
What is a series circuit?
A series circuit is an electrical circuit in which the current flows along a single path, passing through each component one after another. In a series circuit, the components are connected end-to-end, creating a continuous loop for the current to flow through. Any interruption in the circuit will stop the flow of current throughout the entire circuit.
How are the components connected in a series circuit?
In a series circuit, the components are connected one after the other in a single loop so that the current flows through each component in sequence. This means that the same current passes through all the components, and the voltage is divided among them. If one component fails or is disconnected, it breaks the circuit, interrupting the flow of current throughout the entire loop.
What happens to the current in a series circuit?
In a series circuit, the current remains the same at all points throughout the circuit. This means that the flow of electrical charge is constant as it travels through the various components connected in series, such as resistors or lightbulbs. The current is not divided or changed in magnitude as it passes through each component, making it a fundamental characteristic of series circuits.
How is the total resistance calculated in a series circuit?
The total resistance in a series circuit is calculated by adding up the individual resistances of each component in the circuit. This means that if there are multiple resistors connected in series, the total resistance is the sum of all the resistances. Mathematically, the formula for calculating total resistance in a series circuit is R_total = R1 + R2 + R3 + ... + Rn, where R_total is the total resistance and R1, R2, R3, ... Rn are the resistances of each component in the circuit.
What is the voltage across each component in a series circuit?
In a series circuit, the voltage across each component is the same. This means that if you have multiple resistors or other components connected in series, they will all experience the same voltage drop from the power source. This is because the total voltage in a series circuit is shared among all the components in the circuit.
How do you calculate the total voltage in a series circuit?
To calculate the total voltage in a series circuit, you simply add up the individual voltage drops across each component in the circuit. This means adding the voltage of each battery or voltage source in the circuit. The total voltage is equal to the sum of all individual voltage sources in the series circuit.
What happens to the brightness of bulbs in a series circuit if one bulb is removed?
If one bulb is removed from a series circuit, the brightness of the remaining bulbs will decrease. This is because the total resistance in the circuit will decrease, causing an increase in the current flowing through the circuit. As a result, the remaining bulbs will receive more current than they were designed for, causing them to glow brighter.
Can you add more components to a series circuit without changing the power source?
Yes, a series circuit allows you to add more components, such as resistors or light bulbs, without changing the power source. The total voltage of the circuit remains constant and is divided among the components, while the total resistance increases with each additional component. This means that the current flowing through the circuit will decrease as more components are added, affecting the brightness of light bulbs or the heat generated by resistors.
Are the current and voltage the same in all components of a series circuit?
In a series circuit, the current is the same in all components connected in the circuit, but the voltage can vary across different components depending on their individual resistance values.
What happens if the resistors in a series circuit have different resistances?
In a series circuit with resistors of different resistances, the total resistance of the circuit will be equal to the sum of the individual resistances of the resistors. The current flowing through the circuit will be the same throughout all the resistors, but the voltage drop across each resistor will be different, depending on their individual resistances. The resistor with the higher resistance will have a greater voltage drop across it compared to the resistor with lower resistance.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



















Comments